How Many Vertices Does A Pyramid Has
Arias News
Mar 21, 2025 · 5 min read
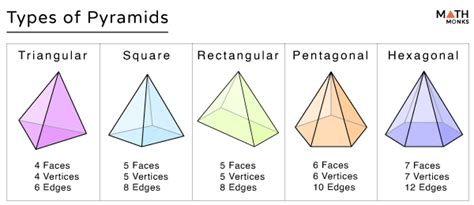
Table of Contents
How Many Vertices Does a Pyramid Have? A Comprehensive Exploration of Polyhedra
Understanding the geometry of pyramids is fundamental to various fields, from architecture and engineering to computer graphics and mathematics. A key aspect of understanding any geometric shape is knowing its constituent parts, specifically its vertices, edges, and faces. This article delves deep into the question: How many vertices does a pyramid have? We'll explore different types of pyramids, delve into the mathematical formulas governing their construction, and touch upon real-world applications.
Defining a Pyramid: Building Blocks of Geometry
Before we jump into counting vertices, let's establish a clear definition of a pyramid. A pyramid is a three-dimensional geometric shape that has a polygonal base and triangular faces that meet at a single point, called the apex. The base can be any polygon – a triangle, square, pentagon, hexagon, or any n-sided polygon. The type of pyramid is named according to the shape of its base. For example:
- Triangular Pyramid (Tetrahedron): A pyramid with a triangular base.
- Square Pyramid: A pyramid with a square base.
- Pentagonal Pyramid: A pyramid with a pentagonal base.
- Hexagonal Pyramid: A pyramid with a hexagonal base.
- n-gonal Pyramid: A pyramid with an n-sided polygon as its base.
This nomenclature is crucial for understanding the variations in the number of vertices, edges, and faces, which ultimately dictate the overall geometry.
Counting Vertices: A Systematic Approach
The number of vertices in a pyramid is directly related to the number of sides (edges) in its base. Let's explore this relationship:
-
The Base: The base of the pyramid contributes vertices equal to the number of sides it has. A triangle has three vertices, a square four, a pentagon five, and so on. An n-sided polygon has 'n' vertices.
-
The Apex: The apex of the pyramid is a single point where all the triangular faces converge. This adds one more vertex to the total count.
Therefore, the general formula to determine the number of vertices in any pyramid is:
Number of Vertices = Number of sides in the base + 1
Or, using 'n' to represent the number of sides in the base:
V = n + 1
Let's apply this formula to different types of pyramids:
- Triangular Pyramid (Tetrahedron): n = 3, V = 3 + 1 = 4 vertices.
- Square Pyramid: n = 4, V = 4 + 1 = 5 vertices.
- Pentagonal Pyramid: n = 5, V = 5 + 1 = 6 vertices.
- Hexagonal Pyramid: n = 6, V = 6 + 1 = 7 vertices.
- n-gonal Pyramid: n = n, V = n + 1 vertices.
Euler's Formula: Connecting Vertices, Edges, and Faces
Euler's formula provides a powerful relationship between the number of vertices (V), edges (E), and faces (F) of any convex polyhedron, including pyramids. The formula states:
V - E + F = 2
While we've focused on vertices, let's explore how Euler's formula connects all three elements for different pyramids:
- Triangular Pyramid (Tetrahedron): V = 4, E = 6, F = 4. 4 - 6 + 4 = 2.
- Square Pyramid: V = 5, E = 8, F = 5. 5 - 8 + 5 = 2.
- Pentagonal Pyramid: V = 6, E = 10, F = 6. 6 - 10 + 6 = 2.
This formula is a fundamental concept in topology and provides a way to verify the counts of vertices, edges, and faces for any correctly constructed pyramid.
Beyond Regular Pyramids: Exploring Irregular Shapes
The formulas and discussions above primarily focus on regular pyramids, where the base is a regular polygon (all sides and angles are equal) and the apex lies directly above the center of the base. However, pyramids can also be irregular. In an irregular pyramid:
- The base can be any irregular polygon.
- The apex does not necessarily lie directly above the center of the base.
Even in irregular pyramids, the basic principle of counting vertices remains the same: The number of vertices is still the number of sides in the base plus one. The irregularity only affects the lengths of the edges and the angles between them.
Real-World Applications: Pyramids in Action
Understanding the geometry of pyramids extends beyond theoretical mathematics. Pyramids are found in various real-world applications:
-
Architecture: The iconic pyramids of Egypt are prime examples of pyramid structures. Modern architecture also utilizes pyramid shapes for aesthetic and structural reasons.
-
Engineering: Pyramid shapes are employed in structural engineering for their stability and load-bearing capabilities.
-
Computer Graphics: Understanding the vertices, edges, and faces of pyramids is crucial in computer graphics for rendering 3D models and simulations.
-
Crystallography: Certain crystal structures exhibit pyramid-like shapes, and understanding their geometry is important in materials science.
Advanced Concepts: Truncated and Augmented Pyramids
While simple pyramids are straightforward, variations exist. For instance:
-
Truncated Pyramids: These are pyramids where the apex has been cut off by a plane, creating a new polygonal face. The number of vertices in a truncated pyramid will be greater than a standard pyramid, depending on the truncation plane.
-
Augmented Pyramids: These involve adding additional shapes or elements to the basic pyramid structure. The number of vertices will again depend on the specific augmentation.
These variations introduce complexity but the fundamental principle of counting vertices in the core pyramid structure remains crucial for understanding the overall geometry.
Conclusion: A Solid Foundation in Geometry
The question of "How many vertices does a pyramid have?" leads to a deeper exploration of the fundamentals of geometry, polyhedra, and their properties. The simple formula, V = n + 1, provides a clear and concise method for determining the number of vertices in any pyramid, regardless of the shape of its base. Understanding this foundational concept, along with Euler's formula, is crucial for anyone working with three-dimensional shapes in various fields. Whether you're an architect designing a building, an engineer creating a structure, or a programmer building a 3D model, a grasp of pyramid geometry is invaluable. The exploration of regular and irregular pyramids, along with variations like truncated and augmented forms, demonstrates the richness and complexity of this fundamental geometric shape.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
States With The Letter Y In Them
Mar 22, 2025
-
How Much Is 500 Mg In Teaspoons
Mar 22, 2025
-
How Many Cups Of Elbow Macaroni Is A Pound
Mar 22, 2025
-
What Colour Does Orange And Pink Make
Mar 22, 2025
-
What Is A 34 Out Of 40
Mar 22, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about How Many Vertices Does A Pyramid Has . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
