What Is The Result Of Division Called
Arias News
Mar 22, 2025 · 5 min read
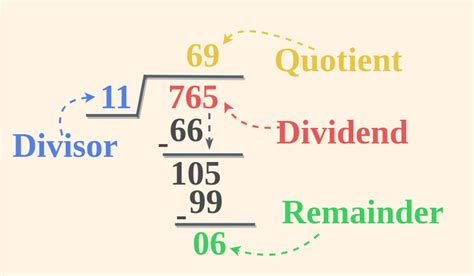
Table of Contents
What is the Result of Division Called? A Deep Dive into Quotients, Remainders, and More
The seemingly simple question, "What is the result of division called?" opens a door to a fascinating exploration of mathematical concepts. While the most common answer is "quotient," the full picture is far richer, encompassing remainders, decimal representations, and even the nuanced terminology used in different mathematical contexts. This comprehensive guide will delve into the intricacies of division's results, providing a clear and detailed understanding for both beginners and those seeking a refresher.
Understanding the Basics: Dividend, Divisor, Quotient, and Remainder
Before we dive into the specifics of what the result of division is called, let's establish the fundamental terminology. In a division problem, we have four key components:
- Dividend: The number being divided. Think of it as the total quantity you're splitting up.
- Divisor: The number you're dividing by. This represents the size of each group or the number of groups you're dividing into.
- Quotient: This is the main result of the division, representing how many times the divisor goes into the dividend evenly. This is the answer most people think of when asked what the result of division is called.
- Remainder: The amount left over after the division is complete. It represents the portion of the dividend that couldn't be evenly divided by the divisor.
Example:
Let's say we're dividing 17 by 5.
- Dividend: 17
- Divisor: 5
- Quotient: 3 (because 5 goes into 17 three times)
- Remainder: 2 (because there are 2 left over after dividing 17 by 5)
Therefore, 17 ÷ 5 = 3 with a remainder of 2. The quotient is 3, and the remainder is 2.
Beyond Whole Numbers: Exploring Decimal Results
When dealing with whole numbers, the remainder is a clear indication of what's left over. However, division doesn't always result in a whole number quotient. When the dividend isn't perfectly divisible by the divisor, we often continue the division process to obtain a decimal representation. In this case, the entire result, including the decimal part, is still often referred to as the quotient.
Example:
Dividing 17 by 4:
- Dividend: 17
- Divisor: 4
- Quotient: 4.25 (4 goes into 17 four times with a remainder of 1. This remainder is then expressed as a decimal fraction: 1/4 = 0.25)
Here, 4.25 is the quotient. There's no separate remainder expressed; it's incorporated into the decimal part of the quotient.
Different Mathematical Contexts, Different Terminology
While "quotient" is the most widely used and understood term for the result of division, the specific terminology can vary depending on the mathematical context. For instance:
In Modular Arithmetic: The Remainder Takes Center Stage
Modular arithmetic focuses on remainders. The result of a division in this context is primarily the remainder. The notation "a ≡ b (mod m)" means "a is congruent to b modulo m," where 'b' is the remainder when 'a' is divided by 'm'. In modular arithmetic, the quotient itself is often less important than the remainder.
In Polynomial Division: Quotients and Remainders in Algebraic Expressions
When dividing polynomials, we still have a quotient and a remainder. The process mirrors division with numbers, but the results are polynomial expressions. The division algorithm for polynomials states that for any polynomials P(x) and D(x) (where D(x) is not the zero polynomial), there exist unique polynomials Q(x) (the quotient) and R(x) (the remainder) such that:
P(x) = D(x)Q(x) + R(x)
where the degree of R(x) is less than the degree of D(x).
In Abstract Algebra: Exploring Generalizations
In abstract algebra, the concept of division extends beyond numbers and polynomials. The notion of a "quotient" can be generalized to other algebraic structures, often in the context of quotient groups or quotient rings. The specific terminology varies widely depending on the structure involved, but the underlying idea of dividing one structure by another to obtain a result remains consistent.
Practical Applications: Why Understanding Division Results Matters
Understanding the different aspects of division's results is crucial in various fields:
- Computer Science: Remainders play a critical role in algorithms such as hashing, random number generation, and cryptography.
- Engineering: Precise calculations involving division are essential in designing and building structures, machines, and systems.
- Finance: Dividing assets, calculating interest rates, and allocating resources all rely on a solid grasp of division.
- Everyday Life: Dividing up resources, calculating unit prices, and sharing items fairly all involve understanding quotients and remainders.
Decimal Quotients: Terminating vs. Repeating Decimals
When the result of division is a decimal, it can be either a terminating decimal or a repeating decimal.
- Terminating Decimal: A decimal that ends after a finite number of digits. For example, 17/4 = 4.25 is a terminating decimal.
- Repeating Decimal: A decimal that has a pattern of digits that repeats infinitely. For example, 1/3 = 0.333... is a repeating decimal.
The nature of the decimal quotient (terminating or repeating) depends on the prime factorization of the divisor. If the divisor's prime factorization only contains 2s and/or 5s (the prime factors of 10), the decimal quotient will terminate. Otherwise, it will repeat.
Advanced Concepts: Division by Zero and Undefined Results
One crucial aspect of division that needs emphasis is that division by zero is undefined. This is because division can be thought of as the inverse operation of multiplication. There is no number that, when multiplied by zero, gives a non-zero result. Therefore, the result of dividing any number by zero is undefined, a concept crucial to grasp in various mathematical and computational contexts.
Conclusion: A Comprehensive View of Division's Results
The seemingly straightforward question of what the result of division is called leads to a rich tapestry of mathematical concepts. While "quotient" is the primary term for the result of division, understanding the role of remainders, the intricacies of decimal representations, and the varying terminology across different mathematical branches is vital. From modular arithmetic to polynomial division and the abstract realms of algebra, the concepts of quotients and remainders remain fundamental and essential for a thorough understanding of mathematics and its applications across diverse fields. This detailed exploration has aimed to equip you with a comprehensive understanding of division's results, enhancing your mathematical proficiency and appreciation for the beauty and complexity hidden within such a seemingly simple operation.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Can A Dog Have Sex With Human
May 09, 2025
-
Is Sugar An Element Compound Or Mixture
May 09, 2025
-
Highest Common Factor Of 27 And 18
May 09, 2025
-
7am To 1am Is How Many Hours
May 09, 2025
-
Is Rope A Short Or Long Vowel
May 09, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Is The Result Of Division Called . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.