What Is A Shape With 20 Sides Called
Arias News
Mar 22, 2025 · 5 min read
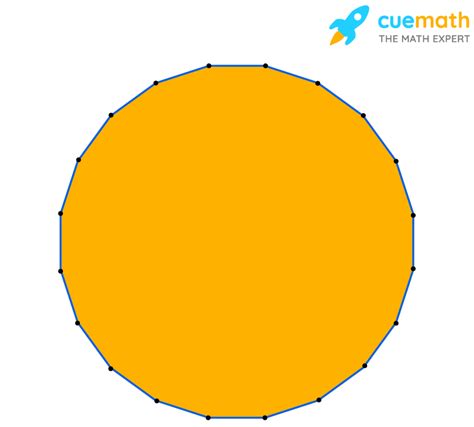
Table of Contents
What is a Shape with 20 Sides Called? A Deep Dive into Icosagons
Have you ever wondered about the name of a shape with 20 sides? It's not as common as a triangle or square, but this fascinating polygon has a name, and it's steeped in mathematical history and intriguing properties. This comprehensive guide will explore the world of icosagons, delving into their characteristics, classifications, and even some surprising applications.
Understanding Polygons: A Foundation for Icosagons
Before we dive into the specifics of a 20-sided shape, let's establish a basic understanding of polygons. A polygon is a closed two-dimensional figure formed by connecting a set of straight line segments. These segments are called sides, and the points where the sides meet are called vertices or corners. Polygons are classified based on the number of sides they possess.
- Triangles: 3 sides
- Quadrilaterals: 4 sides (squares, rectangles, trapezoids, etc.)
- Pentagons: 5 sides
- Hexagons: 6 sides
- Heptagons: 7 sides
- Octagons: 8 sides
- Nonagons: 9 sides
- Decagons: 10 sides
- Hendecagons (or Undecagons): 11 sides
- Dodecagons: 12 sides
- And so on...
As you can see, the naming conventions for polygons often derive from Greek prefixes indicating the number of sides. This pattern continues beyond the commonly known shapes.
The Icosagon: A 20-Sided Polygon
Now, let's focus on our main subject: the icosagon. An icosagon is a polygon with 20 sides and 20 vertices. The name "icosagon" originates from the Greek words "eikosi" (meaning twenty) and "gonia" (meaning angle). This simple etymology clearly identifies its key characteristic.
Properties of an Icosagon
Like all polygons, an icosagon possesses several key properties:
- Number of Sides: 20
- Number of Vertices: 20
- Number of Angles: 20 (interior angles)
- Sum of Interior Angles: The sum of the interior angles of any polygon can be calculated using the formula (n-2) * 180°, where 'n' is the number of sides. For an icosagon, this means the sum of its interior angles is (20-2) * 180° = 3240°.
- Regular vs. Irregular: An icosagon can be either regular or irregular. A regular icosagon has all sides of equal length and all interior angles equal (each angle measuring 162°). An irregular icosagon has sides and angles of varying lengths and measures.
Visualizing an Icosagon
While it's easy to visualize a triangle or square, an icosagon is considerably more complex. Its numerous sides and angles make it challenging to draw perfectly freehand. However, understanding its properties allows for accurate construction using geometric tools like a compass and straightedge, although the process becomes intricate with the increasing number of sides. Software programs and CAD tools can easily generate precise representations of regular and irregular icosagons.
Applications of Icosagons: Beyond Geometry
While not as ubiquitous as simpler polygons, icosagons find applications in various fields, often in more subtle ways:
-
Tessellations and Patterns: Icosagons can be used in creating intricate tessellations and geometric patterns. Combining them with other shapes can lead to visually stunning and complex designs. Think of the potential in artistic endeavors, architectural design, or even fabric patterns.
-
Approximating Circles: A regular icosagon provides a surprisingly accurate approximation of a circle. As the number of sides in a regular polygon increases, it gets closer and closer to a circle. This principle is used in various applications where a close-to-circular shape is needed, but a perfect circle might be impractical to achieve.
-
Design and Architecture: Although not a commonly featured shape in mainstream architecture, its unique properties offer possibilities for creative architects to incorporate it into unique building designs or decorative elements. The potential for innovative designs is vast.
-
Engineering and Construction: The precise geometrical properties of an icosagon can be leveraged in specific engineering applications that require high precision and intricate structures. Though less prevalent than other shapes, it has its niche applications.
-
Computer Graphics and Game Development: Icosagons, like other complex polygons, play a role in computer graphics and game development, particularly when creating three-dimensional models with detailed textures and forms. The more sides a polygon has, the smoother and more refined the 3D models will look.
Deeper Mathematical Explorations: Beyond the Basics
Delving deeper into the mathematical properties of an icosagon opens up a world of fascinating concepts:
-
Symmetry: A regular icosagon exhibits high levels of symmetry. It has rotational symmetry of order 20, and several lines of reflectional symmetry. Understanding these symmetries is crucial in applications where symmetry is essential, such as in designing symmetrical patterns or structures.
-
Interior and Exterior Angles: As mentioned earlier, the sum of interior angles in an icosagon is 3240°. Each interior angle in a regular icosagon measures 162°. The exterior angles, which are supplementary to the interior angles, play a critical role in various mathematical calculations related to the icosagon’s geometry.
-
Area Calculation: The area of a regular icosagon can be calculated using formulas that involve the length of its sides and the apothem (the distance from the center to the midpoint of a side). The calculations are more complex than those for simpler polygons, but they provide a precise measure of the area enclosed by the icosagon.
Conclusion: The Underrated Icosagon
While not as frequently encountered as other polygons, the icosagon holds a significant place in the world of geometry and mathematics. Its properties, both visually and mathematically, offer a compelling study, showcasing the rich tapestry of geometric possibilities. From its intricate symmetrical nature to its potential applications in design and engineering, the icosagon is a testament to the beauty and complexity of geometrical forms. By understanding its characteristics and applications, we gain a deeper appreciation for the multifaceted world of polygons and their roles in shaping our visual and mathematical understanding of the world around us. Its relatively complex nature adds an element of intrigue to this often overlooked member of the polygon family. The next time you encounter a complex pattern or design, consider the possibility of the icosagon subtly contributing to its intricate beauty.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Did Eric Delko Die On Csi Miami
May 09, 2025
-
National Niece And Nephew Day 2024 Usa Time
May 09, 2025
-
How Many Ounces In A Water Glass
May 09, 2025
-
If You Are Born In 1963 How Old Are You
May 09, 2025
-
What Is A Equivalent Fraction For 6 8
May 09, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Is A Shape With 20 Sides Called . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.