How Many Square Feet Will 12000 Btu Cool
Arias News
Mar 28, 2025 · 6 min read
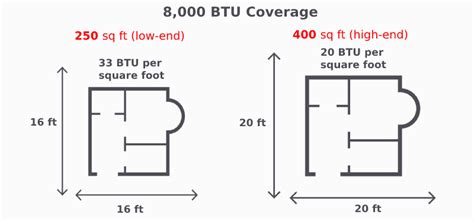
Table of Contents
How Many Square Feet Will 12,000 BTU Cool? A Comprehensive Guide to Air Conditioner Sizing
Choosing the right air conditioner can be a daunting task. One of the most crucial factors is determining the appropriate BTU (British Thermal Unit) rating for your space. A common question is: How many square feet will 12,000 BTU cool? The answer, unfortunately, isn't a simple number. While 12,000 BTU is a frequently used rating, the actual cooling capacity depends on several factors beyond just square footage. This comprehensive guide will delve into these factors and help you determine if a 12,000 BTU air conditioner is the right choice for your needs.
Understanding BTUs and Cooling Capacity
BTUs measure the amount of heat an air conditioner can remove from a space in one hour. A higher BTU rating means more cooling power. While square footage is a starting point for sizing, it's not the sole determinant. Think of it as a rule of thumb, not a precise formula. Ignoring other factors can lead to an underperforming or oversized unit, both of which are undesirable.
Factors that Influence Cooling Needs Beyond Square Footage:
-
Ceiling Height: Higher ceilings require more BTUs to cool the same square footage. The air has more volume to be cooled.
-
Number of Windows and Their Orientation: South-facing windows, especially large ones, receive significantly more direct sunlight and heat, demanding a higher BTU rating. The type of window glazing also plays a role; double- or triple-paned windows offer better insulation than single-pane.
-
Insulation and Energy Efficiency of Your Home: A well-insulated home retains cool air more effectively, reducing the required BTU output. Conversely, poorly insulated homes lose coolness rapidly, necessitating a more powerful unit.
-
Climate and Outside Temperature: The hotter and more humid your climate, the higher the BTU requirement to maintain a comfortable indoor temperature. Extreme heat waves demand more cooling capacity.
-
Number of Occupants and Appliances: People and appliances like computers, televisions, and ovens generate heat. More occupants and appliances mean more heat to remove, impacting BTU needs.
-
Appliance Usage: Frequent use of heat-generating appliances (ovens, stoves) will significantly increase the cooling load.
-
Amount of Direct Sunlight: The amount of direct sunlight entering the room is a critical factor to consider. Rooms with large windows facing the sun will require more cooling.
-
Type of Construction: Different building materials have different thermal properties. Homes built with materials that retain heat will require more powerful AC units.
-
Desired Temperature Difference: The greater the temperature difference you want between the inside and outside, the more cooling capacity your AC unit needs.
General BTU Guidelines (with Cautions)
While we'll explore more precise calculations below, here's a very rough guideline often used as a starting point:
- Small room (under 150 sq ft): 5,000-7,000 BTU
- Medium room (150-300 sq ft): 8,000-12,000 BTU
- Large room (300-500 sq ft): 12,000-18,000 BTU
- Extra-Large Room (500+ sq ft): 18,000 BTU and above
It's crucial to understand that these are estimations and should not be taken as definitive. The actual cooling needs can vary significantly depending on the factors listed above. A 12,000 BTU unit might be sufficient for a 300 sq ft room with good insulation in a moderate climate, but entirely inadequate for a similarly sized room with poor insulation in a hot and humid climate.
Calculating BTU Needs More Accurately
For a more precise calculation, consider using online BTU calculators. These tools often ask for the following information:
-
Square footage of the room: This provides a baseline estimate.
-
Climate zone: This helps account for external temperature variations.
-
Window size and type: This factors in heat gain through windows.
-
Insulation level: This considers the heat retention properties of the building.
-
Ceiling height: This takes into account the volume of air to be cooled.
-
Number of occupants: This accounts for body heat.
-
Appliance heat output: This accounts for heat from electronics and appliances.
Remember, even with a calculator, the result is an approximation. It's always best to err on the side of slightly more BTU capacity than you think you need. An undersized unit will struggle to maintain a comfortable temperature, leading to higher energy bills and discomfort.
Why 12,000 BTU Might Be Suitable (and When it Might Not Be)
A 12,000 BTU air conditioner might be perfectly suitable for a moderate-sized room (around 300-400 sq ft) under ideal conditions: good insulation, limited window exposure, average climate. However, in less-than-ideal situations, it might fall short:
-
Poorly insulated rooms: Heat will escape quickly, rendering the 12,000 BTU unit ineffective.
-
Rooms with extensive window area: Direct sunlight will significantly increase the cooling load.
-
Hot and humid climates: High temperatures and humidity demand higher cooling capacity.
-
Rooms with multiple heat sources: Several occupants, numerous electronics, or appliances using significant energy will overwhelm the unit.
Consequences of Choosing the Wrong Size
Choosing the wrong size air conditioner can lead to several negative consequences:
-
Undersized Unit: Will struggle to reach and maintain the desired temperature, leading to discomfort, higher energy bills (running constantly to compensate), and potential damage to the unit from overworking.
-
Oversized Unit: While seemingly beneficial, an oversized unit can actually be inefficient. It will cool the room too quickly, leading to temperature fluctuations, higher initial cost, and shorter lifespan due to frequent on/off cycles. It may also lead to increased humidity since it doesn't run long enough to dehumidify effectively.
Beyond BTU: Other Important Considerations
BTU is just one piece of the puzzle. When selecting an air conditioner, also consider:
-
Energy Efficiency (SEER Rating): The Seasonal Energy Efficiency Ratio (SEER) indicates how efficiently the unit uses energy. Higher SEER ratings mean lower energy bills.
-
Type of Air Conditioner: Portable, window, split-system, and ductless mini-splits each have advantages and disadvantages depending on your needs and space.
-
Noise Level: Consider the noise level, especially if the unit will be placed in a bedroom or living area.
-
Features: Look for features like programmable timers, thermostats, and filtration systems.
Conclusion: A Balanced Approach to Air Conditioner Sizing
Determining how many square feet a 12,000 BTU air conditioner will cool isn't a simple calculation. While a rough estimate can be made based on square footage, it's essential to consider numerous other factors, including climate, insulation, window exposure, and the number of heat-generating sources. Utilizing online BTU calculators and carefully evaluating your specific situation will help you choose the right-sized unit for optimal comfort and energy efficiency. Remember, an appropriately sized air conditioner is crucial for maintaining a comfortable indoor environment and avoiding unnecessary energy waste and equipment damage. Prioritizing these factors will save you money in the long run and ensure you enjoy a cool and comfortable home.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
How Much Does A Cubic Foot Of Soil Weigh
Mar 31, 2025
-
How Many Square Feet In 28 Acres
Mar 31, 2025
-
Can You Touch Elf On The Shelf On Christmas Eve
Mar 31, 2025
-
How Many Ounces In Pint Of Sour Cream
Mar 31, 2025
-
Harry Potter Goblet Of Fire Ar Answers
Mar 31, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about How Many Square Feet Will 12000 Btu Cool . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
