What Color Does Red White And Blue Make
Arias News
Mar 28, 2025 · 6 min read
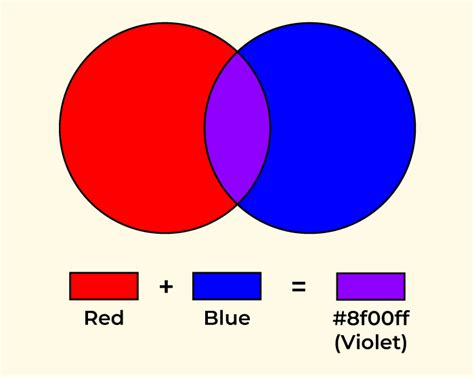
Table of Contents
What Color Does Red, White, and Blue Make? A Comprehensive Exploration of Color Mixing
The seemingly simple question, "What color does red, white, and blue make?" opens a fascinating door into the world of color theory, pigment mixing, and the surprising complexities hidden within seemingly straightforward combinations. While a quick answer might seem obvious, the reality is far more nuanced, depending heavily on the specific shades of red, white, and blue used, and the method of mixing employed. This in-depth exploration will delve into the various possibilities, examining the different results achievable through additive and subtractive color mixing, and exploring the applications of these color combinations in art, design, and everyday life.
Understanding Additive and Subtractive Color Mixing
Before we dive into the specifics of mixing red, white, and blue, it's crucial to understand the fundamental difference between additive and subtractive color mixing. This distinction significantly impacts the final color outcome.
Additive Color Mixing
Additive color mixing involves combining light sources, typically red, green, and blue (RGB). This system is prevalent in digital displays like computer monitors and televisions. When you mix red and green light, you get yellow. Mixing green and blue produces cyan. Combining red and blue yields magenta. When you combine all three – red, green, and blue – you obtain white light.
In the context of red, white, and blue, using additive mixing is less straightforward because white is already a complete mixture of light in this system. Adding red and blue to white light would primarily increase the intensity of those colors within the white spectrum, leading to a brighter, possibly slightly purplish-tinged white, depending on the exact shades of red and blue used. The result won't be a dramatically new color but a modified version of white.
Subtractive Color Mixing
Subtractive color mixing, on the other hand, involves combining pigments, such as paints or inks. This system uses the primary colors cyan, magenta, and yellow (CMY). When you mix cyan and magenta, you get blue. Mixing magenta and yellow creates red. Combining cyan and yellow results in green. Mixing all three – cyan, magenta, and yellow – ideally produces black, though in practice, a muddy dark brown or gray is more common, leading to the addition of black (K) to the system, forming CMYK.
Mixing red, white, and blue using subtractive mixing yields a much more unpredictable result. The outcome heavily relies on the specific pigments used. A vibrant, pure red mixed with a bright blue and a pure white will result in a lighter, desaturated version of the original blue-red mix, leaning towards a lavender or periwinkle depending on the ratios. A duller red and blue might produce a grayish, muted purple. The white acts as a tint, lightening the overall mixture.
Exploring the Nuances of Color Shades
The exact shade of the resulting color when mixing red, white, and blue is highly dependent on the specific hues employed. Let's break down how the nuances in each color impact the final outcome:
The Red Factor
The shade of red greatly influences the final mix. A cool-toned red, leaning towards magenta, will result in a different color than a warm-toned red, closer to orange. A crimson red will give a more intense purple-toned mix, while a scarlet red might create a lighter, more pinkish-lavender.
The White Factor
White acts as a diluting agent, lightening the overall color mixture. The amount of white added significantly affects the lightness and saturation of the final color. More white will result in a lighter, pastel-like shade, while less white will retain more of the original color's intensity.
The Blue Factor
Similarly to red, the shade of blue is a critical factor. A cool-toned blue, like Prussian blue, will yield a different result than a warm-toned blue, like ultramarine. A deeper blue will create a more saturated purple-toned mix, while a lighter blue will lead to a pastel-like lavender.
Practical Applications and Examples
Understanding the variations in color mixing with red, white, and blue is crucial in various applications:
Painting and Fine Arts
Painters often utilize these colors to create a wide range of shades, from vibrant purples to soft lavenders, depending on the proportions of each color and the desired intensity. Artists intuitively adjust the ratios to achieve their artistic vision.
Graphic Design and Web Design
In digital design, designers use variations of red, white, and blue to create visually appealing color palettes. Understanding subtractive color mixing principles is essential for achieving the desired color on printed materials.
Fashion and Textiles
The fashion industry utilizes these colors in a vast array of fabrics and clothing designs. The combination of red, white, and blue can produce eye-catching patterns and textures through various dyeing and printing techniques.
Flag Design and National Symbolism
Many national flags incorporate red, white, and blue, often symbolizing freedom, liberty, and patriotism. The specific shades used and their arrangement on the flag carry significant cultural and historical meaning. The variations in color interpretation highlight the cultural context surrounding these national symbols.
Beyond the Basic Mix: Exploring Related Color Combinations
Let's explore related color combinations that build upon the foundation of red, white, and blue:
-
Adding Black: Incorporating black into the mix darkens the overall tone, creating deep purples, navy blues, and even dark, muted grays, depending on the proportions.
-
Adding Yellow: The addition of yellow creates a wider range of colors, including warmer purples leaning towards violet, and even shades that transition towards muted browns or oranges depending on the other color ratios.
-
Variations in Saturation: By adjusting the saturation levels of the red, white, and blue (using tints, shades, and tones), an extensive range of pastel, muted, or intense color combinations can be achieved.
-
Exploring Different Color Models: Beyond RGB and CMYK, other color models like HSV (hue, saturation, value) and HSL (hue, saturation, lightness) provide different perspectives on color mixing and allow for a more precise manipulation of color attributes.
Conclusion: The Ever-Evolving Palette of Red, White, and Blue
The question of what color red, white, and blue make is not answered with a single definitive color. The answer is a spectrum of possibilities, deeply reliant on the specific shades used, the mixing method (additive or subtractive), and the proportions of each color. Understanding this complexity is essential for anyone working with color, whether in art, design, or any other field involving color manipulation. The seemingly simple combination unlocks a vast world of creative potential, allowing for limitless exploration and expression. The exploration of these combinations showcases the dynamism and intricate nature of color theory, emphasizing the importance of understanding the nuances to achieve desired artistic or design outcomes. Experimentation and a keen eye for color are key to mastering the art of blending red, white, and blue into a truly unique and captivating palette.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
What Is 37 Degrees Fahrenheit In Celsius
Mar 31, 2025
-
How Much Does A Dime Bag Weigh
Mar 31, 2025
-
What Did The Acorn Say When It Grew Up
Mar 31, 2025
-
How Many Gallons In A 35 Pound Oil
Mar 31, 2025
-
How Long Does It Take To Fly 2500 Miles
Mar 31, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Color Does Red White And Blue Make . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
