Is Lettuce A Pure Substance Or Mixture
Arias News
Mar 23, 2025 · 5 min read
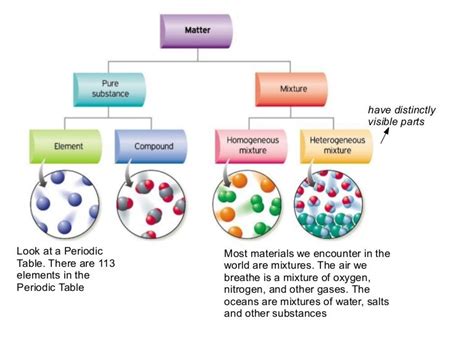
Table of Contents
Is Lettuce a Pure Substance or a Mixture? A Deep Dive into the Composition of a Common Vegetable
Lettuce, a staple in salads and sandwiches worldwide, presents a fascinating case study when considering the scientific classification of matter as either a pure substance or a mixture. At first glance, the answer might seem straightforward, but a closer examination reveals a complex interplay of chemical compounds and physical structures. This article delves into the intricacies of lettuce composition to determine its accurate classification and explore the broader implications for understanding the nature of matter.
Understanding Pure Substances and Mixtures
Before we dissect the composition of lettuce, let's establish a clear understanding of the terms "pure substance" and "mixture."
Pure substances are forms of matter that have a constant composition throughout. They cannot be separated into simpler substances by physical methods. Examples include elements (like oxygen or gold) and compounds (like water or table salt). A pure substance has a defined set of physical and chemical properties, such as melting point and boiling point.
Mixtures, conversely, consist of two or more substances physically combined. These substances retain their individual properties and can be separated by physical methods like filtration, distillation, or evaporation. Mixtures can be homogeneous (uniform composition throughout, like saltwater) or heterogeneous (non-uniform composition, like sand and water).
The Complex Composition of Lettuce
Lettuce, far from being a simple entity, is a complex biological structure comprising a multitude of components. It isn't merely composed of water; it's a dynamic interplay of water, various organic compounds, and inorganic minerals.
Water: The Major Component
Water constitutes the largest percentage of lettuce's mass, typically ranging from 90% to 96%. This water isn't simply absorbed; it's actively transported within the plant's tissues, playing crucial roles in nutrient transport, photosynthesis, and overall plant turgor (rigidity).
Carbohydrates: The Energy Source
Lettuce, like all plants, utilizes carbohydrates as its primary energy source. These carbohydrates are primarily in the form of cellulose, a complex structural carbohydrate that forms the cell walls of lettuce cells, providing rigidity and structure. Other carbohydrates, like starch and sugars, are also present, contributing to the overall energy content and sweetness.
Proteins: The Building Blocks
Proteins are essential for the growth and development of lettuce. These proteins comprise amino acids, the building blocks of all proteins. They contribute to the structure of enzymes, hormones, and other essential cellular components. The types and quantities of proteins vary depending on the lettuce cultivar.
Lipids: Essential for Membrane Function
While present in relatively smaller amounts compared to carbohydrates and proteins, lipids, including fats and oils, play vital roles in maintaining cell membrane integrity and facilitating various metabolic processes. These lipids are crucial for the overall health and function of the lettuce plant.
Vitamins and Minerals: Essential Micronutrients
Lettuce is a good source of various vitamins and minerals, vital for human health. These micronutrients are critical for a variety of bodily functions, and their presence highlights the complexity of the lettuce composition. Key vitamins found in lettuce include vitamin A (beta-carotene), vitamin C, vitamin K, and folate. Minerals present include potassium, calcium, magnesium, and iron. These micronutrients are not uniformly distributed throughout the lettuce leaf.
Pigments: The Colors of Lettuce
The characteristic green color of lettuce stems from chlorophyll, the pigment responsible for photosynthesis. Different lettuce varieties may exhibit variations in color due to the presence of other pigments, like carotenoids, which contribute to yellow, orange, or red hues. These pigments play a crucial role in the plant's ability to absorb light and carry out photosynthesis.
Other Organic Compounds
Beyond the major components mentioned above, lettuce also contains a wide array of other organic compounds, including:
- Fiber: Insoluble fiber primarily contributes to the texture and digestive health benefits.
- Phytochemicals: These bioactive compounds offer potential health advantages, contributing to antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties. Their complexity contributes significantly to the nuanced nature of lettuce’s composition.
- Enzymes: These biological catalysts facilitate numerous metabolic reactions within the plant.
The Conclusion: Lettuce as a Mixture
Given the extensive list of components present in lettuce, it's clear that lettuce is unequivocally a mixture. Its heterogeneous nature is evident in the non-uniform distribution of its components. The various components—water, carbohydrates, proteins, lipids, vitamins, minerals, pigments, and other organic compounds—retain their individual chemical properties and are not chemically bonded in a fixed ratio. Physical separation techniques could potentially isolate some of these components. For example, water could be separated through evaporation.
While the numerous compounds contribute to its overall properties, they are not chemically bonded to form a pure substance. This complex mixture of compounds and the non-uniform distribution of these components confirm lettuce’s classification as a heterogeneous mixture.
Further Considerations: Variability and Cultivars
The exact composition of lettuce can vary significantly depending on several factors:
- Lettuce Cultivar: Different varieties of lettuce have differing concentrations of nutrients and other components. Some cultivars are bred for specific traits, such as increased leaf size or higher nutrient content.
- Growing Conditions: Environmental factors like soil composition, sunlight exposure, water availability, and temperature significantly influence the plant's growth and chemical composition.
- Harvesting and Storage: The time of harvest and post-harvest handling practices can affect the nutritional value and overall quality of the lettuce.
Implications for Nutritional Science and Food Technology
Understanding the complex composition of lettuce has significant implications for nutritional science and food technology. The accurate quantification of its various components is crucial for nutritional labeling and dietary recommendations. Moreover, this knowledge is essential for developing advanced food processing techniques, potentially enhancing the shelf life and nutritional value of lettuce.
Conclusion: A Heterogeneous Mixture of Life
In conclusion, lettuce is definitively a mixture, a complex and heterogeneous blend of various organic and inorganic compounds. Its composition is far from simple, encompassing a wide range of substances that contribute to its nutritional value and overall biological function. The diverse range of components, the variations within different cultivars, and the impact of growing conditions only serve to highlight the complexity of this common vegetable. Understanding this multifaceted nature is crucial for advancing research in fields ranging from agricultural science to human nutrition.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
In Chapter 4 When Gatsby Drives Nick
Mar 25, 2025
-
What Does Dark Blue On A Mood Necklace Mean
Mar 25, 2025
-
Least Common Multiple Of 9 And 7
Mar 25, 2025
-
How Many Quarts Is 64 Fl Oz
Mar 25, 2025
-
Which Conflict Is Most Clearly Related To Cultural Values
Mar 25, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Is Lettuce A Pure Substance Or Mixture . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
