10 In. Hg Is Equivalent To What Psia
Arias News
May 08, 2025 · 5 min read
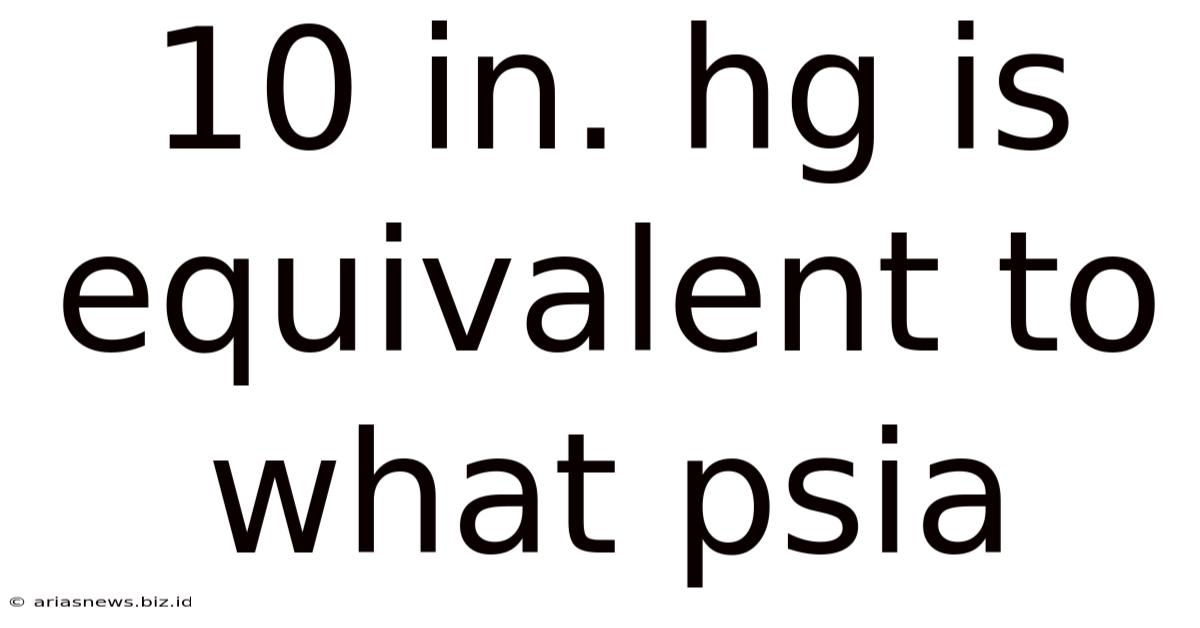
Table of Contents
10 in. Hg is Equivalent to What PSIA? Understanding Pressure Units and Conversions
Understanding pressure units and their conversions is crucial in many fields, from engineering and manufacturing to meteorology and medicine. One common conversion involves inches of mercury (in. Hg) and pounds per square inch absolute (psia). This article will thoroughly explore the conversion of 10 in. Hg to psia, explaining the underlying principles and providing a comprehensive understanding of the involved pressure units. We'll also delve into the practical applications of these conversions and offer tips for accurate calculations.
Understanding Pressure Units
Before we delve into the conversion, let's define the units involved:
-
Inches of Mercury (in. Hg): This unit measures pressure based on the height of a column of mercury. It's a common unit used in barometers to measure atmospheric pressure. A higher column of mercury indicates higher pressure.
-
Pounds per Square Inch Absolute (psia): This unit measures absolute pressure, which is the total pressure exerted on a surface, including atmospheric pressure. It's expressed as the force (in pounds) exerted per unit area (one square inch). This is different from gauge pressure (psig), which only measures the pressure above atmospheric pressure.
The Conversion Factor: From in. Hg to psia
The conversion between in. Hg and psia depends on several factors, primarily the density of mercury and the acceleration due to gravity. The standard conversion factor is based on the following:
- Standard gravity: 32.174 ft/s² (approximately 9.80665 m/s²)
- Density of Mercury: 13.5951 g/cm³ (approximately 849.7 lb/ft³)
Using these standard values, 1 in. Hg is approximately equal to 0.491 psia. This factor can vary slightly based on temperature and altitude, but for most practical purposes, this value is sufficiently accurate.
Calculating 10 in. Hg to psia
To convert 10 in. Hg to psia, we simply multiply the value by the conversion factor:
10 in. Hg * 0.491 psia/in. Hg ≈ 4.91 psia
Therefore, 10 in. Hg is approximately equivalent to 4.91 psia.
Practical Applications of Pressure Conversions
Accurate pressure conversions are critical in various applications, including:
-
HVAC Systems: Designing and maintaining heating, ventilation, and air conditioning (HVAC) systems often involves working with pressure measurements in both in. Hg and psia. Understanding the relationship between these units is essential for proper system performance and efficiency.
-
Aviation: In aviation, maintaining the correct air pressure within aircraft cabins is crucial for passenger safety and comfort. This involves accurate pressure monitoring and control, requiring seamless conversions between different pressure units.
-
Process Engineering: Many industrial processes involve the handling of fluids under pressure. Converting pressure units accurately is paramount for ensuring the safety and efficiency of these processes. This includes applications such as chemical processing, petroleum refining, and power generation.
-
Weather Forecasting: Barometric pressure, often measured in in. Hg, is a key indicator used in weather forecasting. Converting this pressure to psia can be useful for comparing with other atmospheric pressure data and for sophisticated weather models.
-
Medical Applications: While less frequently used in everyday medical scenarios, precise pressure measurements are vital in specific medical devices and procedures. Accurate conversions are essential to ensure the correct functioning of these devices and the safety of the patient.
Factors Affecting Accuracy of Conversion
While the conversion factor of 0.491 psia/in. Hg is widely used, it’s important to acknowledge that slight variations can occur due to several factors:
-
Temperature: The density of mercury varies with temperature. Higher temperatures result in slightly lower density, affecting the conversion factor. For highly precise conversions, temperature correction might be necessary.
-
Gravity: The acceleration due to gravity isn't constant across the Earth's surface; it varies slightly with altitude and latitude. These minor variations can also influence the conversion factor.
-
Mercury Purity: Impurities in the mercury used for measurement can slightly alter its density, introducing a small error into the conversion.
Beyond the Basic Conversion: A Deeper Dive into Pressure
Understanding the conversion between in. Hg and psia is only the beginning. A more complete understanding of pressure requires knowledge of different pressure types:
-
Absolute Pressure: The total pressure exerted on a surface, including atmospheric pressure. This is what psia measures.
-
Gauge Pressure: The pressure above atmospheric pressure. This is often denoted as psig. Gauge pressure is commonly measured using gauges that show zero when exposed to atmospheric pressure.
-
Differential Pressure: The difference in pressure between two points.
Understanding these distinctions is crucial when working with pressure measurements and their conversions. For instance, to convert from in. Hg to psig, you would first convert to psia and then subtract the atmospheric pressure.
Advanced Conversion Techniques and Tools
While simple hand calculations suffice for many purposes, more complex scenarios may necessitate advanced techniques:
-
Pressure Conversion Calculators: Numerous online calculators are available to perform these conversions quickly and accurately, often accounting for temperature and altitude variations.
-
Engineering Software: Specialized engineering software packages often incorporate pressure conversion functionalities, providing more comprehensive results and eliminating the potential for human error.
Ensuring Accurate Conversions and Avoiding Common Mistakes
Accurate pressure conversions are vital to ensure the proper functioning of equipment and systems. Here are some tips to avoid common errors:
-
Double-Check Units: Always double-check that you are using the correct units (in. Hg, psia, etc.) throughout the conversion process.
-
Use Consistent Units: Maintain consistent units throughout your calculations. Converting units multiple times increases the risk of errors.
-
Consider Environmental Factors: If high precision is required, account for variations in temperature, altitude, and gravity.
-
Utilize Reliable Resources: Consult reliable sources for conversion factors and ensure that you are using the most accurate data available.
Conclusion: Mastering Pressure Conversions for Success
Mastering the conversion between inches of mercury (in. Hg) and pounds per square inch absolute (psia) is a fundamental skill in various fields. While the basic conversion is relatively straightforward, a deeper understanding of the underlying principles, factors affecting accuracy, and the different types of pressure measurements ensures reliable and accurate results. By employing the strategies and considerations outlined in this article, you can confidently perform pressure conversions and apply this knowledge to practical applications. Remember to always double-check your calculations and use appropriate tools for increased accuracy, especially in critical applications. Understanding pressure units and their conversions is a crucial skill that will enhance your problem-solving abilities and contribute to your success in various professional settings.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
What Happens When Two Fruit Companies Merged Answer Key
May 08, 2025
-
How Long Does Velveeta Last After Opening
May 08, 2025
-
What Is Half Of 3 3 8 Inches
May 08, 2025
-
How Old Are You If Born In 1995
May 08, 2025
-
How Much Beer In A Yard Glass
May 08, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about 10 In. Hg Is Equivalent To What Psia . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.