How Many Corners Does A Square Have
Arias News
Mar 19, 2025 · 6 min read
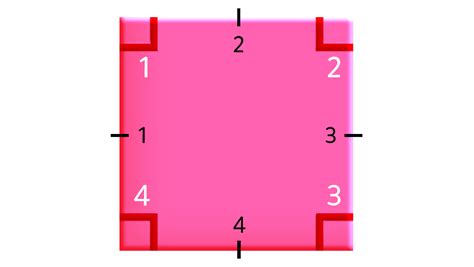
Table of Contents
How Many Corners Does a Square Have? A Deep Dive into Geometry
This seemingly simple question, "How many corners does a square have?", opens the door to a fascinating exploration of geometry, its fundamental concepts, and its practical applications in various fields. While the immediate answer is straightforward, delving deeper allows us to appreciate the underlying principles and the rich tapestry of mathematical thinking woven into this basic shape.
Understanding the Fundamentals: Defining Corners and Squares
Before we definitively answer the question, let's solidify our understanding of the key terms involved.
What is a Corner?
In the context of geometry, a corner, also known as a vertex, is a point where two or more lines or edges meet to form an angle. It's a crucial element in defining the shape and properties of geometric figures. Think of it as a sharp point or a point of intersection. The number of corners directly relates to the shape's complexity and the number of sides it possesses.
Defining a Square: More Than Just Four Sides
A square is a two-dimensional geometric shape defined by several key characteristics:
- Four Sides: It possesses four straight sides.
- Equal Sides: All four sides are of equal length.
- Four Right Angles: Each of its four interior angles measures exactly 90 degrees. These right angles are formed by the intersection of the sides, creating the corners.
- Closed Shape: The four sides connect to form a closed figure; there are no gaps or open ends.
These properties distinguish a square from other quadrilaterals (four-sided shapes) like rectangles (which have four right angles but not necessarily equal sides) or rhombuses (which have equal sides but not necessarily right angles).
The Answer: A Square Has Four Corners
Based on the definition of a square and a corner, the unequivocal answer is: A square has four corners. These four corners are the points where the four sides intersect, forming the four right angles that are characteristic of a square.
Beyond the Obvious: Exploring Related Concepts
While the answer itself is simple, let's explore related concepts to enrich our understanding of squares and their properties:
Angles and Their Measurement
The four corners of a square each contain a 90-degree angle, also known as a right angle. This is a fundamental concept in geometry and is crucial in many applications, from architecture and engineering to computer graphics and game development. Understanding angle measurement is essential for calculating areas, perimeters, and other properties of geometric shapes.
Interior and Exterior Angles
A square has both interior angles (the angles formed inside the shape) and exterior angles (the angles formed by extending one side of the square). The sum of the interior angles of any quadrilateral, including a square, is always 360 degrees. In a square, each interior angle contributes 90 degrees to this total. The exterior angles, when added together, also sum to 360 degrees.
Diagonals and Their Properties
A diagonal is a line segment that connects two non-adjacent vertices (corners) of a polygon. A square has two diagonals, which intersect at a right angle and bisect each other (divide each other into two equal parts). These diagonals also have the same length and are equal to the side length multiplied by the square root of 2.
Symmetry and Transformations
Squares possess a high degree of symmetry. They exhibit both rotational and reflectional symmetry. This means that a square can be rotated by 90, 180, or 270 degrees, and it will still look the same. Similarly, it can be reflected across several lines of symmetry and remain unchanged. This symmetry makes squares highly useful in design and pattern creation.
Area and Perimeter Calculations
The area of a square (the space enclosed within its sides) is calculated by squaring the length of one side (side * side). The perimeter (the total length of its sides) is calculated by multiplying the length of one side by four (4 * side). These simple formulas highlight the importance of understanding the properties of squares for practical calculations.
Squares in Real Life: Applications and Examples
Squares are ubiquitous in our world. Their properties make them highly practical and aesthetically pleasing in various applications:
-
Architecture and Construction: Square shapes are fundamental in building design, from window frames and floor tiles to room layouts and entire building structures. The stability and ease of construction offered by square shapes make them preferred in many applications.
-
Engineering and Design: Squares feature prominently in engineering designs, ranging from simple mechanical parts to complex structural elements. Their predictable geometry simplifies calculations and facilitates precise manufacturing.
-
Art and Design: Squares are used extensively in visual arts, graphic design, and textile patterns. Their symmetrical nature and the ability to create visually appealing arrangements make them a favorite among artists and designers.
-
Games and Puzzles: Many board games, puzzles, and even video games utilize square grids or tiles, demonstrating the versatility and practicality of square shapes.
-
Everyday Objects: Numerous everyday objects, from postage stamps and playing cards to photographs and computer screens, often have a square shape.
Advanced Concepts and Extensions
Let's delve into more advanced concepts related to squares and their broader implications within the field of mathematics:
Higher Dimensions: Cubes and Hypercubes
Moving beyond two dimensions, a square forms the base of a cube (a three-dimensional shape with six square faces) and further into higher dimensions with hypercubes. These higher-dimensional analogues share some properties with squares, including the concept of vertices (corners) and edges. Understanding squares is crucial to grasping the geometry of higher-dimensional spaces.
Tessellations and Tilings
Squares are among the simplest shapes that can tessellate (tile a plane without gaps or overlaps). Their ability to perfectly cover a surface without leaving any spaces makes them suitable for creating various patterns and designs. This concept has applications in architecture, art, and even nature.
Square Numbers and Number Theory
In number theory, square numbers (numbers that are the product of a number multiplied by itself) are closely related to squares. For instance, 9 is a square number (3 x 3), representing the area of a square with side length 3. The study of square numbers provides insights into the relationships between geometry and number theory.
Conclusion: The Enduring Significance of a Simple Shape
While the answer to "How many corners does a square have?" is simply four, exploring this question has provided a springboard for exploring a vast array of geometric concepts and their applications in the real world. From understanding fundamental angles and measurements to appreciating the role of squares in higher-dimensional geometry and number theory, the simple square reveals a richness and depth that belies its apparent simplicity. The ubiquitous nature of the square underscores its enduring significance in mathematics, design, and everyday life. This exploration emphasizes that even seemingly basic questions in mathematics can lead to profound insights and understanding.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
How Do You Write 19 As A Decimal
Mar 19, 2025
-
Can You Wet Your Hair After A Perm
Mar 19, 2025
-
What Do You Call A Person From Belgium
Mar 19, 2025
-
16 Out Of 21 As A Percentage
Mar 19, 2025
-
What Is The Average Iq For A 16 Year Old
Mar 19, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about How Many Corners Does A Square Have . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
