Is The Square Root Of 15 A Rational Number
Arias News
Mar 20, 2025 · 5 min read
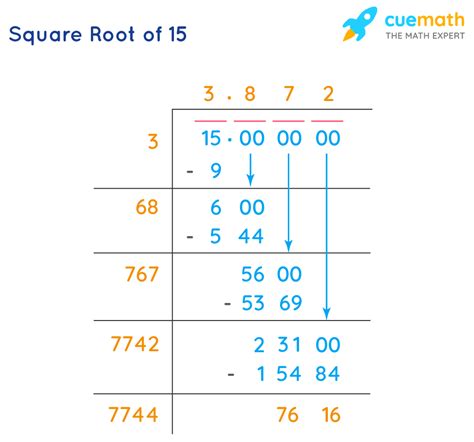
Table of Contents
Is the Square Root of 15 a Rational Number? A Deep Dive into Irrationality
The question of whether the square root of 15 is a rational number is a fundamental concept in mathematics, touching upon the core principles of number theory. Understanding this requires a solid grasp of rational and irrational numbers. This article will delve into the intricacies of this question, providing a comprehensive explanation accessible to a broad audience, from beginners to those seeking a deeper understanding. We will explore definitions, proofs, and related concepts to definitively answer the question and solidify your comprehension of this crucial mathematical topic.
Understanding Rational and Irrational Numbers
Before tackling the square root of 15, let's establish a clear understanding of rational and irrational numbers.
Rational Numbers: These numbers can be expressed as a fraction p/q, where 'p' and 'q' are integers, and 'q' is not zero. Examples include 1/2, 3/4, -2/5, and even integers like 5 (which can be expressed as 5/1). Crucially, rational numbers, when expressed as decimals, either terminate (e.g., 0.75) or have a repeating pattern (e.g., 0.333...).
Irrational Numbers: These numbers cannot be expressed as a fraction of two integers. Their decimal representations are non-terminating and non-repeating. Famous examples include π (pi) and e (Euler's number). The square root of many numbers also falls into this category.
Investigating the Square Root of 15
Now, let's focus on √15. To determine if it's rational or irrational, we can employ a proof by contradiction. This method assumes the opposite of what we want to prove and shows that this assumption leads to a contradiction, thus proving the original statement.
Proof by Contradiction: √15 is Irrational
-
Assumption: Let's assume that √15 is a rational number. This means it can be expressed as a fraction p/q, where p and q are integers, q ≠ 0, and the fraction is in its simplest form (meaning p and q share no common factors other than 1).
-
Equation: If √15 = p/q, then squaring both sides gives us: 15 = p²/q²
-
Rearrangement: Multiplying both sides by q² yields: 15q² = p²
-
Deduction: This equation tells us that p² is a multiple of 15. Since 15 = 3 x 5, it follows that p² must be divisible by both 3 and 5. If p² is divisible by a prime number, then p itself must also be divisible by that prime number (this is a fundamental property of prime numbers). Therefore, p must be divisible by both 3 and 5. We can express this as p = 3 * 5 * k = 15k, where k is an integer.
-
Substitution: Substituting p = 15k into the equation 15q² = p², we get: 15q² = (15k)² = 225k²
-
Simplification: Dividing both sides by 15 simplifies the equation to: q² = 15k²
-
Contradiction: This equation shows that q² is also divisible by 15, and therefore q is divisible by 15. However, this contradicts our initial assumption that p/q is in its simplest form, as both p and q are now divisible by 15.
-
Conclusion: Since our initial assumption leads to a contradiction, the assumption must be false. Therefore, √15 cannot be expressed as a fraction p/q, and it is an irrational number.
Exploring Related Concepts
Understanding the irrationality of √15 opens doors to exploring related concepts in number theory:
Prime Factorization and its Role in Irrationality Proofs
The proof above heavily relied on the prime factorization of 15 (3 x 5). The unique prime factorization of integers is a cornerstone of number theory and plays a critical role in proving the irrationality of square roots of non-perfect squares. A non-perfect square is a number that cannot be obtained by squaring an integer.
Perfect Squares and their Square Roots
A perfect square is a number that is the square of an integer (e.g., 4, 9, 16, 25). The square root of a perfect square is always a rational number (an integer, in fact). The key distinction lies in the fact that non-perfect squares, like 15, do not have rational square roots.
Decimal Representation of Irrational Numbers
The decimal representation of √15 is a non-terminating, non-repeating sequence of digits. While we can approximate its value (approximately 3.87298), we cannot express it precisely as a finite decimal or a repeating decimal. This is a defining characteristic of irrational numbers.
The Density of Irrational Numbers
It's important to note that irrational numbers are far more numerous than rational numbers. While there are infinitely many rational numbers, the number of irrational numbers is infinitely larger. This concept demonstrates the vastness and complexity of the real number system.
Practical Applications and Further Exploration
While the concept of irrational numbers like √15 might seem purely theoretical, it has practical applications in various fields:
-
Geometry: Calculations involving lengths and areas often involve irrational numbers. For instance, the diagonal of a square with side length 1 is √2, an irrational number.
-
Physics: Many physical constants, such as the speed of light or Planck's constant, involve irrational numbers in their precise representations.
-
Computer Science: Approximating irrational numbers efficiently is crucial in many computational tasks, leading to advanced algorithms and techniques.
-
Advanced Mathematics: The study of irrational numbers forms the basis for advanced concepts in analysis, algebra, and number theory.
Conclusion: The Irrationality of √15 and its Significance
In conclusion, the square root of 15 is definitively an irrational number. This fact, demonstrable through a proof by contradiction leveraging the properties of prime factorization, highlights the fundamental differences between rational and irrational numbers. Understanding this distinction is paramount to grasping the richness and complexity of the real number system and its applications across various scientific and mathematical disciplines. Further exploration of number theory and related fields will deepen your appreciation for the elegance and power of mathematical concepts like irrationality. The seemingly simple question of whether √15 is rational unlocks a deeper understanding of the foundational building blocks of mathematics.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
What Happens If You Get Caught Cheating In College
Mar 21, 2025
-
How Do I Send An Evite Reminder
Mar 21, 2025
-
When Performing A Self Rescue When Should You Swim To Shore
Mar 21, 2025
-
How Many Decaliters Are In A Liter
Mar 21, 2025
-
What Note Sits In The Middle Of The Grand Staff
Mar 21, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Is The Square Root Of 15 A Rational Number . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
