Least Common Multiple Of 9 And 15
Arias News
Mar 24, 2025 · 5 min read
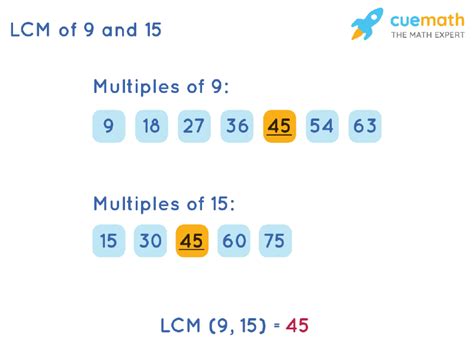
Table of Contents
Unveiling the Least Common Multiple (LCM) of 9 and 15: A Deep Dive
Finding the least common multiple (LCM) might seem like a simple arithmetic task, but understanding its underlying principles and applications reveals a fascinating area of number theory with practical implications in various fields. This comprehensive guide will explore the LCM of 9 and 15, employing multiple methods to solve the problem, and then delve into the broader significance of LCMs in mathematics and beyond.
Understanding Least Common Multiples (LCMs)
Before we tackle the specific LCM of 9 and 15, let's establish a firm grasp of the concept. The least common multiple of two or more integers is the smallest positive integer that is divisible by all the integers without leaving a remainder. It's a fundamental concept in arithmetic and plays a vital role in various mathematical operations and real-world applications.
Key characteristics of LCMs:
- Positive Integer: The LCM is always a positive integer.
- Divisibility: The LCM is divisible by each of the original numbers.
- Minimality: It's the smallest positive integer possessing this divisibility property.
Methods for Calculating the LCM of 9 and 15
Several methods can be employed to determine the LCM of 9 and 15. We will examine three common approaches: listing multiples, prime factorization, and using the greatest common divisor (GCD).
Method 1: Listing Multiples
This is a straightforward method, particularly useful for smaller numbers. We list the multiples of each number until we find the smallest multiple common to both.
Multiples of 9: 9, 18, 27, 36, 45, 54, 63, 72, 81, 90, ...
Multiples of 15: 15, 30, 45, 60, 75, 90, 105, ...
By comparing the lists, we observe that the smallest common multiple is 45. Therefore, the LCM(9, 15) = 45. This method works well for smaller numbers but becomes cumbersome for larger integers.
Method 2: Prime Factorization
This method is more efficient for larger numbers. It involves finding the prime factorization of each number and then constructing the LCM using the highest powers of each prime factor present in the factorizations.
Prime factorization of 9: 3²
Prime factorization of 15: 3 x 5
To find the LCM, we take the highest power of each prime factor present in either factorization:
- The highest power of 3 is 3² = 9.
- The highest power of 5 is 5¹ = 5.
Therefore, LCM(9, 15) = 3² x 5 = 9 x 5 = 45. This method is generally more efficient than listing multiples, especially for larger numbers.
Method 3: Using the Greatest Common Divisor (GCD)
The LCM and GCD are closely related. There's a formula that connects them:
LCM(a, b) x GCD(a, b) = a x b
First, we need to find the GCD of 9 and 15. We can use the Euclidean algorithm for this:
- Divide the larger number (15) by the smaller number (9): 15 = 1 x 9 + 6
- Replace the larger number with the remainder (6) and repeat: 9 = 1 x 6 + 3
- Repeat: 6 = 2 x 3 + 0
The last non-zero remainder is the GCD, which is 3.
Now, we can use the formula:
LCM(9, 15) = (9 x 15) / GCD(9, 15) = (135) / 3 = 45
This method is particularly useful when dealing with larger numbers because finding the GCD is often simpler than directly calculating the LCM.
Applications of Least Common Multiples
The LCM isn't just a theoretical concept; it has numerous practical applications across various fields:
1. Scheduling and Time Management
Imagine two events happening periodically. One event occurs every 9 days, and another every 15 days. The LCM helps determine when both events will occur simultaneously. In this case, LCM(9, 15) = 45, meaning both events will coincide every 45 days. This principle is crucial in scheduling tasks, appointments, and even coordinating complex industrial processes.
2. Fraction Arithmetic
Finding a common denominator when adding or subtracting fractions requires determining the LCM of the denominators. For instance, to add 1/9 and 1/15, we would find the LCM of 9 and 15 (which is 45), and then rewrite the fractions with a common denominator of 45 before performing the addition.
3. Modular Arithmetic and Cryptography
LCMs play a significant role in modular arithmetic, a branch of number theory with applications in cryptography and computer science. Modular arithmetic deals with remainders after division, and LCMs are frequently used in solving modular equations.
4. Music Theory
Musical intervals and harmonies are related to the ratios of frequencies. LCMs help in determining when different musical tones will coincide or create harmonious sounds.
5. Engineering and Construction
In projects involving repetitive patterns or cycles (like the construction of repeating structures or the synchronization of machinery), the LCM can be used to optimize scheduling and resource allocation.
Beyond the Basics: Exploring Further Concepts
While we've focused on the LCM of 9 and 15, the concept extends to more than two numbers. Finding the LCM of multiple integers requires applying the same principles, either by extending the prime factorization method or by iteratively applying the LCM calculation for pairs of numbers.
Conclusion: The Importance of Understanding LCMs
Understanding the least common multiple, even in seemingly simple cases like the LCM of 9 and 15, provides a foundation for tackling more complex mathematical problems. Its applications extend far beyond the classroom, impacting various practical aspects of daily life and specialized fields. By mastering the different methods for calculating LCMs, you equip yourself with a valuable tool for problem-solving and a deeper appreciation for the beauty and utility of number theory. The seemingly straightforward concept of finding the LCM of 9 and 15 opens doors to a wide range of mathematical and real-world applications, highlighting the power and elegance of fundamental mathematical principles.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Subjects Of Special Study Or Research Work
Mar 29, 2025
-
How Many Rotors Does A Car Need
Mar 29, 2025
-
4 Letter Words Starting And Ending With Same Letter
Mar 29, 2025
-
How Many Ml Of Water In A Bottle
Mar 29, 2025
-
How High Is A 6 Story Building
Mar 29, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Least Common Multiple Of 9 And 15 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
