How Many Sides And Corners Does A Octagon Have
Arias News
Mar 26, 2025 · 5 min read
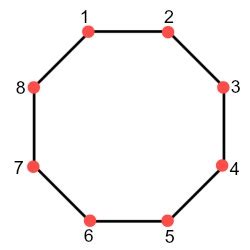
Table of Contents
How Many Sides and Corners Does an Octagon Have? A Deep Dive into Octagonal Geometry
The question, "How many sides and corners does an octagon have?" seems deceptively simple. However, delving deeper reveals a fascinating world of geometric properties, applications, and even historical context. This comprehensive guide will not only answer the fundamental question but will also explore the fascinating characteristics of octagons, their various types, and their presence in art, architecture, and nature.
Understanding the Basics: Sides and Corners of an Octagon
Let's start with the straightforward answer: an octagon has eight sides and eight corners (or vertices). This is the defining characteristic of an octagon – a polygon with eight sides. The term "octagon" itself comes from the Greek words "octa" (meaning eight) and "gonia" (meaning angle).
Distinguishing Sides and Corners: A Visual Explanation
It's crucial to understand the difference between sides and corners. Imagine drawing an octagon. The sides are the straight line segments that form the boundary of the shape. These are the eight lines that make up the octagon's perimeter. The corners, or vertices, are the points where two sides meet. Each corner represents an angle formed by the intersection of two sides.
Types of Octagons: Regular vs. Irregular
Not all octagons are created equal. They can be classified into two main categories:
1. Regular Octagons: Perfect Symmetry
A regular octagon is defined by its perfect symmetry. This means:
- All eight sides are equal in length.
- All eight angles are equal in measure. Each interior angle measures 135 degrees.
- It possesses rotational symmetry. It can be rotated around its center by multiples of 45 degrees and still look identical.
- It possesses reflectional symmetry. It can be reflected across multiple lines of symmetry and remain unchanged.
Regular octagons are often used in design due to their aesthetically pleasing symmetrical nature.
2. Irregular Octagons: A World of Variations
An irregular octagon, on the other hand, lacks the perfect symmetry of its regular counterpart. This means:
- Its sides can have different lengths.
- Its angles can have different measures.
- It may not possess any lines of symmetry.
Irregular octagons can take on a wide range of shapes and appearances, offering more flexibility in design.
Calculating the Interior Angles of an Octagon
The sum of the interior angles of any polygon can be calculated using a simple formula: (n-2) * 180°, where 'n' is the number of sides. For an octagon (n=8), the sum of interior angles is (8-2) * 180° = 1080°.
In a regular octagon, each interior angle is equal, so we can divide the total sum by the number of angles (8) to find the measure of each angle: 1080° / 8 = 135°.
This consistency in angle measurement is a key differentiating factor between regular and irregular octagons.
Octagons in the Real World: Applications and Examples
Octagons, particularly regular octagons, appear in various aspects of our lives:
Architecture and Design:
- Stop signs: The classic octagonal shape of stop signs worldwide is instantly recognizable and ensures high visibility. The shape's symmetry and unique form make it easily distinguishable from other traffic signs.
- Buildings and Structures: Some buildings incorporate octagonal designs in their floor plans or external structures, often for aesthetic reasons or to create unique architectural features. Octagonal towers, for example, can be visually striking.
- Tiles and Mosaics: Octagonal tiles are frequently used in flooring and wall designs, creating visually interesting patterns and geometric arrangements.
- Window Designs: Octagonal windows can add a touch of elegance and uniqueness to a building's facade.
Nature and the Natural World:
While less common than other shapes in nature, octagonal patterns can sometimes be observed in:
- Crystals: Certain crystal structures can exhibit octagonal symmetry in their arrangements of atoms or molecules.
- Natural Rock Formations: Erosion processes might sometimes carve out octagonal shapes in rocks, though these are usually irregular.
Art and Crafts:
- Artwork: Artists incorporate octagons into paintings, sculptures, and other art forms to create visual impact and geometric interest. The symmetrical nature of regular octagons is particularly appealing to artists.
- Jewelry Design: Octagonal-shaped gemstones or settings are frequently used in jewelry design, adding a touch of elegance and geometric precision.
Beyond the Basics: Exploring Octagonal Properties
Beyond the fundamental aspects of sides and angles, octagons possess several intriguing mathematical properties:
- Area Calculation: The area of a regular octagon can be calculated using its side length (a) with the formula: 2(1+√2)a². For irregular octagons, the area calculation is more complex and often requires breaking the octagon down into smaller, simpler shapes.
- Circumradius and Inradius: The circumradius is the radius of the circle that circumscribes the octagon (passes through all its vertices). The inradius is the radius of the circle inscribed within the octagon (tangent to all its sides). These radii can be calculated using the side length of a regular octagon.
- Tessellations: Octagons can be used to create tessellations, which are patterns that cover a surface without any gaps or overlaps. However, regular octagons alone cannot tessellate; they need to be combined with other shapes like squares to create a complete tiling.
Octagons and their Mathematical Significance
The study of octagons extends beyond basic geometry and touches upon more advanced mathematical concepts, including:
- Trigonometry: Trigonometric functions are essential for calculating angles, side lengths, and areas within octagons, especially in the case of irregular octagons.
- Coordinate Geometry: Octagons can be defined using coordinate systems, enabling calculations and analysis within a Cartesian plane.
- Symmetry Groups: The symmetry properties of regular octagons are studied within the broader context of group theory, a branch of abstract algebra.
Conclusion: The Enduring Appeal of the Octagon
The seemingly simple question of how many sides and corners an octagon has opens a gateway to a rich world of geometric principles, real-world applications, and mathematical exploration. From the symmetrical elegance of regular octagons to the diverse shapes of irregular octagons, this eight-sided polygon holds a significant place in geometry, design, and even nature itself. Understanding its properties and applications deepens our appreciation for the intricate beauty and mathematical precision inherent in geometric shapes. The next time you encounter an octagon, remember the wealth of properties and significance hidden within its eight sides and eight corners.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
How Many Cups In A Pound Of Sour Cream
Mar 29, 2025
-
Five Letter Words With I As The Only Vowel
Mar 29, 2025
-
If You Were Born In 1942 How Old Are You
Mar 29, 2025
-
3 To The Power Of Negative 1
Mar 29, 2025
-
How Many Cups Is 8 Ounces Cream Cheese
Mar 29, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about How Many Sides And Corners Does A Octagon Have . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
