Is Vanilla Extract A Mixture Or Compound
Arias News
Mar 31, 2025 · 5 min read
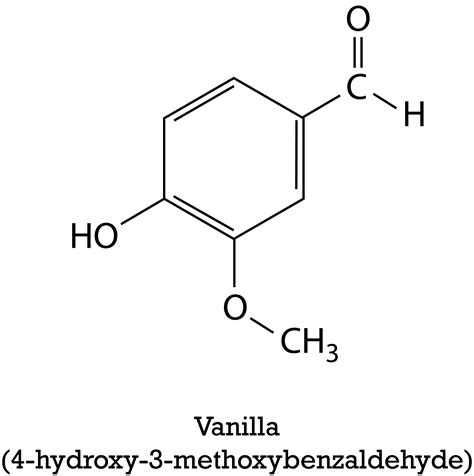
Table of Contents
Is Vanilla Extract a Mixture or a Compound? Decoding the Flavor
Vanilla extract, that ubiquitous kitchen staple lending its warm, comforting aroma and distinctive flavor to countless recipes, often sparks a curious question: is it a mixture or a compound? The answer, as with many things in chemistry, isn't quite as straightforward as a simple "yes" or "no." This article will delve deep into the composition of vanilla extract, exploring its multifaceted nature and clarifying its classification within the chemical world.
Understanding the Fundamentals: Mixtures vs. Compounds
Before we dive into the specifics of vanilla extract, let's establish a clear understanding of the difference between mixtures and compounds.
Compounds: The Building Blocks of Matter
Compounds are substances formed when two or more chemical elements are chemically bonded together. These bonds create a new substance with entirely different properties from its constituent elements. For example, water (H₂O) is a compound formed from the elements hydrogen and oxygen. The properties of water are vastly different from those of hydrogen gas and oxygen gas. The key characteristic of a compound is that its composition is fixed and can only be changed through a chemical reaction.
Mixtures: A Blend of Substances
Mixtures, on the other hand, are physical combinations of two or more substances where each substance retains its individual chemical properties. These substances are not chemically bonded. A simple example is saltwater – the salt and water retain their individual properties, and the mixture can be easily separated through physical methods like evaporation. The composition of a mixture is not fixed and can vary widely.
The Complex Composition of Vanilla Extract
Vanilla extract's classification as a mixture or compound hinges on its composition. Vanilla extract is not a single pure substance; it's a complex solution of various chemical compounds derived from vanilla beans. These compounds contribute to its distinctive flavor, aroma, and overall character. Let's explore the key components:
Vanillin: The Star of the Show
Vanillin (C₈H₈O₃) is the primary aromatic compound responsible for the characteristic flavor and aroma of vanilla. While often considered the defining element of vanilla, it only comprises a portion of the overall flavor profile. Synthesized vanillin, often used in commercially produced extracts, is a pure compound. However, naturally derived vanillin found in vanilla extract is part of a much larger mixture.
Other Aromatic Compounds: The Supporting Cast
Beyond vanillin, hundreds of other volatile organic compounds (VOCs) contribute to vanilla's complex and nuanced flavor. These include:
- Vanillin derivatives: Slight variations in the vanillin molecule create subtle yet significant differences in the overall taste.
- Esters: These contribute fruity and floral notes to the extract.
- Alcohols: Provide subtle sweetness and contribute to the overall mouthfeel.
- Aldehydes and ketones: Influence the spiciness and intensity of the flavor.
- Acids: Balance the sweetness and add complexity.
This rich tapestry of aromatic compounds, all present in varying concentrations depending on the type of vanilla bean, processing methods, and extraction techniques, illustrates the intricate chemical composition of vanilla extract.
Ethanol: The Solvent
Vanilla extract is not just a collection of aromatic compounds; it's a solution. Ethanol (ethyl alcohol) serves as the solvent, dissolving the aromatic compounds from the vanilla beans and creating the liquid extract. Ethanol itself is a compound.
Why Vanilla Extract is Categorically a Mixture
Considering the above, it becomes clear that vanilla extract is unequivocally a mixture. The key reasons are:
- Multiple Components: It contains numerous different chemical compounds, each retaining its individual properties. These compounds are not chemically bonded to each other.
- Variable Composition: The precise ratio of these compounds varies depending on factors like the origin of the vanilla beans, the extraction method, and even the age of the extract. A consistent chemical formula cannot be assigned to vanilla extract.
- Physical Separation: The components of vanilla extract can be separated through physical methods, such as fractional distillation, chromatography, and evaporation. This is a hallmark of mixtures, not compounds.
Exploring the Nuances: Natural vs. Artificial Vanilla Extract
The distinction between natural and artificial vanilla extract further highlights the mixture aspect.
Natural Vanilla Extract: A Complex Natural Mixture
Natural vanilla extract is derived directly from vanilla beans through an extraction process using ethanol as a solvent. The resulting extract is a complex mixture of hundreds of compounds naturally present in the vanilla bean. This composition varies considerably depending on factors such as the bean's origin, climate, and curing methods, hence the wide variety of flavors and aromas among natural vanilla extracts.
Artificial Vanilla Extract: Primarily a Mixture, but with a Simplified Composition
Artificial vanilla extract, on the other hand, mainly consists of synthetic vanillin dissolved in ethanol. While primarily a mixture of synthetic vanillin and ethanol, it still isn't a single chemical compound. The lack of the hundreds of other flavor compounds present in the natural variant is its major difference.
The Significance of Understanding Vanilla Extract's Composition
Understanding that vanilla extract is a mixture, not a compound, is crucial for several reasons:
- Flavor Complexity: The diverse range of compounds in the mixture contributes to its rich and nuanced flavor profile.
- Quality Variation: The variable composition explains why different vanilla extracts have different flavor characteristics.
- Extraction Techniques: The understanding informs the development of optimized extraction methods to maximize the yield and quality of desirable aromatic compounds.
- Food Science Applications: Knowing the composition helps in understanding how vanilla extract interacts with other ingredients in food and beverage applications.
Conclusion: A Deliciously Complex Mixture
In conclusion, vanilla extract is unequivocally a mixture, a complex and fascinating blend of numerous chemical compounds, primarily vanillin and ethanol. Its composition's variability, the capacity for physical separation of its components, and the retention of individual chemical properties by each component confirm its classification as a mixture. This understanding is essential for appreciating the nuances of vanilla flavor, optimizing extraction techniques, and exploring its diverse applications in the culinary and food science worlds. The next time you use that bottle of vanilla extract, you can appreciate the intricate chemistry behind its delightful aroma and flavor, recognizing it as a beautifully complex mixture.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
5 Ft 4 In Inches In Meters
Apr 01, 2025
-
What Is The Answer For A Subtraction Problem Called
Apr 01, 2025
-
How Do You Say Say Cheese In Spanish
Apr 01, 2025
-
How Tall Is 33 Inches In Feet
Apr 01, 2025
-
How Many Zeros Are In 1 5 Million
Apr 01, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Is Vanilla Extract A Mixture Or Compound . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
