What Is A Equivalent Fraction To 1/2
Arias News
Mar 21, 2025 · 6 min read
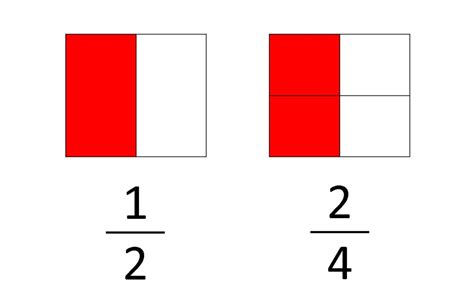
Table of Contents
What is an Equivalent Fraction to 1/2? A Deep Dive into Fraction Equivalence
Understanding equivalent fractions is a cornerstone of mathematical proficiency. This concept, seemingly simple at first glance, underpins numerous mathematical operations and real-world applications. This comprehensive guide will explore the meaning of equivalent fractions, focusing specifically on fractions equivalent to 1/2, providing you with a thorough understanding and practical methods for identifying and generating them. We'll delve into the underlying principles, explore multiple approaches to finding these equivalents, and discuss the significance of this concept in various mathematical contexts.
Understanding Equivalent Fractions
Equivalent fractions represent the same proportion or part of a whole, even though they appear different numerically. Think of cutting a pizza: one half (1/2) is the same as two quarters (2/4), or four eighths (4/8). These are all equivalent fractions, visually representing the same portion of the pizza. The key is that the ratio between the numerator (top number) and the denominator (bottom number) remains constant.
The Fundamental Principle: To create an equivalent fraction, you must multiply both the numerator and the denominator by the same non-zero number. This process essentially scales the fraction up or down, preserving its value. Dividing both the numerator and the denominator by their greatest common divisor (GCD) simplifies the fraction to its lowest terms.
Finding Equivalent Fractions to 1/2
Let's focus on finding equivalent fractions for 1/2. Using the fundamental principle, we can multiply both the numerator (1) and the denominator (2) by any non-zero integer:
Method 1: Multiplying by Whole Numbers
- Multiply by 2: (1 x 2) / (2 x 2) = 2/4
- Multiply by 3: (1 x 3) / (2 x 3) = 3/6
- Multiply by 4: (1 x 4) / (2 x 4) = 4/8
- Multiply by 5: (1 x 5) / (2 x 5) = 5/10
- Multiply by 10: (1 x 10) / (2 x 10) = 10/20
- Multiply by 100: (1 x 100) / (2 x 100) = 100/200
This process can continue infinitely; there are infinitely many equivalent fractions to 1/2. Each fraction represents the same proportion – one-half.
Method 2: Visual Representation
Visual aids can significantly enhance understanding. Imagine a rectangle divided into two equal parts. One part represents 1/2. Now, divide each of these two parts into two equal parts again. You now have four parts, and two of them represent the same area as the original half – illustrating that 2/4 is equivalent to 1/2. Continue subdividing the rectangles to visually represent 3/6, 4/8, and so on.
Method 3: Using a Table
Creating a table can systematically generate equivalent fractions:
| Numerator | Denominator | Fraction | Simplified Fraction |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 1/2 | 1/2 |
| 2 | 4 | 2/4 | 1/2 |
| 3 | 6 | 3/6 | 1/2 |
| 4 | 8 | 4/8 | 1/2 |
| 5 | 10 | 5/10 | 1/2 |
| 10 | 20 | 10/20 | 1/2 |
| 100 | 200 | 100/200 | 1/2 |
This organized approach helps visualize the pattern of equivalent fractions.
Identifying Equivalent Fractions
Sometimes, you'll need to determine if two fractions are equivalent. There are several ways to do this:
Method 1: Cross-Multiplication
Cross-multiply the numerators and denominators of the two fractions. If the products are equal, the fractions are equivalent. For example, let's check if 3/6 is equivalent to 1/2:
(3 x 2) = 6 and (6 x 1) = 6. Since the products are equal, 3/6 and 1/2 are equivalent.
Method 2: Simplifying Fractions
Simplify both fractions to their lowest terms by dividing both the numerator and denominator by their greatest common divisor (GCD). If both fractions simplify to the same fraction, they are equivalent. For instance, to check if 10/20 is equivalent to 1/2:
The GCD of 10 and 20 is 10. Dividing both by 10, we get 1/2. Since both fractions simplify to 1/2, they are equivalent.
The Importance of Equivalent Fractions
Equivalent fractions are crucial for several mathematical concepts and applications:
-
Adding and Subtracting Fractions: Before adding or subtracting fractions, you need to find a common denominator. This often involves converting fractions to equivalent fractions with the same denominator.
-
Comparing Fractions: Determining which of two fractions is larger or smaller often requires finding equivalent fractions with a common denominator.
-
Simplifying Fractions: Reducing a fraction to its simplest form involves finding an equivalent fraction with the smallest possible numerator and denominator.
-
Ratios and Proportions: Equivalent fractions are fundamental to understanding ratios and solving proportions, crucial in many real-world applications, such as scaling recipes, calculating percentages, and understanding map scales.
-
Decimal Conversion: Converting fractions to decimals and vice versa often involves finding equivalent fractions with denominators that are powers of 10 (10, 100, 1000, etc.). For example, 1/2 is equivalent to 5/10, which is equal to 0.5.
Practical Applications of Equivalent Fractions: Real-World Examples
The concept of equivalent fractions isn't confined to the classroom; it has numerous practical applications:
-
Cooking and Baking: Scaling recipes up or down requires understanding equivalent fractions. If a recipe calls for 1/2 cup of sugar, and you want to double the recipe, you'll need 2/4 cup or 1 cup of sugar.
-
Construction and Engineering: Precise measurements and proportions are crucial in construction. Equivalent fractions help ensure accuracy in calculations involving dimensions and materials.
-
Finance: Calculating percentages, interest rates, and proportions of budgets all rely on the understanding of equivalent fractions.
-
Map Reading: Interpreting map scales involves working with proportions and equivalent fractions to determine real-world distances from map measurements.
Beyond 1/2: Extending the Concept
The principles discussed here for finding equivalent fractions to 1/2 apply to any fraction. To find equivalent fractions for any given fraction, simply multiply (or divide) both the numerator and the denominator by the same non-zero number. This fundamental principle underpins the entire concept of fraction equivalence and its various applications in mathematics and beyond.
Conclusion
Understanding equivalent fractions, particularly finding those equivalent to 1/2, is fundamental to mastering fractions and their applications. By understanding the underlying principles and employing the various methods outlined above, you can confidently identify, generate, and utilize equivalent fractions in diverse mathematical contexts and real-world scenarios. Remember, the ability to work fluently with equivalent fractions is a key stepping stone to more advanced mathematical concepts and problem-solving. Consistent practice and a visual approach will solidify your understanding and build your confidence in handling these essential mathematical tools.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
How Many Units Are In A Milliliter
Mar 28, 2025
-
How Many Ounces In Cream Cheese Block
Mar 28, 2025
-
How Many Marshmallows In A 10 Oz Bag
Mar 28, 2025
-
How Many Cups Is A Pound Of Sour Cream
Mar 28, 2025
-
How Fast Can You Walk 1 Mile At 4mph
Mar 28, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Is A Equivalent Fraction To 1/2 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
