What Is The Common Multiple Of 7 And 8
Arias News
Mar 22, 2025 · 4 min read
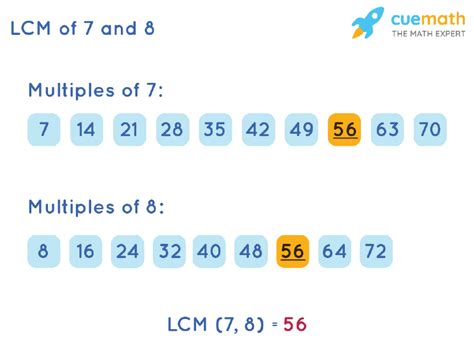
Table of Contents
What is the Least Common Multiple (LCM) of 7 and 8? A Deep Dive into Finding LCMs
Finding the least common multiple (LCM) of two numbers is a fundamental concept in mathematics, with applications ranging from simple fraction arithmetic to complex scheduling problems. This article will explore the LCM of 7 and 8 in detail, explaining various methods to calculate it, demonstrating its practical uses, and expanding upon the broader concept of LCMs and their significance.
Understanding Least Common Multiples (LCMs)
Before we delve into the specifics of 7 and 8, let's establish a clear understanding of LCMs. The least common multiple of two or more integers is the smallest positive integer that is a multiple of each of the numbers. In simpler terms, it's the smallest number that both numbers divide into evenly.
For example, let's consider the numbers 2 and 3. Multiples of 2 are 2, 4, 6, 8, 10, 12... Multiples of 3 are 3, 6, 9, 12, 15... The smallest number that appears in both lists is 6. Therefore, the LCM of 2 and 3 is 6.
Finding the LCM of 7 and 8: Three Proven Methods
There are several ways to find the LCM of 7 and 8. We'll explore three common methods:
Method 1: Listing Multiples
This is the most straightforward method, especially for smaller numbers like 7 and 8. We list the multiples of each number until we find the smallest common multiple.
- Multiples of 7: 7, 14, 21, 28, 35, 42, 49, 56, 63, 70...
- Multiples of 8: 8, 16, 24, 32, 40, 48, 56, 64, 72, 80...
Notice that the smallest number that appears in both lists is 56. Therefore, the LCM of 7 and 8 is 56.
Method 2: Prime Factorization
This method is more efficient for larger numbers. It involves finding the prime factorization of each number and then constructing the LCM from the prime factors.
- Prime factorization of 7: 7 (7 is a prime number)
- Prime factorization of 8: 2 x 2 x 2 = 2³
To find the LCM, we take the highest power of each prime factor present in either factorization:
- The highest power of 2 is 2³ = 8
- The highest power of 7 is 7¹ = 7
Multiply these together: 8 x 7 = 56. The LCM of 7 and 8 is 56.
Method 3: Using the Formula (LCM & GCD Relationship)
The LCM and the greatest common divisor (GCD) of two numbers are related through a simple formula:
LCM(a, b) x GCD(a, b) = a x b
Where 'a' and 'b' are the two numbers.
First, we need to find the GCD of 7 and 8. Since 7 is a prime number and 8 is not divisible by 7, the GCD of 7 and 8 is 1.
Now, we can use the formula:
LCM(7, 8) x GCD(7, 8) = 7 x 8 LCM(7, 8) x 1 = 56 LCM(7, 8) = 56
Real-World Applications of LCMs
The concept of LCMs isn't just an abstract mathematical exercise; it has practical applications in many real-world scenarios:
-
Scheduling: Imagine two buses that leave the station at different intervals. One bus leaves every 7 minutes, and the other leaves every 8 minutes. The LCM (56 minutes) tells us when both buses will leave the station simultaneously again.
-
Fraction Addition and Subtraction: Finding a common denominator when adding or subtracting fractions involves finding the LCM of the denominators. This ensures we're working with equivalent fractions before performing the operation.
-
Cyclic Patterns: Many events in nature or in designed systems follow cyclical patterns. Finding the LCM helps determine when these cycles will coincide. For instance, if two planets have orbital periods of 7 and 8 years, the LCM helps determine when they will be in the same relative position.
-
Project Management: In project planning, tasks might have different durations or completion cycles. Determining the LCM can assist in synchronizing the completion of multiple tasks efficiently.
Expanding on the Concept: LCM of More Than Two Numbers
The methods discussed above can be extended to find the LCM of more than two numbers. The prime factorization method remains the most efficient approach for larger numbers or more than two numbers. For example, to find the LCM of 7, 8, and 9:
-
Prime factorize each number:
- 7 = 7
- 8 = 2³
- 9 = 3²
-
Identify the highest power of each prime factor:
- 2³ = 8
- 3² = 9
- 7¹ = 7
-
Multiply the highest powers together: 8 x 9 x 7 = 504
Therefore, the LCM of 7, 8, and 9 is 504.
Conclusion: The Importance of Understanding LCMs
Understanding least common multiples is crucial for a strong foundation in mathematics and its applications. Whether you're solving simple fraction problems or tackling complex scheduling challenges, the ability to efficiently calculate LCMs is a valuable skill. The methods outlined in this article – listing multiples, prime factorization, and utilizing the relationship with GCD – provide versatile tools for determining the LCM of any set of integers, allowing you to confidently approach various mathematical and real-world problems. Remember, mastering the concept of LCMs opens doors to a deeper understanding of mathematical relationships and their practical implications across numerous fields.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
How Many In A Peck Of Oysters
Mar 23, 2025
-
How Long Does It Take To Drive 26 Miles
Mar 23, 2025
-
How Much Does A Can Of Coke Weigh
Mar 23, 2025
-
Which Term Most Clearly Describes A Medium
Mar 23, 2025
-
How Much Protein Is 8 Oz Of Chicken
Mar 23, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Is The Common Multiple Of 7 And 8 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
