How To Find The Radius Of A Cylinder
Arias News
Mar 22, 2025 · 5 min read
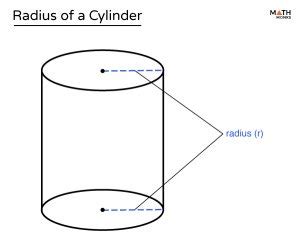
Table of Contents
How to Find the Radius of a Cylinder: A Comprehensive Guide
Finding the radius of a cylinder might seem straightforward, but the approach varies depending on the information you have available. This comprehensive guide will walk you through various scenarios, providing clear explanations and practical examples to help you master this fundamental geometrical concept. We'll cover everything from using the diameter, circumference, volume, and surface area to understand the different ways you can determine a cylinder's radius.
Understanding the Cylinder and its Radius
Before we delve into the methods, let's establish a clear understanding of what a cylinder is and what its radius represents. A cylinder is a three-dimensional solid object with two parallel circular bases and a curved surface connecting them. The radius of a cylinder is the distance from the center of either circular base to any point on the circumference of that base. It's a crucial dimension for calculating various properties of the cylinder, such as its volume, surface area, and lateral surface area.
Methods to Find the Radius of a Cylinder
Let's explore the different ways to calculate the radius of a cylinder, depending on the given information:
1. Using the Diameter
This is perhaps the simplest method. The diameter of a circle (and therefore the circular base of a cylinder) is twice its radius. Therefore:
Radius (r) = Diameter (d) / 2
Example: If the diameter of a cylinder's base is 10 cm, then its radius is 10 cm / 2 = 5 cm.
2. Using the Circumference
The circumference of a circle is the distance around it. It's related to the radius by the following formula:
Circumference (C) = 2πr
To find the radius using the circumference, we rearrange the formula:
Radius (r) = C / 2π
Where π (pi) is approximately 3.14159.
Example: If the circumference of a cylinder's base is 30 cm, then its radius is 30 cm / (2 * 3.14159) ≈ 4.77 cm.
3. Using the Volume
The volume of a cylinder is the amount of space it occupies. It's calculated using the formula:
Volume (V) = πr²h
Where 'h' is the height of the cylinder. To find the radius, we need to rearrange the formula:
Radius (r) = √(V / πh)
Example: Let's say the volume of a cylinder is 150 cubic cm and its height is 10 cm. Then the radius is √(150 cm³ / (3.14159 * 10 cm)) ≈ 2.19 cm. Remember to always check your units for consistency!
4. Using the Surface Area
The surface area of a cylinder is the total area of its curved surface and its two circular bases. The formula for the total surface area (TSA) is:
TSA = 2πr² + 2πrh
This formula includes the area of the two circular bases (2πr²) and the lateral surface area (2πrh). Solving for 'r' directly from this equation is complex and involves solving a quadratic equation. However, if you know the lateral surface area (LSA = 2πrh) separately, you can use this simpler formula:
Radius (r) = LSA / (2πh)
Example: If the lateral surface area of a cylinder is 100 square cm and its height is 5 cm, then the radius is 100 cm² / (2 * 3.14159 * 5 cm) ≈ 3.18 cm.
5. Using the Lateral Surface Area and Volume
Combining the formulas for lateral surface area (LSA = 2πrh) and volume (V = πr²h), we can eliminate 'h' to derive an equation relating radius, LSA and volume:
h = LSA / (2πr)
Substituting this into the volume formula:
V = πr² * (LSA / 2πr)
This simplifies to:
V = (r * LSA) / 2
And finally, solving for 'r':
Radius (r) = 2V / LSA
Example: Suppose the volume of a cylinder is 200 cubic cm and its lateral surface area is 80 square cm. Then, the radius would be (2 * 200 cm³) / 80 cm² = 5 cm.
Practical Applications and Real-World Examples
Understanding how to find the radius of a cylinder is essential in numerous real-world applications:
- Engineering: Calculating the volume and surface area of cylindrical components is critical in designing and manufacturing various products, from pipes and tanks to engine cylinders and structural elements. Accurately determining the radius is paramount for ensuring structural integrity and optimal performance.
- Architecture: Architects use cylindrical shapes in building designs, and accurate radius calculations are needed for structural stability and material estimations. Columns, towers, and even some dome structures utilize cylindrical elements.
- Packaging: Companies that manufacture goods in cylindrical containers need to know the radius to optimize packaging size, material use, and shipping costs.
- Manufacturing: From food cans to industrial components, understanding the cylinder's radius aids in efficient manufacturing processes and waste reduction.
- Science: Calculating the radius is crucial in various scientific experiments and analyses, particularly in fields like fluid dynamics and material science, where the dimensions of cylindrical containers and instruments are critical factors.
Troubleshooting Common Mistakes
Several common mistakes can lead to inaccurate radius calculations. Here are some points to keep in mind:
- Unit Consistency: Ensure all measurements (diameter, circumference, height, volume, surface area) are in the same units (cm, meters, inches, etc.) before performing calculations. Inconsistency in units is a major source of errors.
- Using the Correct Formula: Selecting the appropriate formula based on the given information is crucial. Using the wrong formula will invariably yield incorrect results.
- Accurate Measurements: The accuracy of your radius calculation directly depends on the accuracy of your initial measurements. Use precise measuring tools to minimize errors.
- Calculator Accuracy: For complex calculations, using a scientific calculator with sufficient precision is essential to avoid rounding errors.
- Understanding π: Remember to use an appropriate approximation for π (pi). While 3.14 is a common approximation, more precise calculations might require using more decimal places (e.g., 3.14159).
Conclusion
Finding the radius of a cylinder is a fundamental skill with broad applications across various fields. By mastering the different methods outlined in this guide and paying close attention to detail, you can confidently calculate the radius of any cylinder, regardless of the available information. Remember to always double-check your work and ensure unit consistency for accurate and reliable results. Practice with different examples, and you'll quickly become proficient in this essential geometrical calculation.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
How Many Car Lengths Is 100 Feet
Mar 22, 2025
-
How Many Cups In 15 Oz Of Pumpkin
Mar 22, 2025
-
How Do You Beat Level 12 On Bloxorz
Mar 22, 2025
-
How Old Are You If You Were Born In 1954
Mar 22, 2025
-
How Many Tablespoons In 8 Ounces Of Cream Cheese
Mar 22, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about How To Find The Radius Of A Cylinder . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
