Square Root Of Pi Divided By 2
Arias News
Mar 21, 2025 · 6 min read
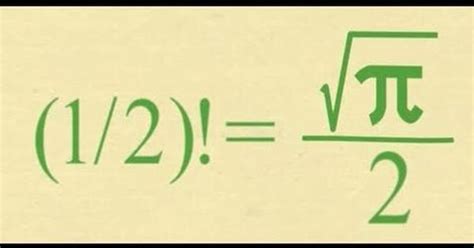
Table of Contents
The Enigmatic √π/2: Exploring a Mathematical Constant
The seemingly simple expression √π/2, or the square root of pi divided by two, holds a surprising depth and significance within various mathematical and scientific fields. While not as immediately recognizable as π (pi) itself, this constant appears in unexpected places, highlighting the interconnectedness of mathematical concepts and the beauty of mathematical relationships. This article delves into the nature of √π/2, exploring its properties, its appearances in different mathematical contexts, and its broader implications within the realm of mathematics and beyond.
Understanding the Components: π and the Square Root
Before delving into the specifics of √π/2, let's revisit the fundamental components: π and the square root operation.
Pi (π): The Circle Constant
Pi (π), approximately equal to 3.14159, is a mathematical constant representing the ratio of a circle's circumference to its diameter. Its transcendental nature – meaning it's not the root of any non-zero polynomial with rational coefficients – signifies its profound importance and its unique position within the number system. Pi appears extensively in geometry, trigonometry, calculus, and numerous scientific applications, underscoring its fundamental role in describing circular and periodic phenomena.
The Square Root Operation: Finding the Principal Root
The square root of a number, denoted as √x, is a value that, when multiplied by itself, results in the original number (x). For positive numbers, there are always two square roots: one positive and one negative. However, convention usually refers to the principal square root, which is the positive square root. Applying this to √π/2, we are considering the positive square root of π divided by two. This subtlety is crucial for understanding its application in various formulas and equations.
√π/2: Appearances and Applications
√π/2 emerges surprisingly often in diverse mathematical contexts. Its presence is often not immediately obvious, requiring some mathematical manipulation to reveal its underlying form. Here are some notable examples:
1. Probability and Statistics: The Normal Distribution
The normal distribution, also known as the Gaussian distribution, is a ubiquitous probability distribution in statistics. It describes many natural phenomena, from human height and weight to measurement errors. The probability density function of the standard normal distribution (mean = 0, standard deviation = 1) involves √π/2 in its normalization constant, ensuring the total area under the curve equals 1. This connection showcases the constant's importance in calculating probabilities related to normally distributed data. Understanding the normalization constant is crucial for statistical inference and hypothesis testing.
2. Integral Calculus: Gaussian Integrals
The constant √π/2 appears prominently in the evaluation of Gaussian integrals, a type of definite integral involving the exponential function e<sup>-x²</sup>. These integrals are fundamental in various areas of mathematics and physics, including probability theory, quantum mechanics, and signal processing. The specific integral ∫<sub>-∞</sub><sup>∞</sup> e<sup>-x²</sup> dx = √π is a classic result, and its close relation to √π/2 highlights the constant's underlying role in integral calculus. Solving these integrals often involves clever techniques of substitution and polar coordinates, leading to the appearance of this specific constant.
3. Physics: Quantum Mechanics and Wave Functions
In quantum mechanics, the constant √π/2 often appears in the normalization of wave functions. Wave functions describe the state of a quantum system, and their normalization ensures that the probability of finding the particle within all possible states sums to 1. Various quantum mechanical calculations, especially those dealing with Gaussian wave packets, involve √π/2 in the normalization factor. This further underlines the constant's connection to probability distributions and its significance in describing the probabilistic nature of quantum phenomena. The appearance of this constant is a direct consequence of the mathematical framework used to describe the quantum world.
4. Special Functions: The Error Function
The error function, denoted erf(x), is a special function that is closely related to the normal distribution. It’s defined as an integral involving the Gaussian function. The constant √π/2 plays a significant role in the definition and properties of the error function, appearing directly in its formula and in various related mathematical identities. Understanding the error function and its connection to the normal distribution is critical for solving numerous problems in statistics, probability, and physics.
5. Fourier Analysis: Fourier Transforms of Gaussian Functions
The Fourier transform, a powerful tool for analyzing signals and functions, transforms a function from one domain (e.g., time) to another (e.g., frequency). The Fourier transform of a Gaussian function also involves √π/2, emphasizing the constant's role in signal processing and analysis. This connection is vital in various applications, including image processing, audio processing, and communications engineering, where Gaussian functions often model real-world signals.
Approximations and Numerical Methods
Since π is an irrational number, √π/2 is also irrational, meaning its decimal representation is non-terminating and non-repeating. However, accurate approximations are readily available using numerical methods. These methods provide increasingly precise estimates of √π/2 by utilizing iterative algorithms or series expansions. The level of precision depends on the specific method used and the desired accuracy. High-precision approximations are crucial for applications requiring high accuracy in calculations, like scientific simulations and engineering computations. For most practical purposes, a few decimal places provide sufficient accuracy.
Significance and Further Exploration
The constant √π/2, although seemingly simple, embodies a profound connection between various areas of mathematics and physics. Its repeated appearance in different contexts highlights the interconnectedness of mathematical concepts and the elegant harmony of mathematical structures. Understanding its properties and applications is crucial for tackling numerous problems in probability, statistics, integral calculus, quantum mechanics, and signal processing. Further research into its properties and connections with other mathematical constants may reveal even deeper insights into the mathematical universe.
Future research could focus on exploring the constant's role in more advanced mathematical areas like complex analysis, number theory, and fractal geometry. Investigating its connections to other mathematical constants and special functions could potentially lead to the discovery of new relationships and mathematical identities. The seemingly simple √π/2 opens a gateway to a rich and complex landscape of mathematical exploration. Its enduring presence across different fields serves as a testament to the power and beauty of mathematics and its profound influence on our understanding of the world.
This article has explored the multifaceted nature of the constant √π/2, from its constituent parts to its appearances in diverse applications. It has highlighted its importance in various fields, emphasizing the remarkable connections within mathematics and its significant implications for scientific understanding. The exploration of this seemingly simple mathematical constant provides a glimpse into the vast and interconnected world of mathematics, demonstrating the elegance and power of its fundamental concepts. It encourages further investigation and underscores the beauty of mathematical relationships, inspiring continued exploration within this fascinating field.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
How Long Does Eggnog Last After Opening
Mar 27, 2025
-
Greatest Common Factor Of 9 And 6
Mar 27, 2025
-
Algebra With Pizzazz Page 158 Answer Key
Mar 27, 2025
-
In The Diagram Below Qt 7 And Rs 7
Mar 27, 2025
-
What Is A Group Of Nine Called
Mar 27, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Square Root Of Pi Divided By 2 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
