Least Common Multiple Of 4 And 12
Arias News
Mar 15, 2025 · 5 min read
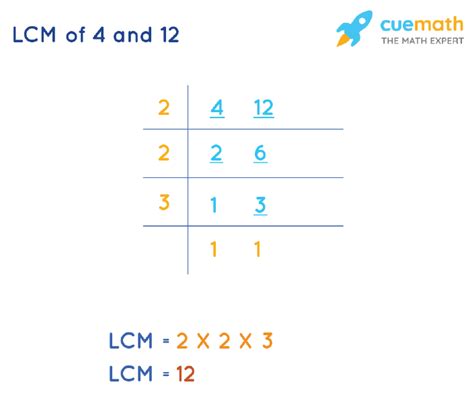
Table of Contents
Unveiling the Least Common Multiple (LCM) of 4 and 12: A Deep Dive
Finding the least common multiple (LCM) might seem like a simple arithmetic task, but understanding its underlying principles and applications opens doors to more advanced mathematical concepts. This article delves into the LCM of 4 and 12, exploring various methods for calculation, illustrating its relevance in real-world scenarios, and connecting it to broader mathematical ideas. We'll move beyond simply stating the answer and instead provide a comprehensive understanding of the concept.
Understanding Least Common Multiple (LCM)
The least common multiple (LCM) of two or more integers is the smallest positive integer that is divisible by all the integers. Think of it as the smallest number that contains all the given numbers as factors. This concept is fundamental in various mathematical fields and has practical applications in everyday life.
For example, if you're organizing events that repeat at different intervals, finding the LCM helps determine when those events will coincide. This concept is crucial in scheduling, planning, and even music theory.
Methods to Find the LCM of 4 and 12
Several methods can determine the LCM of 4 and 12. Let's explore three common approaches:
1. Listing Multiples Method
This is a straightforward method, especially for smaller numbers. We list the multiples of each number until we find the smallest common multiple.
- Multiples of 4: 4, 8, 12, 16, 20, 24, 28, 32...
- Multiples of 12: 12, 24, 36, 48...
The smallest multiple present in both lists is 12. Therefore, the LCM of 4 and 12 is 12.
2. Prime Factorization Method
This method is more efficient for larger numbers. We find the prime factorization of each number and then construct the LCM using the highest powers of each prime factor.
- Prime factorization of 4: 2²
- Prime factorization of 12: 2² x 3
The highest power of 2 is 2², and the highest power of 3 is 3¹. Therefore, the LCM is 2² x 3 = 4 x 3 = 12.
3. Greatest Common Divisor (GCD) Method
This method uses the relationship between the LCM and the greatest common divisor (GCD) of two numbers. The formula connecting LCM and GCD is:
LCM(a, b) x GCD(a, b) = a x b
First, we find the GCD of 4 and 12 using the Euclidean algorithm or prime factorization.
- Prime factorization of 4: 2²
- Prime factorization of 12: 2² x 3
The common prime factor is 2², so the GCD(4, 12) = 4.
Now, we can use the formula:
LCM(4, 12) x 4 = 4 x 12
LCM(4, 12) = (4 x 12) / 4 = 12
Real-World Applications of LCM
The LCM isn't just a theoretical concept; it has numerous practical applications across various fields:
1. Scheduling and Planning
Imagine two machines in a factory operating on different cycles. One runs every 4 hours, and the other every 12 hours. To determine when both machines will be simultaneously idle for maintenance, you need to find the LCM of 4 and 12, which is 12. Both machines will be idle together every 12 hours.
This principle extends to scheduling meetings, appointments, and coordinating events with repeating intervals.
2. Music Theory
Musical rhythms and harmonies are often based on the LCM. If one instrument plays a note every 4 beats and another every 12 beats, the LCM (12) determines when their notes coincide, creating a specific harmonic effect.
3. Fractions and Arithmetic
The LCM is crucial when adding or subtracting fractions with different denominators. To find a common denominator, you need the LCM of the denominators. For example, adding 1/4 and 1/12 requires finding the LCM of 4 and 12 (which is 12), allowing us to rewrite the fractions with a common denominator before adding them.
4. Calculating Ratios and Proportions
Understanding LCM helps in solving problems involving ratios and proportions where you need to find equivalent fractions or quantities with a common denominator.
Connecting LCM to Other Mathematical Concepts
The LCM is intrinsically linked to other fundamental mathematical concepts:
1. GCD (Greatest Common Divisor):
As shown earlier, the LCM and GCD are intimately related. Knowing one allows you to easily calculate the other using the formula: LCM(a, b) x GCD(a, b) = a x b. This relationship highlights the interconnectedness of these core arithmetic concepts.
2. Prime Factorization:
Prime factorization provides a systematic and efficient way to find both the LCM and GCD. Breaking down numbers into their prime factors reveals the building blocks of the numbers and facilitates the calculation of LCM and GCD. This connection emphasizes the importance of prime numbers in number theory.
3. Modular Arithmetic:
The LCM plays a role in modular arithmetic, a system of arithmetic for integers, where numbers "wrap around" upon reaching a certain value (the modulus). The LCM helps in determining when certain patterns or congruences repeat themselves in modular arithmetic.
4. Abstract Algebra:
The concept of LCM generalizes to more abstract algebraic structures. In ring theory, the least common multiple concept extends to ideals within rings, connecting the elementary arithmetic notion to higher-level algebra.
Beyond the Basics: Exploring More Complex Scenarios
While this article focused on the LCM of 4 and 12, the principles discussed apply to finding the LCM of any set of integers. For larger sets of numbers or when dealing with larger numbers, the prime factorization method generally proves most efficient. For example, to find the LCM of 12, 18, and 30, you would find the prime factorization of each number:
- 12 = 2² x 3
- 18 = 2 x 3²
- 30 = 2 x 3 x 5
The LCM would then be 2² x 3² x 5 = 180.
Conclusion: The Significance of LCM in Mathematics and Beyond
The least common multiple of 4 and 12, while seemingly simple, serves as a gateway to a deeper understanding of fundamental mathematical concepts. From its practical applications in scheduling and music theory to its theoretical significance in number theory and abstract algebra, the LCM demonstrates the interconnectedness of mathematical ideas. Mastering the LCM is not just about finding the answer; it's about understanding the underlying principles and appreciating its far-reaching implications in various aspects of life and advanced mathematics. This comprehensive exploration goes beyond a simple calculation, providing a solid foundation for further exploration of number theory and its applications.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
How Long Does It Take To Drive 90 Miles
Mar 17, 2025
-
How Much Does A Gallon Of Ice Cream Weigh
Mar 17, 2025
-
Is Red Pepper The Same As Cayenne
Mar 17, 2025
-
How Long Would It Take To Walk 60 Miles
Mar 17, 2025
-
How Many Pounds Of Peaches In A Bushel
Mar 17, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Least Common Multiple Of 4 And 12 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
