Line S Is The Perpendicular Bisector Of Jk
Arias News
Mar 19, 2025 · 6 min read
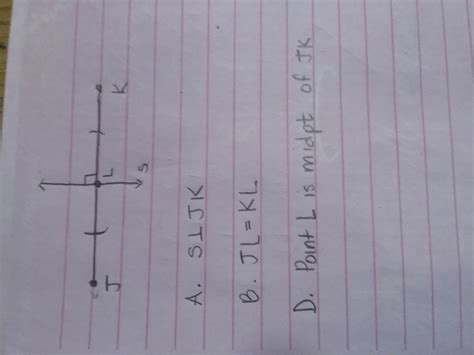
Table of Contents
Line S is the Perpendicular Bisector of JK: A Deep Dive into Geometry
Geometry, at its core, is the study of shapes, sizes, relative positions of figures, and the properties of space. Within this fascinating field, the concept of perpendicular bisectors holds significant importance. Understanding this concept unlocks the door to solving various geometrical problems and lays a foundation for more advanced topics. This article delves into the properties of perpendicular bisectors, focusing specifically on line 's' as the perpendicular bisector of line segment JK. We will explore its definition, properties, theorems, proofs, and practical applications.
Defining the Perpendicular Bisector
Before we delve into the specifics of line 's' bisecting JK, let's establish a clear understanding of the term "perpendicular bisector." A perpendicular bisector of a line segment is a line that is perpendicular to the line segment and passes through its midpoint. This means it intersects the segment at a 90-degree angle and divides the segment into two equal parts. Crucially, every point on the perpendicular bisector is equidistant from the endpoints of the line segment it bisects. This equidistance property is key to many proofs and applications.
In our case, line 's' is defined as the perpendicular bisector of line segment JK. This implies two critical facts:
- Perpendicularity: Line 's' intersects line segment JK at a right angle (90 degrees).
- Bisecting: Line 's' passes through the midpoint of JK, dividing JK into two congruent segments of equal length. Let's denote the midpoint of JK as M. Then, JM = MK.
Properties of the Perpendicular Bisector
The perpendicular bisector possesses several key properties that make it a powerful tool in geometry:
-
Equidistance Property: As mentioned earlier, this is the most important property. Any point on line 's' is equidistant from points J and K. This means that the distance from any point on 's' to J is equal to the distance from that same point to K. This property is often used in proofs and constructions.
-
Uniqueness: For any given line segment, there is only one perpendicular bisector. This uniqueness ensures consistency and predictability in geometric constructions and proofs.
-
Construction: The perpendicular bisector can be constructed using a compass and straightedge. This construction method relies on the equidistance property and is a fundamental technique in Euclidean geometry.
-
Applications in Coordinate Geometry: The equation of the perpendicular bisector can be derived using the coordinates of the endpoints of the line segment. This allows for algebraic manipulation and problem-solving in coordinate geometry.
Theorems Related to Perpendicular Bisectors
Several important theorems in geometry relate directly to perpendicular bisectors. These theorems provide powerful tools for solving problems and deducing geometrical relationships:
-
The Perpendicular Bisector Theorem: This theorem formally states the equidistance property. If a point lies on the perpendicular bisector of a line segment, then it is equidistant from the endpoints of the segment. Conversely, if a point is equidistant from the endpoints of a line segment, then it lies on the perpendicular bisector of the segment. This theorem forms the basis for many geometric constructions and proofs.
-
Converse of the Perpendicular Bisector Theorem: This theorem is the converse of the Perpendicular Bisector Theorem. It states that if a point is equidistant from the endpoints of a line segment, then it lies on the perpendicular bisector of that line segment. This is often used to prove that a point lies on a specific line.
Proving the Properties: A Step-by-Step Approach
Let's formally prove the equidistance property of the perpendicular bisector. Consider the line segment JK, and let 's' be its perpendicular bisector, intersecting JK at point M (the midpoint). Let P be any arbitrary point on line 's'.
Proof:
-
Construct Triangles: Construct right-angled triangles ΔJMP and ΔKMP. These triangles share the common side MP.
-
Congruent Sides: Since M is the midpoint of JK, JM = MK. Also, by definition, ∠JMA = ∠KMA = 90°.
-
Congruent Triangles: We have JM = MK (given), MP = MP (common side), and ∠JMA = ∠KMA (both 90°). Therefore, by the Side-Angle-Side (SAS) congruence theorem, ΔJMP ≅ ΔKMP.
-
Equidistance: Since ΔJMP ≅ ΔKMP, their corresponding sides are congruent. Thus, JP = KP. This proves that any point P on the perpendicular bisector 's' is equidistant from J and K.
This proof demonstrates the fundamental relationship between the perpendicular bisector and the equidistance property. This property is incredibly useful in various geometric problem-solving scenarios.
Practical Applications of Perpendicular Bisectors
The concept of perpendicular bisectors extends beyond theoretical geometry; it finds practical applications in various fields:
-
Construction and Engineering: Perpendicular bisectors are used in surveying and construction to determine the midpoint of a line segment, essential for laying out foundations, roads, and other structures. Accurate measurements and precise alignment are crucial, and the perpendicular bisector provides a reliable method for achieving this.
-
Computer Graphics and Animation: In computer-aided design (CAD) and animation, perpendicular bisectors are used in algorithms for creating symmetric shapes and objects. This is vital for generating realistic and aesthetically pleasing visuals.
-
Navigation and Mapping: Perpendicular bisectors can be used to locate a point equidistant from two known points, which is useful in navigation and geographic information systems (GIS). Imagine needing to find a location equally distant from two landmarks – the perpendicular bisector helps determine this point.
-
Problem Solving in Geometry: As already emphasized, understanding perpendicular bisectors is crucial for solving many complex geometry problems. These problems often involve proving congruence, finding distances, or constructing geometric shapes.
Advanced Concepts and Extensions
The concept of perpendicular bisectors can be extended to more complex geometrical settings:
-
Circumcenters and Triangles: The perpendicular bisectors of the sides of a triangle intersect at a single point called the circumcenter. This point is equidistant from all three vertices of the triangle and is the center of the circle that passes through the three vertices (the circumcircle).
-
Three-Dimensional Geometry: The concept of perpendicular bisectors extends to three dimensions. The perpendicular bisector of a line segment in 3D space is a plane.
-
Applications in Linear Algebra: Perpendicular bisectors find applications in linear algebra, particularly in concepts related to vector spaces and orthogonal projections.
Conclusion: The Significance of Line 's'
Understanding that line 's' is the perpendicular bisector of line segment JK unlocks a wealth of geometrical knowledge. From its fundamental properties to its diverse applications, the perpendicular bisector holds a prominent position in geometry. Its equidistance property allows for elegant proofs and efficient solutions to various geometric problems. Mastering the concept of perpendicular bisectors equips you with valuable tools for tackling complex geometrical challenges, whether in theoretical mathematics or practical applications in various fields. The seemingly simple concept of a line bisecting another at a right angle opens up a world of possibilities in the study of shapes and spaces. This article has only scratched the surface; further exploration into the advanced applications and related theorems will only deepen your appreciation for this fundamental geometric concept.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Did Joe From American Jewelry And Loan Go To Jail
Mar 19, 2025
-
The Ultimate Element Crossword Puzzle Answer Key
Mar 19, 2025
-
How Many Times Can 8 Go Into 30
Mar 19, 2025
-
How To Say Wrong Number In Spanish
Mar 19, 2025
-
If You Are 55 Today When Were You Born
Mar 19, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Line S Is The Perpendicular Bisector Of Jk . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
