How Many Side Does A Hexagon Have
Arias News
Mar 17, 2025 · 5 min read
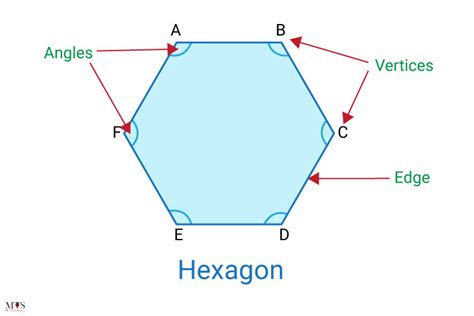
Table of Contents
How Many Sides Does a Hexagon Have? A Deep Dive into Hexagonal Geometry
The question, "How many sides does a hexagon have?" might seem trivial at first glance. The answer, of course, is six. However, a simple question can open the door to a fascinating exploration of geometry, its applications, and its rich history. This article delves beyond the simple answer, examining the properties of hexagons, their prevalence in nature and human design, and the mathematical concepts that underpin their unique characteristics.
Understanding the Hexagon: Definition and Properties
A hexagon is a polygon, a closed two-dimensional figure formed by connecting straight line segments. What sets a hexagon apart is the number of sides and angles it possesses: six of each. The word "hexagon" itself is derived from the Greek words "hex" (six) and "gonia" (angle). This etymology perfectly encapsulates its defining feature.
Regular vs. Irregular Hexagons
Not all hexagons are created equal. We can categorize hexagons into two main types:
-
Regular Hexagons: These possess six equal sides and six equal angles. Each interior angle measures 120 degrees, and the sum of all interior angles is 720 degrees. Regular hexagons exhibit a high degree of symmetry, making them visually appealing and structurally efficient.
-
Irregular Hexagons: These hexagons have sides and angles of varying lengths and measures. While they still have six sides, they lack the symmetrical properties of their regular counterparts.
Key Properties of Regular Hexagons:
- Interior Angle: 120 degrees
- Sum of Interior Angles: 720 degrees
- Exterior Angle: 60 degrees (sum of exterior angles always equals 360 degrees for any polygon)
- Symmetry: Six lines of symmetry (three lines of reflectional symmetry and three rotational symmetries)
- Tessellation: Regular hexagons can tessellate, meaning they can tile a plane without any gaps or overlaps. This property is crucial in various applications, as we'll explore later.
Hexagons in Nature: A Ubiquitous Shape
The hexagon's unique properties make it a prevalent shape found throughout the natural world. Its ability to tessellate perfectly is a major contributing factor to its natural occurrence.
Honeycomb Structure: The Classic Example
Perhaps the most well-known example of hexagonal structures in nature is the honeycomb built by honeybees. Bees instinctively construct their honeycombs using hexagonal cells. This arrangement is remarkably efficient, maximizing storage space while minimizing the amount of wax needed to build the structure. The hexagonal shape allows for a strong, stable, and space-saving design.
Other Natural Occurrences:
While honeycombs are the most striking example, hexagonal patterns appear in many other natural phenomena:
- Giant's Causeway (Ireland): This geological formation features thousands of interlocking basalt columns, many of which are hexagonal in shape. The hexagonal columns formed during the cooling and contraction of volcanic lava.
- Snowflakes: Although seemingly infinitely varied, many snowflakes display hexagonal symmetry, reflecting the crystalline structure of ice.
- Certain Crystals: Many minerals form crystalline structures with hexagonal symmetry.
- Eyes of Insects: The compound eyes of many insects exhibit hexagonal patterns, each facet (ommatidium) contributing to the insect's overall vision.
Hexagons in Human Design and Technology: A Versatile Shape
The hexagon's inherent strength, tessellation capabilities, and symmetrical properties have led to its widespread use in various human-designed structures and technologies.
Architecture and Engineering:
- Tiles and Flooring: Hexagonal tiles are frequently used in flooring and wall coverings because of their aesthetic appeal and efficient packing.
- Structural Components: Hexagonal shapes can provide exceptional strength and stability, making them suitable for use in various structural elements.
- Honeycomb Structures in Aerospace: The lightweight yet strong properties of hexagonal honeycomb structures are utilized in aerospace engineering to create efficient and durable components.
Other Applications:
- Nuts and Bolts: The hexagonal shape of nuts and bolts allows for a firm grip and efficient tightening.
- Game Design: Hexagonal grids are used in many board games and strategy games, offering a unique and often more strategic playing field than square grids.
- Computer Graphics and Game Development: Hexagonal tiling is often preferred in game development due to its efficient pathfinding and easier neighbor-finding algorithms.
- Art and Design: Hexagons frequently appear in artistic creations, often for their visual symmetry and balanced aesthetic qualities.
The Mathematics Behind Hexagons: Exploring Angles and Area
Understanding the mathematics behind hexagons is crucial to appreciating their unique properties.
Calculating the Area of a Regular Hexagon:
The area of a regular hexagon can be calculated using the following formula:
Area = (3√3/2) * s²
Where 's' is the length of one side of the hexagon.
This formula is derived from dividing the hexagon into six equilateral triangles and calculating the area of each triangle.
Calculating the Interior and Exterior Angles:
As mentioned earlier, the interior angle of a regular hexagon is 120 degrees. This can be calculated using the formula for the sum of interior angles of any polygon:
Sum of Interior Angles = (n - 2) * 180°
Where 'n' is the number of sides. For a hexagon (n=6), the sum is 720°. Dividing by the number of angles (6) gives the measure of each interior angle (120°).
The exterior angle of a regular hexagon is 60 degrees (180° - 120°). The sum of exterior angles for any polygon is always 360°.
Beyond the Basics: Advanced Hexagonal Concepts
The study of hexagons extends beyond basic geometry. More advanced concepts include:
- Hexagonal Tessellations and their Properties: Investigating different ways hexagons can be arranged to tile a plane.
- Hexagonal Number Systems: Exploring mathematical systems that utilize hexagonal grids.
- Hexagonal Geometry in Higher Dimensions: Extending the concept of hexagons to three-dimensional and higher-dimensional spaces.
- Applications in Graph Theory: Using hexagonal grids to model networks and analyze their properties.
Conclusion: The Enduring Significance of the Hexagon
While the answer to "How many sides does a hexagon have?" is straightforward, the exploration of this seemingly simple shape reveals a world of fascinating mathematical properties and diverse applications. From the natural elegance of honeycombs to the technological marvels of aerospace engineering, the hexagon's six sides represent a surprisingly versatile and impactful geometrical form. Its enduring significance lies not just in its basic definition but in its underlying mathematical principles and its pervasiveness across various fields, showcasing its enduring relevance in both the natural and man-made worlds. The next time you encounter a hexagon, remember that it's more than just a six-sided shape; it's a testament to the elegance and efficiency found in the mathematical structures that shape our world.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
If Im 42 What Year Was I Born
Mar 17, 2025
-
How Many Miles Are In 5 Acres
Mar 17, 2025
-
How Many Pints In Half A Gallon
Mar 17, 2025
-
How Much Is Half A Pound In Ounces
Mar 17, 2025
-
How Long Does It Take To Drive 50 Miles
Mar 17, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about How Many Side Does A Hexagon Have . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
