How Many Corners Does A Triangle Have
Arias News
Mar 14, 2025 · 5 min read
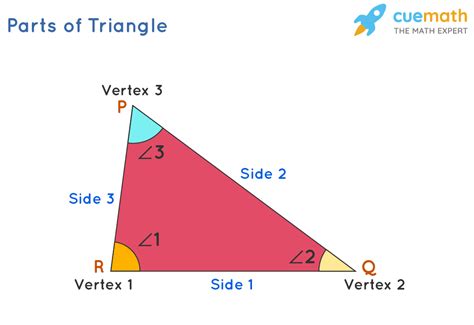
Table of Contents
How Many Corners Does a Triangle Have? A Deep Dive into Geometry
The seemingly simple question, "How many corners does a triangle have?" opens a door to a fascinating exploration of geometry, its fundamental concepts, and its surprising applications in our daily lives. While the immediate answer is three, delving deeper reveals the richness and complexity hidden within this basic shape. This article will not only answer the question definitively but will also delve into the properties of triangles, their classifications, and their significance in various fields.
Understanding Corners (Vertices) in Geometry
Before we definitively answer the question about a triangle's corners, let's clarify the terminology. In geometry, the points where two or more lines meet to form an angle are called vertices (singular: vertex). These are often referred to informally as "corners." Therefore, when we talk about the corners of a triangle, we are referring to its vertices.
The Triangle: A Three-Cornered Figure
A triangle, by definition, is a polygon with three sides and three angles. The very name, "triangle," directly indicates its defining characteristic: three angles. And because each angle is formed by the intersection of two sides, a triangle inherently possesses three vertices, or corners. This is a fundamental property that holds true for all triangles, regardless of their size, shape, or orientation.
Classifying Triangles: Exploring Different Types
While all triangles possess three corners, they can be classified in various ways based on their sides and angles. This classification adds another layer of understanding to our exploration:
Classification by Sides:
- Equilateral Triangles: These triangles have three sides of equal length. Consequently, all three angles are also equal, measuring 60 degrees each.
- Isosceles Triangles: These triangles have at least two sides of equal length. The angles opposite these equal sides are also equal.
- Scalene Triangles: These triangles have all three sides of different lengths. Naturally, all three angles are also different.
Classification by Angles:
- Acute Triangles: All three angles in an acute triangle are less than 90 degrees.
- Right Triangles: One angle in a right triangle is exactly 90 degrees (a right angle). The other two angles are acute angles. Right triangles are crucial in many areas of mathematics and physics, particularly trigonometry.
- Obtuse Triangles: One angle in an obtuse triangle is greater than 90 degrees (an obtuse angle). The other two angles are acute.
The Significance of Triangles in Various Fields
Triangles are not just abstract geometric shapes; they are fundamental building blocks in various fields:
Engineering and Architecture:
Triangles are exceptionally strong and stable structures. This is why they are extensively used in architecture and engineering to create rigid frameworks for buildings, bridges, and other constructions. The triangular shape effectively distributes weight and resists forces, making structures more robust and less prone to collapse. From the simple truss bridges to the complex support structures in skyscrapers, triangles are ubiquitous.
Surveying and Cartography:
Triangles play a vital role in surveying and mapping. Triangulation, a technique that uses the principles of trigonometry to determine the positions of points, relies heavily on the properties of triangles. Surveyors use this method to accurately measure distances and create precise maps of land areas.
Computer Graphics and Image Processing:
In computer graphics and image processing, triangles are the fundamental building blocks for representing complex 3D models and surfaces. Through a process called triangulation, complex shapes are broken down into a collection of smaller triangles. This makes rendering and manipulation of images more efficient and computationally manageable.
Physics and Mechanics:
Triangles are critical in understanding concepts in physics and mechanics. For example, the concept of vectors, which represent physical quantities such as force and velocity, is often visualized and analyzed using triangles. The use of vector addition and resolution helps in determining the resultant force or velocity acting on an object.
Art and Design:
Triangles have been used throughout history in art and design to create visually appealing compositions. The strong lines and angles of triangles can convey a sense of stability, dynamism, or tension, depending on their arrangement and orientation within a design. Many famous works of art use triangular forms effectively to guide the viewer's eye and create a sense of balance.
Beyond the Three Corners: Exploring Deeper Concepts
While we've established that a triangle has three corners, exploring deeper geometric concepts related to triangles reveals even more fascinating aspects:
Angles and Their Sum:
The sum of the interior angles of any triangle always equals 180 degrees. This is a cornerstone theorem in geometry and has far-reaching implications in various mathematical and scientific calculations.
Area Calculation:
The area of a triangle can be calculated using different formulas, depending on the available information. Common formulas involve base and height, or the lengths of all three sides (Heron's formula). Understanding these formulas is crucial in various applications requiring area calculation.
Similar and Congruent Triangles:
Two triangles are considered similar if their corresponding angles are equal, even if their sides are different in length. Two triangles are congruent if their corresponding sides and angles are all equal. These concepts are foundational in geometry and are frequently applied in proving geometric theorems and solving problems.
Trigonometry:
Trigonometry, the study of triangles and their properties, is an essential branch of mathematics that uses trigonometric functions (sine, cosine, and tangent) to relate the angles and sides of a triangle. Trigonometry has widespread applications in physics, engineering, surveying, and many other scientific fields.
Conclusion: The Enduring Importance of the Triangle
The seemingly simple question of how many corners a triangle has leads us on a journey through the fundamental concepts of geometry, highlighting the profound importance of this basic shape. From its structural strength to its applications in advanced mathematics and diverse scientific fields, the triangle's three corners serve as the foundation for a wealth of knowledge and innovation. Understanding the properties of triangles is essential not only for mathematicians and engineers but for anyone seeking a deeper understanding of the world around us. So, while the answer is three, the implications are far more extensive and deeply rooted in our understanding of the world.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
What Is 4 To The Power Of 2
Mar 14, 2025
-
Can A Speech Be Considered An Artile
Mar 14, 2025
-
How Long Do Catfish Live Out Of Water
Mar 14, 2025
-
What Is Something That Weighs A Gram
Mar 14, 2025
-
48 Degrees Celsius Is What In Fahrenheit
Mar 14, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about How Many Corners Does A Triangle Have . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
