How Many Vertices Does A Hexagon Have
Arias News
Mar 21, 2025 · 5 min read
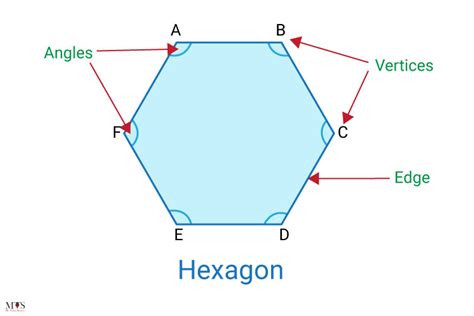
Table of Contents
How Many Vertices Does a Hexagon Have? A Deep Dive into Hexagonal Geometry
The question, "How many vertices does a hexagon have?" might seem trivial at first glance. The answer, of course, is six. However, a simple question can open the door to a fascinating exploration of geometry, its properties, and its applications in various fields. This article will delve into the world of hexagons, explaining not only the number of vertices but also exploring their properties, different types of hexagons, and their significance in diverse areas, from nature to engineering.
Understanding Basic Geometric Terminology
Before we dive deeper into hexagons, let's refresh some fundamental geometrical terms:
- Polygon: A closed two-dimensional figure formed by connecting straight line segments. Hexagons are a type of polygon.
- Vertex (Plural: Vertices): A point where two or more line segments meet to form a corner or angle of a polygon. These are the "corners" of the shape.
- Side: A straight line segment forming part of the boundary of a polygon.
- Angle: The space between two intersecting lines or surfaces at or close to the point where they meet. In a polygon, angles are formed at each vertex.
The Hexagon: A Six-Sided Wonder
A hexagon is a polygon with six sides and, consequently, six vertices. This seemingly simple definition belies the rich geometrical properties and varied applications of hexagons. Their six sides and six vertices create a structure with unique characteristics that make them appear in nature and human design in many fascinating ways.
Regular vs. Irregular Hexagons
Hexagons can be categorized into two main types:
-
Regular Hexagon: A regular hexagon has all six sides of equal length and all six interior angles equal (120 degrees each). It exhibits perfect symmetry.
-
Irregular Hexagon: An irregular hexagon has sides and angles of varying lengths and measures. It lacks the symmetrical properties of a regular hexagon.
The number of vertices remains consistent – six – regardless of whether the hexagon is regular or irregular. The difference lies in the lengths of the sides and the measure of the angles.
Properties of Hexagons
The properties of a hexagon, particularly a regular hexagon, are well-defined and contribute to its unique characteristics:
- Interior Angles: The sum of the interior angles of any hexagon is always 720 degrees. In a regular hexagon, each interior angle measures 120 degrees.
- Exterior Angles: The sum of the exterior angles of any hexagon is always 360 degrees.
- Diagonals: A hexagon has nine diagonals. Diagonals are line segments connecting non-adjacent vertices.
- Symmetry: Regular hexagons possess rotational symmetry of order 6 (they can be rotated 60 degrees and still look the same) and six lines of reflectional symmetry.
- Tessellation: Regular hexagons can tessellate, meaning they can cover a plane without any gaps or overlaps. This property is crucial in various applications, including honeycomb structures.
Hexagons in Nature and Human Design
The prevalence of hexagons in nature and human design highlights their inherent efficiency and stability:
Hexagons in Nature:
- Honeycombs: The most iconic example is the honeycomb structure created by bees. Bees instinctively build hexagonal cells, maximizing space and minimizing the amount of wax needed. This is a testament to the efficiency of hexagonal geometry.
- Snowflakes: Many snowflakes exhibit hexagonal symmetry, although the exact shapes and patterns vary widely.
- Basalt Columns: Giant's Causeway in Ireland is a dramatic example of naturally occurring hexagonal basalt columns, formed by the cooling and contraction of lava.
- Crystal Structures: Some crystals also exhibit hexagonal structures at a microscopic level.
Hexagons in Human Design:
- Architecture: Hexagonal structures are used in architecture for their strength and aesthetic appeal. From architectural designs to paving patterns, hexagons provide both functionality and visual interest.
- Engineering: The strength and stability of hexagonal shapes make them suitable for various engineering applications, including nut and bolt designs. Hexagonal nuts provide a better grip than other shapes.
- Graphic Design: The symmetrical nature of regular hexagons provides a pleasing aesthetic and balance to designs, making them a popular choice in logos, patterns and other graphic elements.
- Games and Puzzles: Hexagons feature in various games and puzzles, including board games, tile-based games, and logic puzzles.
Mathematical Explorations Related to Hexagons
The hexagon's geometry opens doors to various mathematical explorations:
- Calculating Area: The area of a regular hexagon can be calculated using its side length (s): Area = (3√3/2) * s².
- Calculating Perimeter: The perimeter of a hexagon is simply six times the length of one side (if it's a regular hexagon).
- Coordinate Geometry: Hexagons can be represented and analyzed using coordinate geometry, allowing for precise calculations of distances, angles, and areas.
- Trigonometry: Trigonometric functions play a significant role in determining angles and side lengths within hexagons, especially when dealing with irregular hexagons.
Beyond the Basic: Advanced Hexagonal Concepts
The study of hexagons extends beyond simple shapes:
- Hexagonal Number: A hexagonal number is a figurate number that can be represented as a dot pattern arranged in the shape of a hexagon.
- Hexagonal Grids: Hexagonal grids are used in various applications, from mapping to video games, due to their efficiency in space filling and connectivity.
- Hexagonal Tiling: As mentioned earlier, the ability of regular hexagons to tessellate is a key property. This tiling is used in various contexts, from artistic designs to material science.
- Spherical Hexagons: While less common than planar hexagons, hexagons can also exist on a spherical surface, with their properties modified by the curvature of the sphere.
Conclusion: The Enduring Significance of Hexagons
The seemingly simple question of how many vertices a hexagon has has led us on a journey through the world of geometry. The answer – six – is only the starting point. The properties, applications, and mathematical significance of hexagons highlight their importance in nature, design, and various scientific fields. From the intricate beauty of honeycombs to the structural integrity of engineering designs, the hexagon's six vertices and six sides contribute to a fascinating and versatile geometric form that continues to intrigue and inspire. This exploration hopefully demonstrates the depth and richness that even seemingly basic geometrical concepts can offer. The world of geometry is full of such discoveries, encouraging us to continue exploring the shapes and patterns that surround us.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Upon Your Release A Dod Public Affairs
Mar 22, 2025
-
How Many Cups Is 4 Oz Chocolate Chips
Mar 22, 2025
-
How Do You Say I Love You In Hawaiian
Mar 22, 2025
-
How Many Questions Can I Wrong If Theres 16 Questions
Mar 22, 2025
-
What Fraction Is Equivalent To 5 6
Mar 22, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about How Many Vertices Does A Hexagon Have . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
