What Is A 16 Out Of 21
Arias News
Mar 15, 2025 · 6 min read
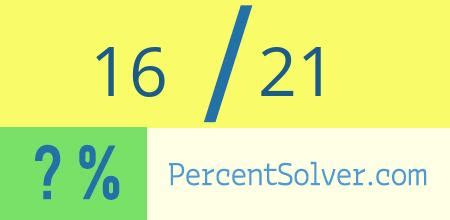
Table of Contents
What is a 16 out of 21? Understanding Scores, Percentages, and Context
The simple question, "What is a 16 out of 21?" might seem straightforward, but its answer depends heavily on context. Understanding the meaning requires analyzing the score as a fraction, a percentage, and within the larger framework of whatever system produced that score. This article will delve into different interpretations, potential applications, and the importance of understanding the context for accurate assessment.
16 out of 21 as a Fraction and Percentage
At its most basic level, "16 out of 21" represents a fraction: 16/21. This fraction can be simplified slightly, but it remains an irreducible fraction. To understand its magnitude better, we can convert it to a percentage.
To convert 16/21 to a percentage, we divide 16 by 21 and then multiply by 100:
(16/21) * 100 ≈ 76.19%
Therefore, a score of 16 out of 21 is approximately 76.19%. This is a relatively high score, suggesting a strong performance, but the precise interpretation depends entirely on what the 21 represents.
Context is King: Interpreting 16 out of 21 in Different Scenarios
The meaning of 16 out of 21 drastically changes depending on the context. Let's explore some examples:
1. Academic Assessment:
-
Exam Score: If this score represents an exam with 21 questions, achieving 16 correct answers indicates a good understanding of the material. A 76.19% would likely be a B or B+ grade in many grading systems, though the exact letter grade depends on the specific grading scale used by the institution.
-
Assignment Grading Rubric: If the 21 points represent different criteria on an assignment, achieving 16 points suggests the assignment met most of the requirements. The specific criteria that were met or missed would need to be examined to understand the strengths and weaknesses of the submitted work.
-
Project Evaluation: In a project with 21 possible points across multiple stages, 16 points might represent near-completion with a few minor aspects needing improvement. The specific feedback given by the evaluator is crucial for understanding the areas where further work is required.
2. Sporting Events and Competitions:
-
Points in a Game: In a game or competition where a maximum of 21 points is possible, 16 points is a significant score, possibly representing a win or a strong showing depending on the opponent's score.
-
Accuracy in a Sport: If the 21 represents attempts and 16 represents successful attempts (like free throws in basketball or shots in archery), then 76.19% accuracy is a solid performance.
3. Surveys and Polls:
-
Responses in a Questionnaire: If a survey has 21 questions, and 16 respondents answered a particular question in a specific way, that response represents a significant portion of the surveyed group.
-
Statistical Significance: Whether 16 out of 21 responses hold statistical significance depends on the total sample size of the survey and the statistical test applied. A larger sample size would be needed to draw confident conclusions.
4. Quality Control and Manufacturing:
-
Defect Rate: If 21 items are inspected and 16 pass inspection, that means 5 failed (a 23.81% defect rate). This rate's acceptability depends on industry standards and the cost associated with defects.
-
Production Efficiency: 16 out of 21 could represent the number of successfully manufactured items, highlighting efficiency (76.19%) or needing improvement.
The Importance of Contextual Analysis: Moving Beyond the Numbers
The core takeaway is that a score of 16 out of 21, while mathematically equivalent to 76.19%, lacks intrinsic meaning without context. The numbers themselves are just a starting point; the true significance lies in the specific situation they represent.
To fully understand the implications of any score, always ask these crucial questions:
- What does the total (21) represent? Is it a number of questions, points, attempts, units, or something else entirely?
- What is the nature of the assessment? Is it an exam, a competition, a survey, or a quality control check?
- What are the accepted standards or benchmarks? What constitutes a good, average, or poor performance in this context?
- What are the specific implications of the score? Does it indicate success, failure, or an area requiring further attention?
By carefully considering these points, you can move beyond the surface level interpretation of "16 out of 21" and arrive at a richer, more nuanced, and ultimately more meaningful understanding. Failure to do so can lead to inaccurate judgments and potentially flawed decision-making.
Beyond the Basics: Statistical Considerations and Further Analysis
In many scenarios, simply calculating the percentage might not suffice. More sophisticated statistical analyses might be necessary, depending on the nature of the data. For example:
-
Standard Deviation and Normal Distribution: If the score of 16 out of 21 is part of a larger dataset, calculating the standard deviation and comparing the score to the mean would provide a more precise understanding of its relative position within the distribution. A score of 76.19% might be exceptional in one dataset but average in another.
-
Confidence Intervals: When dealing with surveys and polls, confidence intervals are crucial for understanding the reliability of the data. A 76.19% positive response rate might not be statistically significant unless the confidence interval accounts for the margin of error.
-
Hypothesis Testing: Statistical tests like t-tests or chi-squared tests can help determine whether a score of 16 out of 21 is statistically different from a baseline or control group.
-
Regression Analysis: If the score is influenced by multiple factors, regression analysis can be used to determine the relative importance of these factors. For instance, in academic performance, this could involve identifying the contribution of study time, prior knowledge, and teaching methods.
Practical Applications and Real-World Examples
The concept of "16 out of 21" finds applications in many areas of life. Here are just a few examples:
-
Education: Teachers use scores like this regularly to assess student performance and identify areas for improvement.
-
Business: Companies track key performance indicators (KPIs) using similar metrics to evaluate productivity and efficiency.
-
Healthcare: Patient outcomes are frequently measured using numerical scores, and 16 out of 21 might represent a specific improvement in a particular health indicator.
-
Sports Analytics: Teams analyze player statistics to identify strengths and weaknesses, make strategic decisions, and improve performance.
Understanding how to interpret these types of scores is crucial for effective decision-making in all these fields. Focusing solely on the raw percentage can be misleading without considering the broader context and the underlying data.
Conclusion: The Power of Contextual Understanding
In summary, "16 out of 21" is more than just a simple fraction or percentage; it's a data point that requires careful contextual analysis for accurate interpretation. By considering the source of the data, the specific meaning of the numbers, and relevant statistical considerations, we can transform a simple score into a powerful tool for understanding performance, identifying areas for improvement, and making informed decisions across a wide range of applications. Remember: Context is king when evaluating numerical scores. Always delve deeper than the surface to uncover the true meaning and implications.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
If I Was Born In 94 How Old Am I
Mar 15, 2025
-
How Many Cups In 5 Lb Bag Of Sugar
Mar 15, 2025
-
How Many Kg Are In A Meter
Mar 15, 2025
-
How Many Cups Are In 1 Pound Of Pasta
Mar 15, 2025
-
How Much Does Ace Charge To Cash A Check
Mar 15, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Is A 16 Out Of 21 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
