When Derivatively Classifying Information Where Can You
Arias News
Mar 15, 2025 · 6 min read
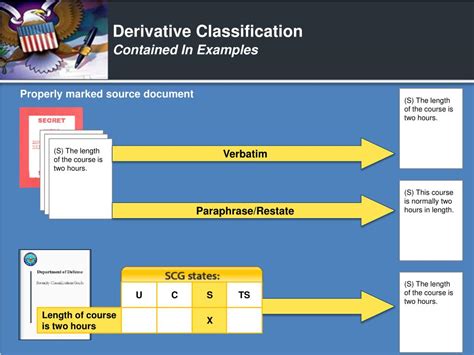
Table of Contents
- When Derivatively Classifying Information Where Can You
- Table of Contents
- When Derivatively Classifying Information: Where Can You?
- Understanding Derivative Classification
- Key Aspects of Derivative Classification
- Where Derivative Classification Can Be Applied
- 1. Summaries and Analyses of Classified Information
- 2. Translations of Classified Documents
- 3. Compilations of Classified Information
- 4. Abstracts and Excerpts of Classified Information
- 5. Reformatting of Classified Information
- Determining the Appropriate Classification Level
- Factors to Consider:
- Preventing Misclassification: Best Practices
- Legal and Ethical Considerations
- Conclusion
- Latest Posts
- Latest Posts
- Related Post
When Derivatively Classifying Information: Where Can You?
Derivatively classifying information is a critical aspect of information security and management, especially within organizations handling sensitive data. Understanding the nuances of derivative classification is crucial to ensuring compliance and preventing security breaches. This comprehensive guide delves into the intricacies of derivative classification, explaining where it can be applied and the critical considerations involved.
Understanding Derivative Classification
Derivative classification is the process of assigning a security classification to information that is not original but is derived from already classified information. This means the information itself wasn't created at a classified level, but its content is inherently tied to classified material, thus inheriting its classification. It's crucial to note that derivative classification isn't simply copying classified information; it involves understanding the context and impact of the derived information to correctly assign its classification.
Key Aspects of Derivative Classification
- Source Material: The foundation of derivative classification is the pre-existing classified information. Accurate identification and understanding of the source material's classification is paramount.
- Context and Content: Simply containing classified elements doesn't automatically result in derivative classification. The context and how the information is presented are equally important. A summary of a top-secret document might warrant a lower classification if it doesn't reveal sensitive details.
- Marking and Handling: Once derivatively classified, the information must be clearly marked with the appropriate classification level and handling instructions. Failure to do so is a serious security breach.
- Authority: Only authorized individuals with the necessary clearance and knowledge can perform derivative classification. This usually involves specific training and understanding of the classification system.
Where Derivative Classification Can Be Applied
Derivative classification isn't a haphazard process. It's applied in specific scenarios where information is derived from classified sources. Let's explore several common application areas:
1. Summaries and Analyses of Classified Information
Creating summaries, analyses, or interpretations of classified material often necessitates derivative classification. Even if the summary doesn't directly quote the original, it might still contain information that's inherently classified due to its contextual relation to the source. For example, an analysis of a classified intelligence report might itself be classified because the conclusions drawn are based on secret information.
2. Translations of Classified Documents
Translating a classified document into another language requires derivative classification. The translated document inherits the classification of the original, even though the words and sentence structure are different. This is because the information itself remains classified. The translated version must maintain the same classification markings and handling instructions.
3. Compilations of Classified Information
When multiple classified documents or portions of documents are combined to create a single document or database, the resulting compilation requires derivative classification. The classification level will be determined by the highest classification level of the source materials. This ensures that all sensitive information remains adequately protected.
4. Abstracts and Excerpts of Classified Information
Extracting specific portions or writing abstracts of classified materials frequently requires derivative classification. Even if only a small part of the original is included, the context and potential impact on national security must be considered. This is particularly important when dealing with highly sensitive information where even seemingly minor details can compromise security.
5. Reformatting of Classified Information
Changing the format of a classified document, for instance, from a printed document to a digital file or vice versa, necessitates derivative classification. The new format still contains classified information, requiring the same level of security. This applies to various formats, such as converting a classified PowerPoint presentation to a PDF or a classified image file into a different format.
Determining the Appropriate Classification Level
One of the most challenging aspects of derivative classification is accurately determining the appropriate classification level. This involves a careful assessment of the information's content, context, and potential impact. It's not simply a matter of copying the source material's classification; a thorough evaluation is required.
Factors to Consider:
- Sensitivity of the Information: How sensitive is the information contained in the derived document? Does it reveal sensitive details about national security, intelligence operations, or other critical areas?
- Potential Damage: What is the potential damage if the information were to be released to unauthorized individuals or entities? Could it compromise national security, endanger lives, or cause significant economic damage?
- Source Material Classification: The classification level of the source materials significantly influences the classification of the derived information. However, it's crucial to assess the derived information's independent impact.
- Context and Presentation: How is the information presented in the derived document? Does the context reveal additional sensitive information not explicitly stated in the source material?
- Guidance and Regulations: Always refer to the applicable classification guides and regulations. These documents provide detailed instructions and examples for classifying information.
Preventing Misclassification: Best Practices
Misclassifying information can have serious consequences, from fines and disciplinary action to compromising national security. Implementing robust procedures and adhering to best practices are crucial for accurate derivative classification:
- Thorough Training: Ensure all personnel involved in handling classified information receive comprehensive training on derivative classification procedures. This includes understanding classification guidelines, identifying sensitive information, and correctly assigning classification levels.
- Clear Guidelines and Procedures: Establish clear, well-documented guidelines and procedures for derivative classification. These procedures must be readily accessible to all personnel involved.
- Regular Reviews and Audits: Implement regular reviews and audits of the derivative classification process to identify and correct any inconsistencies or errors. This proactive approach helps prevent misclassification and maintains security.
- Independent Verification: When possible, have a second individual review and verify the classification of derivatively classified documents. This provides an independent check and reduces the risk of errors.
- Documentation: Maintain thorough records of the derivative classification process, including the source materials, the methods used to determine the classification level, and the individuals involved. This documentation is vital for audits and investigations.
Legal and Ethical Considerations
Derivative classification is not only a security matter; it also has significant legal and ethical implications. Organizations must comply with relevant laws and regulations, ensuring that all information is classified appropriately. Mishandling classified information can lead to severe penalties, including fines, imprisonment, and reputational damage. Ethical considerations involve the responsible handling of sensitive information, respecting the confidentiality of sources, and protecting the integrity of the classification system.
Conclusion
Derivative classification is a complex but necessary process for maintaining the security of sensitive information. Understanding the principles, procedures, and best practices involved is crucial for organizations handling classified information. By adhering to these guidelines and implementing robust security measures, organizations can minimize the risks associated with derivative classification and ensure the protection of sensitive data. The responsible and accurate classification of information is not merely a compliance issue; it's a fundamental aspect of maintaining national security and safeguarding critical information. Remember, consistent training, clear procedures, and diligent oversight are paramount to effectively and ethically managing derivatively classified information.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Circumference Of A Roll Of Toilet Paper
Mar 16, 2025
-
How Tall Is 1 75 Meters In Feet
Mar 16, 2025
-
Where Did Usher Go To High School
Mar 16, 2025
-
How Old Are You If Your Born In 1995
Mar 16, 2025
-
What Is That Planet Next To The Moon
Mar 16, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about When Derivatively Classifying Information Where Can You . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
