What Is 3 To The 5th Power
Arias News
Mar 20, 2025 · 5 min read
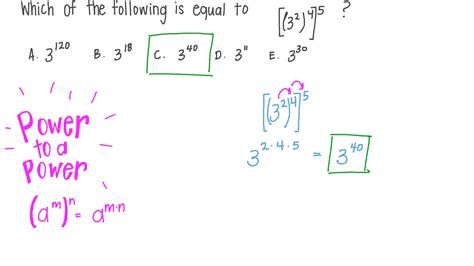
Table of Contents
What is 3 to the 5th Power? A Deep Dive into Exponents and Their Applications
Understanding exponents is fundamental to mathematics and numerous fields. This article will thoroughly explore the meaning of "3 to the 5th power," explain the concept of exponents, delve into their practical applications, and even touch upon some related mathematical concepts. By the end, you'll have a robust understanding not just of 3⁵, but of exponents in general.
Understanding Exponents: The Basics
Before we tackle 3 to the 5th power, let's establish a solid foundation in exponential notation. An exponent, also known as a power or index, indicates how many times a number (the base) is multiplied by itself. It's written as a small superscript number to the right of the base.
For instance, in the expression 3⁵, '3' is the base and '5' is the exponent. This means:
3⁵ = 3 × 3 × 3 × 3 × 3
This is simply 3 multiplied by itself five times.
Key Terminology:
- Base: The number being multiplied repeatedly. In 3⁵, the base is 3.
- Exponent: The number indicating how many times the base is multiplied by itself. In 3⁵, the exponent is 5.
- Power: Another term for exponent. We often say "3 raised to the power of 5."
Calculating 3 to the 5th Power
Now, let's calculate 3⁵:
3 × 3 = 9 9 × 3 = 27 27 × 3 = 81 81 × 3 = 243
Therefore, 3 to the 5th power is 243.
Expanding on Exponents: Rules and Properties
Understanding the calculation of 3⁵ is just the beginning. Exponents follow several key rules and properties that are crucial for working with them effectively:
1. Product of Powers:
When multiplying two numbers with the same base, you add their exponents:
aᵐ × aⁿ = aᵐ⁺ⁿ
For example: 2³ × 2² = 2³⁺² = 2⁵ = 32
2. Quotient of Powers:
When dividing two numbers with the same base, you subtract their exponents:
aᵐ ÷ aⁿ = aᵐ⁻ⁿ (where a ≠ 0)
For example: 5⁴ ÷ 5² = 5⁴⁻² = 5² = 25
3. Power of a Power:
When raising a power to another power, you multiply the exponents:
(aᵐ)ⁿ = aᵐⁿ
For example: (2²)³ = 2²ˣ³ = 2⁶ = 64
4. Power of a Product:
When raising a product to a power, you raise each factor to that power:
(ab)ⁿ = aⁿbⁿ
For example: (2 × 3)² = 2² × 3² = 4 × 9 = 36
5. Power of a Quotient:
When raising a quotient to a power, you raise both the numerator and the denominator to that power:
(a/b)ⁿ = aⁿ/bⁿ (where b ≠ 0)
For example: (4/2)³ = 4³/2³ = 64/8 = 8
Beyond 3⁵: Exploring Other Exponents
The concept of exponents isn't limited to positive integers. Let's explore other types of exponents:
1. Exponent of 0:
Any non-zero number raised to the power of 0 is 1:
a⁰ = 1 (where a ≠ 0)
For example: 3⁰ = 1
2. Negative Exponents:
A negative exponent indicates the reciprocal of the base raised to the positive exponent:
a⁻ⁿ = 1/aⁿ (where a ≠ 0)
For example: 3⁻² = 1/3² = 1/9
3. Fractional Exponents (Radicals):
A fractional exponent represents a root. For example:
a^(m/n) = ⁿ√(aᵐ)
This means the nth root of a raised to the power of m. For example:
4^(3/2) = √(4³) = √64 = 8
Practical Applications of Exponents
Exponents are far from abstract mathematical concepts. They have widespread applications across various fields:
1. Science and Engineering:
- Compound Interest: Calculating compound interest involves exponents. The formula uses an exponential function to determine the future value of an investment.
- Exponential Growth and Decay: Many natural phenomena, such as population growth, radioactive decay, and the spread of diseases, follow exponential patterns. Exponents are crucial for modeling and predicting these processes.
- Physics: Exponents appear in numerous physics equations, including those describing motion, energy, and forces.
2. Computer Science:
- Big O Notation: In computer science, Big O notation uses exponents to describe the efficiency of algorithms. It helps determine how an algorithm's runtime or memory usage scales with the input size.
- Binary Numbers: The binary number system, fundamental to computing, utilizes powers of 2.
3. Finance:
- Compounding: As mentioned earlier, understanding exponents is essential for calculating compound interest and other financial calculations.
- Present Value and Future Value Calculations: Determining the present value of future cash flows also involves exponential functions.
4. Biology:
- Population Growth: Modeling population growth often requires exponential functions.
- Bacterial Growth: The rapid growth of bacterial populations follows an exponential pattern.
Beyond the Basics: Exponential Functions and Logarithms
The concept of exponents leads to more advanced mathematical ideas:
- Exponential Functions: These are functions where the independent variable appears as an exponent. They are characterized by their rapid growth or decay.
- Logarithms: Logarithms are the inverse of exponential functions. They allow us to solve for the exponent when the base and result are known.
Conclusion: Mastering Exponents for a Broader Understanding
This comprehensive exploration of "What is 3 to the 5th power?" has extended far beyond a simple calculation. We've delved into the fundamentals of exponents, their properties, various types of exponents, and a wide range of practical applications. By grasping these concepts, you've gained a powerful tool for tackling mathematical problems in various fields and understanding the world around us better. The seemingly simple calculation of 3⁵ opens the door to a fascinating realm of mathematical possibilities. Continue exploring these concepts, and you'll discover even more applications and interconnected ideas. Remember to practice regularly and explore more advanced topics like exponential functions and logarithms to further enhance your understanding.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
How Do You Make A Dog Horny
Mar 20, 2025
-
What Happened When Two Fruit Companies Merged
Mar 20, 2025
-
Which Of The Following Is Considered A Safe Refueling Practice
Mar 20, 2025
-
How Long Is Jello Good For In The Fridge
Mar 20, 2025
-
How Many Meters Are In 5 Miles
Mar 20, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Is 3 To The 5th Power . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
