How Many Pattern Block Trapezoids Would Create 2 Hexagons
Arias News
Mar 20, 2025 · 5 min read
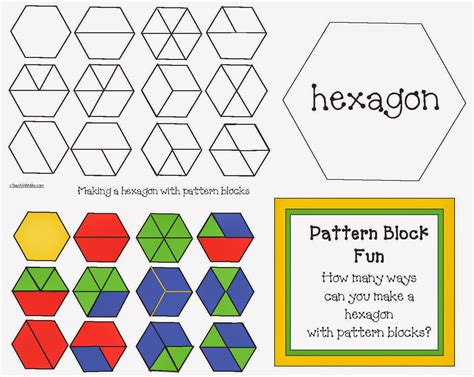
Table of Contents
How Many Pattern Block Trapezoids Create 2 Hexagons? A Deep Dive into Geometry and Problem-Solving
Pattern blocks are a fantastic tool for exploring geometric concepts, fostering creativity, and developing problem-solving skills. This article delves into a specific geometric puzzle: determining how many trapezoidal pattern blocks are needed to construct two hexagons. We'll not only solve this puzzle but also explore the underlying mathematical principles, alternative solutions, and the broader implications for learning and teaching geometry.
Understanding the Shapes: Trapezoids and Hexagons
Before we tackle the central question, let's solidify our understanding of the key shapes involved: trapezoids and hexagons.
Trapezoids: A Quick Review
A trapezoid is a quadrilateral (a four-sided polygon) with at least one pair of parallel sides. These parallel sides are called bases, and the other two sides are called legs. Pattern block trapezoids are isosceles trapezoids, meaning their legs are of equal length. This specific characteristic is crucial when arranging them to form other shapes.
Hexagons: Six-Sided Wonders
A hexagon is a polygon with six sides. A regular hexagon, as seen in pattern blocks, has all sides of equal length and all interior angles equal (120 degrees). This regular nature makes it particularly amenable to tessellations and constructions using other shapes.
Solving the Puzzle: Constructing Two Hexagons from Trapezoids
The primary objective is to determine the minimum number of trapezoidal pattern blocks required to create two hexagons. There are several approaches to solving this problem:
Method 1: Visual Construction and Counting
The most straightforward method is to physically manipulate pattern blocks (or draw them) and experimentally arrange trapezoids to form two hexagons. Through trial and error, one can discover a configuration that achieves this. This hands-on approach is invaluable for developing spatial reasoning skills. By carefully arranging the trapezoids, you'll visually confirm the solution and understand the geometric relationships involved. This method often leads to discovering the most efficient solution.
Method 2: Geometric Decomposition and Reasoning
Instead of directly manipulating the blocks, we can approach the problem using geometric decomposition. Consider the area and properties of both the trapezoid and the hexagon. A hexagon can be divided into smaller shapes, including equilateral triangles (which can be constructed from trapezoids) and even rhombuses. Analyzing the area relationships between these shapes can help determine the number of trapezoids required.
Let's break down the hexagon: A regular hexagon can be divided into six equilateral triangles. Each equilateral triangle can be further divided or constructed using trapezoids. This decomposition method provides a more theoretical approach to solving the puzzle.
Method 3: Mathematical Formula Derivation
A more advanced method involves deriving a mathematical formula. This would require understanding the area of both the trapezoid and the hexagon, and establishing a relationship between the two. This method provides a generalized solution applicable to any size of trapezoid and hexagon (though we are focusing on standard pattern block sizes here). This approach could involve variables to represent the lengths of the trapezoid sides, leading to a formula that calculates the number of trapezoids needed for n hexagons. This is a more challenging approach suitable for students with a strong mathematical background.
The Solution and its Significance
Through any of the above methods (visual construction, geometric decomposition, or mathematical formula), you will discover that it takes six trapezoids to construct two hexagons.
This solution holds important implications for several aspects of learning and teaching:
- Spatial Reasoning: This puzzle directly challenges and enhances spatial reasoning skills. Students must visualize how different shapes can be combined and rearranged to create new forms.
- Problem-Solving: The process of finding the solution fosters problem-solving skills. Students must experiment, strategize, and potentially revise their approaches.
- Geometric Understanding: It reinforces the understanding of the properties of trapezoids and hexagons, including their area, sides, and angles.
- Mathematical Connections: This puzzle reveals the interconnectedness of various geometric concepts, demonstrating how shapes relate to each other in terms of area and composition.
- Tessellations: The construction of the hexagons from trapezoids touches upon the concept of tessellations, which is the arrangement of shapes to cover a surface without gaps or overlaps.
Extending the Puzzle: More Complex Challenges
Once the basic puzzle is solved, it's beneficial to extend the challenge to deepen understanding and engagement:
- Different Arrangements: Explore different ways to arrange the six trapezoids to create the two hexagons. Are there multiple valid configurations?
- Larger Hexagons: How many trapezoids would be needed to create three hexagons? Four? Can a general formula be developed?
- Other Shapes: Challenge yourself to construct other shapes using trapezoids, such as octagons, parallelograms, or other polygons.
- Combining Shapes: Use a combination of trapezoids and other pattern blocks (e.g., triangles, squares, rhombuses) to build complex patterns and shapes.
Conclusion: The Power of Pattern Blocks
The simple puzzle of constructing two hexagons from trapezoidal pattern blocks offers a surprisingly rich learning opportunity. It's not just about finding the answer (six trapezoids); it's about the journey of exploration, the development of spatial reasoning and problem-solving skills, and the deeper understanding of geometric relationships. Pattern blocks provide a hands-on, engaging way to learn abstract mathematical concepts, making them a valuable tool in classrooms and beyond. By exploring this puzzle and its extensions, students and anyone interested in geometry can gain a new appreciation for the power of visual manipulation and mathematical reasoning. The seemingly simple act of arranging shapes can lead to a profound understanding of geometric principles and enhance critical thinking capabilities.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
How Many Miles Is 2 Gallons Of Gas
Mar 21, 2025
-
1 2 Cup Fresh Parsley To Dried
Mar 21, 2025
-
3 4 Ounce Is How Many Tablespoons
Mar 21, 2025
-
What Year Would I Be Born If I Was 17
Mar 21, 2025
-
What Is Longer A Kilometer Or A Mile
Mar 21, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about How Many Pattern Block Trapezoids Would Create 2 Hexagons . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
