Shape With A Square Base And Four Triangular Faces
Arias News
Mar 16, 2025 · 6 min read
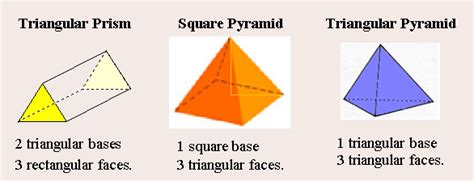
Table of Contents
Understanding the Square Pyramid: A Deep Dive into its Geometry and Applications
The world of geometry is filled with fascinating shapes, each with its unique properties and applications. One such shape, intriguing for its simple yet elegant structure, is the square pyramid. This article will delve deep into the characteristics of a square pyramid, exploring its geometric properties, formulas for calculating its volume and surface area, and its diverse applications across various fields. We'll also touch upon its historical significance and cultural relevance.
Defining the Square Pyramid: A Geometric Overview
A square pyramid is a three-dimensional geometric shape characterized by a square base and four triangular faces that meet at a single point called the apex or vertex. The triangular faces are typically isosceles triangles, meaning two of their sides are equal in length. However, if all the edges connecting the base to the apex are equal, it's a right square pyramid. This distinction is crucial when performing calculations.
Key Components of a Square Pyramid:
- Base: A square forming the foundation of the pyramid.
- Apex (Vertex): The single point where all four triangular faces meet.
- Lateral Faces: The four triangular faces that connect the base to the apex.
- Lateral Edges: The edges that connect the vertices of the base to the apex.
- Base Edges: The four edges forming the sides of the square base.
- Slant Height: The height of each triangular face, measured from the apex to the midpoint of a base edge. This is distinct from the height of the pyramid itself.
- Height: The perpendicular distance from the apex to the center of the square base.
Calculating the Volume of a Square Pyramid
The volume of a square pyramid is the amount of three-dimensional space it occupies. The formula for calculating the volume (V) is remarkably straightforward:
V = (1/3) * B * h
Where:
- B represents the area of the square base (side * side).
- h represents the height of the pyramid.
Let's break this down with an example: Imagine a square pyramid with a base side length of 6 cm and a height of 8 cm.
- Calculate the base area (B): B = 6 cm * 6 cm = 36 cm²
- Apply the volume formula: V = (1/3) * 36 cm² * 8 cm = 96 cm³
Therefore, the volume of this square pyramid is 96 cubic centimeters.
Calculating the Surface Area of a Square Pyramid
The surface area of a square pyramid is the total area of all its faces. This involves calculating the area of the square base and the four triangular lateral faces. The formula is:
SA = B + 2bs
Where:
- B is the area of the square base (side * side).
- b is the length of one side of the square base.
- s is the slant height of the pyramid.
Calculating the slant height (s) often requires using the Pythagorean theorem, especially when dealing with a right square pyramid. The theorem states:
s² = h² + (b/2)²
Where:
- h is the height of the pyramid.
- b is the length of one side of the square base.
Let's use the same example as before (base side = 6 cm, height = 8 cm):
- Calculate the base area (B): B = 6 cm * 6 cm = 36 cm²
- Calculate the slant height (s): s² = 8² cm + (6/2)² cm = 64 cm² + 9 cm² = 73 cm², therefore s = √73 cm ≈ 8.54 cm
- Calculate the surface area (SA): SA = 36 cm² + 2 * 6 cm * 8.54 cm ≈ 36 cm² + 102.48 cm² ≈ 138.48 cm²
Therefore, the surface area of this square pyramid is approximately 138.48 square centimeters.
Variations and Types of Square Pyramids
While the basic definition provides a solid understanding, it's important to note variations:
- Right Square Pyramid: This is the most common type, where the apex lies directly above the center of the square base. The lateral faces are congruent isosceles triangles.
- Oblique Square Pyramid: In this case, the apex is not directly above the center of the base, resulting in irregular lateral triangles. Calculating the volume and surface area becomes more complex.
- Regular Square Pyramid: This term is often used interchangeably with a right square pyramid, emphasizing the congruency of the lateral faces and the regularity of the base.
Understanding these distinctions is crucial for accurate calculations and applications.
Applications of Square Pyramids in Real Life
Square pyramids, despite their seemingly simple geometry, find numerous applications in various fields:
Architecture and Construction:
- Ancient Pyramids: The most iconic example is the Egyptian pyramids, marvels of engineering and testaments to human ingenuity. These monumental structures serve as tombs and hold significant cultural and historical importance. Their design, incorporating principles of geometry and structural engineering, allowed them to withstand the test of time.
- Modern Architecture: Square pyramids, though less common than other shapes, appear in contemporary architecture, often as design elements or as functional parts of buildings. Their strong, stable base makes them suitable for certain structural applications.
Engineering and Design:
- Structural Support: The pyramid's shape provides inherent strength and stability, making it useful in structural engineering for load-bearing applications.
- Packaging and Product Design: The pyramid shape is sometimes used in product packaging, offering unique aesthetics and providing protection for fragile items.
Science and Mathematics:
- Geometric Models: Square pyramids serve as valuable models in geometry, allowing for practical demonstrations of volume, surface area calculations, and other geometrical concepts.
- Crystallography: Certain crystalline structures exhibit square pyramid shapes, making an understanding of the geometry crucial in mineralogy and materials science.
Other Applications:
- Games and Toys: Square pyramid shapes can be found in various games and toys, ranging from building blocks to puzzles.
- Art and Design: The shape has inspired artists and designers across various mediums, reflecting its aesthetic appeal and geometric simplicity.
Historical and Cultural Significance
The square pyramid's cultural significance is undeniable, especially in ancient Egypt. The great pyramids of Giza stand as symbols of power, engineering prowess, and enduring human achievement. Their construction required meticulous planning, advanced mathematics, and a highly organized workforce. Their symbolism extends beyond their physical presence, often representing immortality, divinity, and the journey to the afterlife.
Beyond Egypt, variations of pyramid structures can be found in other cultures, each with its own unique meaning and application. This demonstrates the broad appeal and enduring relevance of the square pyramid across different societies and time periods.
Exploring Further: Advanced Concepts and Related Shapes
While this article provides a comprehensive overview, there are further aspects to explore:
- Euler's Formula: This fundamental concept in topology relates the number of vertices, edges, and faces of polyhedra, including the square pyramid.
- Similar and Congruent Pyramids: Understanding the relationships between similar and congruent pyramids deepens geometrical understanding.
- Truncated Pyramids: These are pyramids with their apex cut off, creating a truncated base.
- Relationship to other Polyhedra: Exploring the connections between square pyramids and other geometric solids, such as octahedrons and cubes, broadens perspective.
Conclusion: The Enduring Allure of the Square Pyramid
The square pyramid, although seemingly simple, reveals a wealth of geometric properties and practical applications. From its iconic presence in ancient architecture to its continued use in various fields, this shape represents a fascinating intersection of geometry, engineering, and cultural significance. This article has hopefully provided a thorough understanding of its characteristics and importance, encouraging further exploration and appreciation of its enduring allure. The consistent application of formulas and the understanding of its different variations are key to mastering this geometric form and appreciating its wide range of applications. Its study provides a solid foundation in geometry and offers insights into the world of mathematics and its practical applications in the real world.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
How Many Cups Is 12 Ounces Of Pasta
Mar 17, 2025
-
How Much Is 2 Liters Of Water In Bottles
Mar 17, 2025
-
What Did The Blind Old Buck Say To His Doe
Mar 17, 2025
-
Time To Say Goodbye Meaning Of Song
Mar 17, 2025
-
How Many Words Can You Make Out Of Merry Christmas
Mar 17, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Shape With A Square Base And Four Triangular Faces . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
