To Change From Psig To Psia You Must
Arias News
Mar 20, 2025 · 5 min read
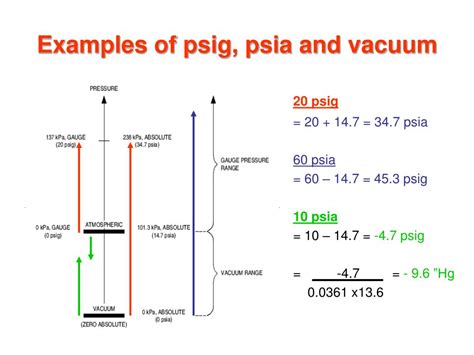
Table of Contents
To Change from PSIG to PSIA You Must… Understand Pressure Units and Conversion
Pressure is a fundamental concept in many fields, from engineering and manufacturing to meteorology and medicine. Understanding different pressure units and how to convert between them is crucial for accurate calculations and safe operations. This article will delve deep into the conversion between PSIG (pounds per square inch gauge) and PSIA (pounds per square inch absolute), explaining the process, its importance, and offering practical examples.
Understanding PSIG and PSIA: The Key Difference
Before we dive into the conversion process, let's clarify the distinction between PSIG and PSIA. Both units measure pressure in pounds per square inch, but they differ in their reference points:
-
PSIG (pounds per square inch gauge): This measures pressure relative to atmospheric pressure. A reading of 0 PSIG indicates that the pressure is the same as the surrounding atmospheric pressure. Any value above 0 represents pressure in excess of atmospheric pressure. Think of a tire pressure gauge; it reads PSIG.
-
PSIA (pounds per square inch absolute): This measures pressure relative to a perfect vacuum, meaning zero pressure. It takes into account both atmospheric pressure and the gauge pressure. This is often used in engineering calculations where precise pressure values are critical.
The crucial difference lies in the inclusion of atmospheric pressure. PSIA always includes atmospheric pressure, while PSIG does not.
The Conversion Formula: Adding Atmospheric Pressure
To convert from PSIG to PSIA, you simply need to add the current atmospheric pressure to the PSIG reading. The formula is straightforward:
PSIA = PSIG + Atmospheric Pressure (in PSIA)
This means that the conversion isn't a fixed numerical calculation; it's dependent on the atmospheric pressure at the time and location of the measurement. Atmospheric pressure fluctuates based on altitude, weather conditions, and temperature.
Determining Atmospheric Pressure
Determining the atmospheric pressure is crucial for accurate conversion. Several methods exist:
-
Using a barometer: A barometer directly measures atmospheric pressure in inches of mercury (inHg), millibars (mbar), or other units. You'll then need to convert these units to PSIA using appropriate conversion factors. One standard atmosphere is approximately 14.7 PSIA, 29.92 inHg, or 1013.25 mbar.
-
Consulting weather data: Many weather websites and apps provide real-time atmospheric pressure readings for specific locations. This is a convenient way to obtain the current atmospheric pressure without using a barometer.
-
Using a standard value: In some instances, particularly for educational purposes or simplified calculations, a standard atmospheric pressure of 14.7 PSIA is used. However, remember that this is an approximation and may lead to inaccuracies in precise applications. Always strive to use the actual measured atmospheric pressure for the most accurate results.
Practical Examples of PSIG to PSIA Conversion
Let's illustrate the conversion with a few examples:
Example 1: Standard Atmospheric Pressure
Let's assume you have a pressure gauge reading of 50 PSIG, and the atmospheric pressure is 14.7 PSIA.
PSIA = 50 PSIG + 14.7 PSIA = 64.7 PSIA
Therefore, a gauge pressure of 50 PSIG equates to an absolute pressure of 64.7 PSIA under standard atmospheric conditions.
Example 2: Higher Altitude
At a higher altitude, the atmospheric pressure might be lower. Let's say the atmospheric pressure is 12.5 PSIA, and the gauge pressure is still 50 PSIG.
PSIA = 50 PSIG + 12.5 PSIA = 62.5 PSIA
This demonstrates how the absolute pressure changes depending on the atmospheric pressure.
Example 3: Pressure below Atmospheric Pressure
What happens if the gauge pressure is negative (a vacuum)? Let's assume the gauge pressure is -5 PSIG, and the atmospheric pressure is 14.7 PSIA.
PSIA = -5 PSIG + 14.7 PSIA = 9.7 PSIA
A negative gauge pressure means the pressure is less than atmospheric pressure. The absolute pressure remains positive because it's still relative to a perfect vacuum.
Example 4: Converting from Inches of Mercury (inHg) to PSIA
Suppose your barometer reads 28 inHg, and your gauge pressure is 30 PSIG. You need to convert the 28 inHg to PSIA first. Using the conversion factor (approximately 1 inHg = 0.491 PSIA), we get:
Atmospheric pressure in PSIA = 28 inHg * 0.491 PSIA/inHg ≈ 13.75 PSIA
Now, we can convert to PSIA:
PSIA = 30 PSIG + 13.75 PSIA = 43.75 PSIA
The Importance of Accurate Conversion
Accurate conversion between PSIG and PSIA is vital in several applications:
-
Engineering Design: Many engineering calculations, especially those involving fluid mechanics and thermodynamics, require absolute pressure values. Using PSIG in these calculations can lead to significant errors and potentially dangerous consequences.
-
Process Control: In industrial processes, accurate pressure measurement and control are essential for maintaining safety and efficiency. Using the wrong pressure units can disrupt the process and compromise product quality.
-
Scientific Research: In scientific experiments involving gases or liquids, accurate pressure measurements are critical for data analysis and interpretation.
-
Aviation and Aerospace: In aviation and aerospace applications, accurate pressure measurements are vital for the safe operation of aircraft and spacecraft.
Beyond the Basics: More Complex Scenarios
While the basic conversion is straightforward, some situations might require additional considerations:
-
Temperature Effects: Both pressure and atmospheric pressure are influenced by temperature. For highly precise applications, you may need to account for temperature variations when performing the conversion.
-
Altitude Corrections: Atmospheric pressure decreases with altitude. Accurate conversions at high altitudes require appropriate altitude corrections for the atmospheric pressure value.
-
Non-Standard Atmospheric Conditions: In extreme weather conditions or specific environments, the atmospheric pressure may deviate significantly from standard values. Using a reliable barometer or local weather data is crucial in these cases.
Conclusion: Master PSIG to PSIA Conversions for Accurate Results
Converting from PSIG to PSIA is a fundamental skill for anyone working with pressure measurements. Understanding the difference between gauge pressure and absolute pressure, along with the factors influencing atmospheric pressure, is crucial for accurate calculations and safe operations. By meticulously following the conversion formula and utilizing reliable data for atmospheric pressure, you can ensure your pressure calculations are accurate and reliable across various applications. Remember that precision is paramount, especially in scenarios with potential safety implications. Always double-check your work and use the appropriate tools for the most accurate results.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
How Many Fluid Ounces Are In 2 Quarts
Mar 21, 2025
-
How Old Is Someone Born In 1967
Mar 21, 2025
-
How To Spell A Little In Spanish
Mar 21, 2025
-
How Far Is A 6k In Miles
Mar 21, 2025
-
Zach Galifianakis In Two And A Half Men
Mar 21, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about To Change From Psig To Psia You Must . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
