Is Boston North Or South Of Paris
Arias News
Mar 24, 2025 · 5 min read
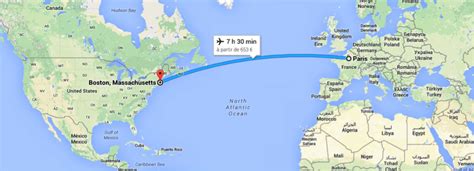
Table of Contents
Is Boston North or South of Paris? A Geographical Deep Dive
The question, "Is Boston north or south of Paris?" might seem simple at first glance. After all, we have readily available maps and geographical tools at our fingertips. However, a deeper exploration reveals a fascinating interplay of geography, cartography, and the very nature of directional terms. The answer isn't simply "north" or "south," but a nuanced exploration of relative location and the complexities of a spherical world projected onto a flat map.
Understanding Latitude and Longitude: The Foundation of Geographic Location
Before we tackle the core question, let's establish a foundational understanding of latitude and longitude. These are the coordinates used to pinpoint any location on Earth.
-
Latitude: Measured in degrees north or south of the equator (0°). The equator divides the Earth into the Northern and Southern Hemispheres. 90° North is the North Pole, and 90° South is the South Pole.
-
Longitude: Measured in degrees east or west of the Prime Meridian (0°), which runs through Greenwich, England. Longitude lines run from pole to pole.
By using latitude and longitude, we can precisely locate any point on Earth's surface. This precision is crucial for accurate geographical comparisons, including answering our central question about Boston and Paris.
Locating Boston and Paris: A Coordinated Approach
To determine the relative position of Boston and Paris, we need their respective coordinates:
-
Boston, Massachusetts, USA: Approximately 42.36° North, 71.06° West.
-
Paris, France: Approximately 48.86° North, 2.34° East.
Notice that both cities lie in the Northern Hemisphere, as their latitude values are positive. However, their longitudes differ significantly. Boston is located in the Western Hemisphere (West of the Prime Meridian), while Paris is in the Eastern Hemisphere (East of the Prime Meridian).
The Complication of a Spherical Earth and Map Projections
The challenge in answering "Is Boston north or south of Paris?" stems from the fact that we are dealing with a spherical Earth represented on a flat map. Map projections, the methods used to translate the spherical surface onto a flat plane, inevitably introduce distortions. Different projections emphasize different aspects of the Earth's surface, leading to variations in the relative positions of locations.
For instance, a Mercator projection, commonly used in world maps, exaggerates distances at higher latitudes. While useful for navigation, it can distort the relative north-south positioning of cities at different longitudes. Other projections, like the Robinson projection, attempt to minimize these distortions but might not be as accurate for determining precise north-south relationships.
Analyzing the Latitude: The Primary Determinant
Despite the complexities introduced by map projections, the latitude remains the primary factor in determining whether one city is north or south of another. Since Boston (42.36°N) has a lower latitude than Paris (48.86°N), Boston is south of Paris.
This conclusion remains consistent regardless of the map projection used. While the visual representation might vary slightly, the fundamental geographical relationship based on latitude remains unchanged.
Addressing the Longitude: A Secondary Consideration
The difference in longitude between Boston and Paris (Boston being west and Paris east) is a secondary consideration in this context. Longitude doesn't directly determine whether a city is north or south of another; it determines its east-west position. The longitude values merely indicate that the cities are separated by a considerable distance east-west. This distance is significant, highlighting the vast geographical separation across the Atlantic Ocean.
Visualizing the Relationship: A Mental Map Exercise
To further solidify understanding, imagine drawing a line connecting Boston and Paris on a globe. This line would pass through various points, neither strictly north-south nor strictly east-west, but rather a combination. However, the line's overall southward slant is determined by the latitude difference. The line would initially move eastward from Boston towards Paris as we approach Paris, crossing the Atlantic ocean.
This mental exercise underscores that while the longitudinal difference is important in understanding the overall distance and direction, the latitudinal difference is definitive in determining the north-south relationship.
Practical Implications and Real-World Applications
Understanding the relative geographical positions of cities like Boston and Paris has various practical implications:
-
Air Travel: Air travel routes are planned considering not only distance but also the Earth's curvature and prevailing winds. Knowledge of the relative north-south and east-west positions aids in efficient route planning.
-
Climate and Weather: The latitudinal positions of Boston and Paris influence their respective climates. Paris, being at a higher latitude, generally experiences colder winters and milder summers compared to Boston.
-
International Relations and Trade: Understanding the geographical relationship between countries contributes to understanding patterns of trade, cultural exchange, and international relations.
-
Navigation: Precise geographical coordinates are essential for various navigation systems, from GPS devices to maritime and aviation navigation.
Beyond the Simple Answer: A Broader Perspective
While the straightforward answer to "Is Boston north or south of Paris?" is south, this exploration has shown the question's deeper meaning. It highlights the complexities involved in translating a three-dimensional sphere onto a two-dimensional surface, the critical role of latitude and longitude, and the interconnectedness of geography with many aspects of our lives. The question might appear simple, but its answer requires a more sophisticated understanding of geographical concepts and their practical applications.
Further Exploration: Delving Deeper into Geographic Concepts
For those interested in expanding their understanding, further exploration could include:
-
Different Map Projections: Investigate various map projections and how they affect the relative positioning of cities.
-
Great Circle Distances: Calculate the great circle distance between Boston and Paris, the shortest distance between two points on a sphere.
-
Time Zones: Explore the time difference between Boston and Paris and its relationship to longitude.
-
Geopolitical Implications: Analyze the geopolitical implications of the geographical distance and relative positions of Boston and Paris in a global context.
By engaging with these deeper aspects of geography, we can move beyond the simple answer and gain a richer understanding of our world's spatial organization. The seemingly simple question "Is Boston north or south of Paris?" thus serves as a springboard for a fascinating exploration of geography and its complexities.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
How Many Ounces In 5 Gallons Of Water
Mar 28, 2025
-
Explain Why Goals Should Follow The Aeiou Theory
Mar 28, 2025
-
How Many Rhode Islands Fit In Texas
Mar 28, 2025
-
What Is A 43 Out Of 50
Mar 28, 2025
-
Naked And Afraid How Much Do They Get Paid
Mar 28, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Is Boston North Or South Of Paris . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
