Sum Of Interior Angles Of A Heptagon
Arias News
Mar 19, 2025 · 6 min read
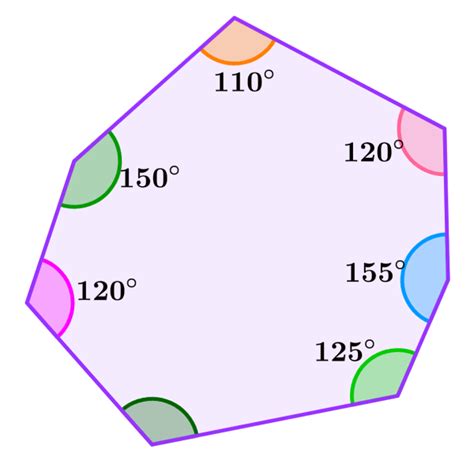
Table of Contents
Sum of Interior Angles of a Heptagon: A Comprehensive Guide
The heptagon, a polygon with seven sides and seven angles, holds a fascinating place in geometry. Understanding its properties, particularly the sum of its interior angles, opens doors to various mathematical explorations and real-world applications. This comprehensive guide delves into the calculation, proof, and practical implications of the sum of interior angles in a heptagon.
Understanding Polygons and Heptagons
Before diving into the specifics of heptagons, let's establish a foundational understanding of polygons. A polygon is a closed two-dimensional figure formed by connecting a set of straight line segments. These segments are called the sides of the polygon, and the points where the sides meet are called the vertices or angles. Polygons are classified based on the number of sides they possess: triangle (3 sides), quadrilateral (4 sides), pentagon (5 sides), hexagon (6 sides), heptagon (7 sides), octagon (8 sides), and so on.
A heptagon, also known as a septagon, is a polygon with seven sides and seven angles. Heptagons can be regular, meaning all their sides and angles are equal in measure, or irregular, where sides and angles have varying lengths and measures. Understanding the properties of a heptagon, especially the sum of its interior angles, is crucial for solving various geometric problems and understanding spatial relationships.
Calculating the Sum of Interior Angles of a Heptagon
The sum of the interior angles of any polygon can be determined using a simple formula. This formula is directly related to the number of sides (or angles) the polygon possesses. The formula is:
Sum of Interior Angles = (n - 2) × 180°
Where 'n' represents the number of sides of the polygon.
For a heptagon, n = 7. Substituting this value into the formula, we get:
Sum of Interior Angles = (7 - 2) × 180° = 5 × 180° = 900°
Therefore, the sum of the interior angles of any heptagon, whether regular or irregular, is always 900 degrees. This is a fundamental property of heptagons and holds true regardless of the shape or size of the heptagon.
Proof of the Formula: Triangulation Method
The formula (n - 2) × 180° can be proven using the method of triangulation. This involves dividing the polygon into a series of triangles by drawing diagonals from a single vertex.
-
Triangulation: Consider a heptagon. Choose one vertex and draw diagonals to all other non-adjacent vertices. This will divide the heptagon into five triangles. Note that this process works for any polygon; the number of triangles formed is always two less than the number of sides.
-
Sum of Angles in a Triangle: The sum of the interior angles in any triangle is always 180°.
-
Total Angle Sum: Since the heptagon is divided into five triangles, the total sum of the interior angles of the heptagon is the sum of the angles in all five triangles. This is 5 × 180° = 900°.
This triangulation method provides a visual and intuitive proof of the formula (n - 2) × 180° for calculating the sum of interior angles of any polygon, including a heptagon.
Regular vs. Irregular Heptagons: Angle Measures
While the sum of interior angles remains constant at 900° for all heptagons, the individual angle measures differ between regular and irregular heptagons.
-
Regular Heptagon: In a regular heptagon, all seven sides and angles are congruent. To find the measure of each interior angle, divide the total sum of interior angles (900°) by the number of angles (7):
900° / 7 ≈ 128.57°
Each interior angle in a regular heptagon measures approximately 128.57°.
- Irregular Heptagon: In an irregular heptagon, the angles have different measures. The only constraint is that the sum of these angles must still equal 900°. The specific measure of each angle depends on the shape of the irregular heptagon. You would need additional information about the individual angles or side lengths to determine their exact measures.
Applications of Heptagon Geometry
The concept of the sum of interior angles in a heptagon, along with other geometrical properties, finds applications in various fields:
-
Architecture and Design: Heptagons, though less common than other polygons like squares and triangles, appear in certain architectural designs and building structures. Understanding their angle properties is crucial for accurate construction and structural integrity.
-
Engineering: Precise calculations involving angles are vital in various engineering disciplines, from mechanical engineering (designing gears and components) to civil engineering (structural analysis of bridges and buildings). The principles of heptagon geometry contribute to these calculations.
-
Computer Graphics and Game Development: In computer graphics and game development, accurate representation of shapes and their interactions is crucial. The mathematical understanding of heptagons and their angle properties is essential for creating realistic and functional virtual environments.
-
Tessellations and Patterns: Exploring the ability of polygons to tile a plane (tessellations) is a fascinating area of geometry. While regular heptagons cannot tessellate, understanding their angles and relationships contributes to exploring more complex tessellations with combinations of various polygons.
-
Art and Design: Heptagons and their properties can inspire artistic creations and decorative patterns. The unique angles and shapes offer visual appeal and creative possibilities.
Solving Problems Involving Heptagons
Let's consider a few examples illustrating how the knowledge of the sum of interior angles of a heptagon can be used to solve problems:
Example 1:
A heptagon has six angles measuring 110°, 125°, 130°, 140°, 150°, and 160°. Find the measure of the seventh angle.
Solution:
The sum of the interior angles of a heptagon is 900°. We add the given six angles: 110° + 125° + 130° + 140° + 150° + 160° = 815°. Subtracting this sum from 900° gives us the measure of the seventh angle: 900° - 815° = 85°.
Example 2:
An irregular heptagon has angles measuring x, x + 10°, x + 20°, x + 30°, x + 40°, x + 50°, and x + 60°. Find the value of x and the measure of each angle.
Solution:
The sum of the angles is 7x + 210°. This must equal 900°. Therefore:
7x + 210° = 900° 7x = 690° x = 98.57°
Substituting x back into the expressions for each angle gives the individual angle measures.
Conclusion: The Significance of Heptagon Geometry
The sum of interior angles of a heptagon, always equaling 900°, is a fundamental property with significant implications across various disciplines. Understanding this property, along with the broader principles of polygon geometry, allows for problem-solving, creative exploration, and practical applications in numerous fields. Whether in architecture, engineering, computer graphics, or art, a solid grasp of heptagon geometry contributes to accuracy, efficiency, and innovation. This guide serves as a foundation for further exploration and deeper understanding of this fascinating geometric figure.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
How Many Cups Is 16 Oz Of Confectioners Sugar
Mar 19, 2025
-
Did Joe From American Jewelry And Loan Go To Jail
Mar 19, 2025
-
The Ultimate Element Crossword Puzzle Answer Key
Mar 19, 2025
-
How Many Times Can 8 Go Into 30
Mar 19, 2025
-
How To Say Wrong Number In Spanish
Mar 19, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Sum Of Interior Angles Of A Heptagon . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
