Least Common Multiple Of 7 And 9
Arias News
Mar 24, 2025 · 5 min read
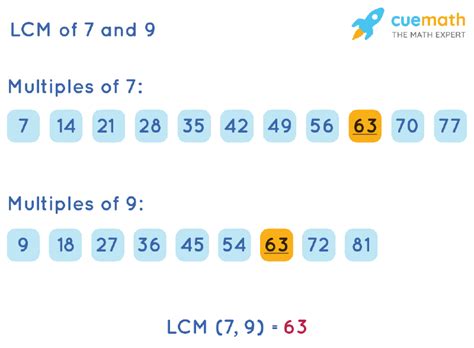
Table of Contents
Finding the Least Common Multiple (LCM) of 7 and 9: A Comprehensive Guide
The least common multiple (LCM) is a fundamental concept in mathematics, particularly in number theory and algebra. Understanding LCM is crucial for various applications, from simplifying fractions to solving problems involving rhythmic cycles. This article dives deep into finding the LCM of 7 and 9, exploring different methods and illustrating the broader implications of this mathematical concept.
What is the Least Common Multiple (LCM)?
The least common multiple (LCM) of two or more integers is the smallest positive integer that is divisible by all the integers. In simpler terms, it's the smallest number that contains all the numbers as factors. For instance, the LCM of 2 and 3 is 6 because 6 is the smallest positive integer that is divisible by both 2 and 3.
The concept of LCM extends beyond just two numbers. You can find the LCM of any number of integers. Understanding LCM is key in various mathematical operations and real-world scenarios.
Methods for Finding the LCM of 7 and 9
There are several methods to determine the LCM of 7 and 9. Let's explore the most common and effective approaches:
1. Listing Multiples Method
This is a straightforward method, especially useful for smaller numbers like 7 and 9. We list the multiples of each number until we find the smallest common multiple.
- Multiples of 7: 7, 14, 21, 28, 35, 42, 49, 56, 63, 70...
- Multiples of 9: 9, 18, 27, 36, 45, 54, 63, 72...
By comparing the lists, we can see that the smallest common multiple is 63. Therefore, the LCM(7, 9) = 63.
This method is simple but can become tedious for larger numbers.
2. Prime Factorization Method
This is a more efficient method, particularly for larger numbers. It involves finding the prime factorization of each number and then constructing the LCM using the highest powers of all prime factors.
- Prime factorization of 7: 7 (7 is a prime number)
- Prime factorization of 9: 3² (9 = 3 x 3)
To find the LCM, we take the highest power of each prime factor present in the factorizations:
- The highest power of 3 is 3² = 9
- The highest power of 7 is 7¹ = 7
Therefore, LCM(7, 9) = 3² x 7 = 9 x 7 = 63
This method is generally more efficient than listing multiples, especially when dealing with larger numbers or a greater number of integers.
3. Using the Formula: LCM(a, b) = (|a x b|) / GCD(a, b)
This method utilizes the greatest common divisor (GCD) of the two numbers. The GCD is the largest positive integer that divides both numbers without leaving a remainder.
-
Finding the GCD of 7 and 9: Since 7 and 9 share no common factors other than 1, their GCD is 1. GCD(7, 9) = 1.
-
Applying the formula: LCM(7, 9) = (|7 x 9|) / GCD(7, 9) = 63 / 1 = 63
This method requires knowing the GCD, which can be found using various techniques like the Euclidean algorithm (especially efficient for larger numbers).
Applications of LCM
The concept of LCM has practical applications in diverse areas:
1. Fraction Simplification
Finding the LCM is crucial when adding or subtracting fractions with different denominators. We find the LCM of the denominators and then rewrite the fractions with this common denominator before performing the addition or subtraction.
For example, adding 1/7 and 1/9: The LCM of 7 and 9 is 63. We rewrite the fractions as 9/63 and 7/63, respectively. Then, 9/63 + 7/63 = 16/63.
2. Cyclic Events
LCM is used extensively to solve problems involving events that repeat cyclically. Consider scenarios like:
-
Meeting scheduling: Two friends meet every 7 days and every 9 days, respectively. When will they meet again? The LCM(7, 9) = 63 days. They'll meet again after 63 days.
-
Gear rotations: Two gears with 7 and 9 teeth will be in the same position again after LCM(7, 9) = 63 rotations of the smaller gear.
-
Musical rhythms: In music, finding the LCM helps synchronize different rhythmic patterns.
3. Algebra and Number Theory
LCM plays a significant role in various algebraic manipulations and theorems in number theory. It's fundamental to concepts like modular arithmetic, solving Diophantine equations, and other advanced mathematical concepts.
Choosing the Right Method
The best method for finding the LCM depends on the context and the size of the numbers involved:
-
Listing Multiples: Suitable for small numbers and introductory learning.
-
Prime Factorization: More efficient for larger numbers and provides a deeper understanding of number properties.
-
GCD Formula: Efficient for larger numbers, especially when the GCD is readily available or easily calculated.
Conclusion: LCM(7, 9) = 63, and Beyond
We have thoroughly explored different methods for determining the least common multiple of 7 and 9, arriving at the answer: 63. This seemingly simple calculation highlights a fundamental mathematical concept with far-reaching applications. Understanding LCM is not just about finding the answer; it's about mastering a tool that unlocks solutions in various mathematical and real-world problems. By grasping the different methods and understanding their strengths, you can confidently tackle LCM problems of varying complexity, whether it's simplifying fractions, synchronizing cyclic events, or delving deeper into the intricacies of number theory. The ability to efficiently calculate the LCM is a valuable skill in mathematics and beyond. This knowledge empowers you to solve problems effectively and appreciate the elegance of mathematical relationships.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
How Many Cups Is 32 Oz Of Frozen Hash Browns
Mar 28, 2025
-
40 Quarts Is How Many Cubic Feet
Mar 28, 2025
-
How Much Does A Slice Of Bread Weigh
Mar 28, 2025
-
How Many Chips Are In 1 Oz
Mar 28, 2025
-
Why Did Gyro Go Into A Bakery
Mar 28, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Least Common Multiple Of 7 And 9 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
