What Are The Similarities Between Parliamentary And Presidential Democracies
Arias News
Mar 29, 2025 · 6 min read
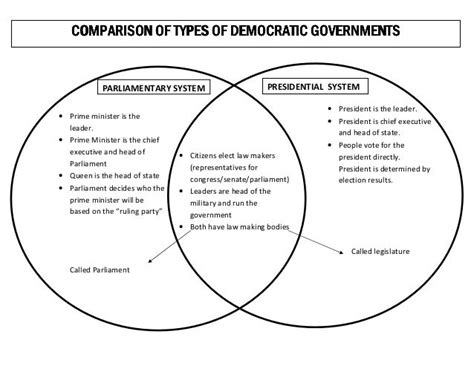
Table of Contents
Unveiling the Similarities: A Comparative Analysis of Parliamentary and Presidential Democracies
While parliamentary and presidential democracies are often presented as diametrically opposed systems, a closer examination reveals surprising similarities underpinning their operation. Both systems strive for the same fundamental goals: representing the will of the people, ensuring accountability of the government, and protecting fundamental rights and freedoms. However, their mechanisms for achieving these goals differ significantly, leading to distinct strengths and weaknesses. This article will delve into the common ground shared by these seemingly disparate systems, highlighting the underlying principles that unite them despite their structural differences.
Shared Principles: The Foundation of Democratic Governance
At their core, both parliamentary and presidential democracies are rooted in the same democratic ideals. These include:
1. Popular Sovereignty: The People's Mandate
Both systems derive their legitimacy from the principle of popular sovereignty. The ultimate authority rests with the people, who elect representatives to govern on their behalf. This principle manifests in regular, free, and fair elections, which are central to both models. While the specific mechanisms for electing representatives may differ (e.g., proportional representation in parliamentary systems versus winner-takes-all in some presidential systems), the underlying principle of popular mandate remains constant.
2. Rule of Law: Equality Before the Law
Both parliamentary and presidential democracies are built on the foundation of the rule of law. This means that everyone, including the government and its officials, is subject to and accountable under the law. This principle ensures predictability, fairness, and limits the arbitrary exercise of power. An independent judiciary, responsible for interpreting and enforcing the law, is crucial in both systems to uphold the rule of law effectively.
3. Separation of Powers (with Nuances): Checks and Balances
While the separation of powers is implemented differently in each system, the underlying principle of preventing the concentration of power in a single entity remains crucial. Presidential systems typically feature a clear separation between the executive, legislative, and judicial branches, each with distinct powers and responsibilities. Parliamentary systems, while blurring the lines between the executive and legislative branches, still employ mechanisms to check and balance power, such as an independent judiciary, a free press, and robust civil society organizations.
4. Protection of Fundamental Rights: Safeguarding Liberty
Both parliamentary and presidential democracies prioritize the protection of fundamental rights and freedoms. These rights, often enshrined in constitutions or other legal frameworks, guarantee individual liberties such as freedom of speech, assembly, religion, and the press. Independent judiciaries play a critical role in upholding these rights, providing a mechanism for redress against government infringement. The specific mechanisms for protection might differ, but the commitment to safeguarding fundamental rights is a shared cornerstone.
Similarities in Governmental Structure and Function: A Closer Look
Beyond shared principles, several structural and functional similarities exist between parliamentary and presidential democracies:
1. The Role of Legislatures: Lawmaking and Scrutiny
Both systems feature a legislature responsible for making laws. In parliamentary systems, the legislature plays a more central role in forming and holding the executive accountable. In presidential systems, the legislature shares power with the executive, acting as a check on executive authority through oversight committees, budget approval, and the power to impeach. Despite the differences in their relationship with the executive, both legislatures function as essential components of the democratic process, representing the people and engaging in lawmaking and scrutiny.
2. The Executive Branch: Implementing Policy
In both systems, the executive branch is responsible for implementing and enforcing laws passed by the legislature. While the method of selecting the executive differs significantly (direct election in presidential systems and parliamentary election in parliamentary systems), both executives strive to translate the legislative agenda into tangible policies and programs. Both also share the responsibility of representing the nation domestically and internationally.
3. The Judiciary: Upholding the Law and Protecting Rights
The judicial branch plays a vital role in both systems, ensuring the fair and impartial application of the law. Independent judiciaries interpret the constitution, resolve disputes, and protect the rights of individuals and groups. Although judicial review might vary in scope and application, the commitment to an independent judiciary upholding the rule of law is a shared element.
4. Political Parties: Organizing and Representing the People
Political parties are integral to both parliamentary and presidential democracies. They organize political life, articulate policy positions, recruit candidates, and represent diverse interests within society. While the party systems might differ in structure and influence (e.g., multi-party systems versus two-party systems), their fundamental role in representing the electorate and facilitating governance is common to both systems.
5. Civil Society: Advocating and Monitoring
A vibrant and active civil society, composed of non-governmental organizations, community groups, and other independent actors, plays a crucial role in both systems. Civil society organizations act as a check on government power, advocate for diverse interests, and monitor government actions. They contribute to democratic participation, promoting transparency and accountability.
Nuances and Distinctions: Understanding the Differences
While acknowledging the significant similarities, it's crucial to acknowledge the critical differences that shape the functioning of these two systems. The most fundamental difference lies in the relationship between the executive and legislative branches. In presidential systems, the executive is independent of the legislature, while in parliamentary systems, the executive is drawn from and accountable to the legislature. This difference leads to distinct dynamics in government formation, stability, and accountability.
Presidential systems tend to offer greater separation of powers, but can also experience gridlock if the executive and legislative branches are controlled by opposing parties. Parliamentary systems offer greater executive-legislative harmony but potentially at the cost of executive accountability if the ruling party commands a large majority.
These differences are further amplified by varying electoral systems, the role of the judiciary, and the degree of decentralization within each system. The specific historical, cultural, and social contexts also shape the evolution and characteristics of each type of democracy.
Conclusion: Finding Common Ground in Democratic Diversity
In conclusion, despite their apparent differences, parliamentary and presidential democracies share core principles and several structural similarities. Both are founded on popular sovereignty, the rule of law, the protection of fundamental rights, and the importance of checks and balances, albeit implemented differently. Both utilize legislatures, executives, and judiciaries to govern, utilizing political parties and civil society organizations as vital actors in the democratic process.
Recognizing these commonalities allows for a deeper understanding of the diverse landscape of democratic governance. It allows us to appreciate the various mechanisms through which democratic principles are implemented while acknowledging that different systems can achieve similar goals through diverse structures and processes. By understanding the shared principles and identifying commonalities, we can foster cross-system learning and promote a more nuanced appreciation of the intricate workings of democratic institutions worldwide. This understanding is critical for strengthening democratic governance and promoting effective and responsive government in diverse contexts.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Is Penny Gilley Related To Mickey Gilley
Mar 31, 2025
-
How Has The Internet Of Things Affected Business Apex
Mar 31, 2025
-
How Many Quarts Is 1 5 Cubic Feet
Mar 31, 2025
-
How Many Cc In A Pint Of Blood
Mar 31, 2025
-
How Do You Say A Little Bit In Spanish
Mar 31, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Are The Similarities Between Parliamentary And Presidential Democracies . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
