Which Action Is An Example Of Public Policy
Arias News
Mar 25, 2025 · 6 min read
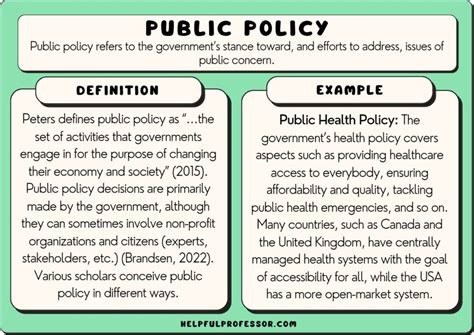
Table of Contents
Which Action is an Example of Public Policy? Understanding the Scope and Impact
Public policy, a term often thrown around in political discussions and academic circles, can seem nebulous. What exactly is public policy, and how can we identify it in action? This comprehensive guide delves into the definition, characteristics, and numerous examples of public policy, illustrating its pervasive influence on our daily lives. We'll explore various levels of government involvement, the policy-making process, and the far-reaching consequences of these decisions.
Defining Public Policy: More Than Just Laws
Public policy isn't simply a collection of laws. It's a broader concept encompassing the actions (or inactions) of government, at all levels—local, state, federal, and even international—that aim to address societal problems or achieve specific goals. These actions can take many forms, including:
- Legislation: The most obvious manifestation, laws passed by legislatures at different governmental levels.
- Regulations: Rules, guidelines, and restrictions implemented by government agencies to enforce laws or manage specific sectors.
- Judicial Decisions: Court rulings that interpret laws and establish precedents, effectively shaping policy.
- Executive Orders: Directives issued by the executive branch (e.g., the President or Governor) to guide government action.
- Government Spending (Budgetary Policy): Allocation of public funds to various programs and initiatives, reflecting policy priorities.
- Taxation Policies: The system of levying taxes, influencing economic activity and resource distribution.
- Non-action (or Inaction): A conscious decision by the government not to intervene in a specific area, which itself constitutes a policy choice.
Key Characteristics of Public Policy
To distinguish public policy from other governmental activities, we need to consider its defining features:
- Purposeful Action: Public policy is deliberate; it's not accidental or random. It arises from a conscious decision by government actors to address a perceived problem or pursue a specific objective.
- Authoritative Allocation of Values: Public policies reflect societal values and priorities. They allocate resources and determine who benefits and who bears the costs. This allocation often involves resolving conflicts of interest among various groups.
- Government Involvement: The involvement of some level of government is essential. It's the government that initiates, implements, and enforces public policies.
- Impact on Society: Public policies have a measurable impact on citizens' lives, affecting their rights, opportunities, and well-being.
Examples of Public Policy Across Different Sectors
The scope of public policy is vast, impacting virtually every aspect of our lives. Let's examine examples across different sectors:
1. Economic Policy
- Taxation: Progressive income tax systems, aiming for a more equitable distribution of wealth, are a prime example. Similarly, tax breaks for specific industries or investment incentives are forms of public policy designed to stimulate economic growth.
- Monetary Policy: Central banks manipulating interest rates to control inflation and influence economic activity.
- Trade Policy: Tariffs, quotas, and trade agreements all exemplify public policy designed to regulate international commerce. For instance, the North American Free Trade Agreement (NAFTA) and its successor, USMCA, significantly shaped trade relations between Canada, Mexico, and the United States.
- Minimum Wage Legislation: Setting a minimum hourly wage impacts the employment market and income levels of low-wage earners.
2. Social Welfare Policy
- Social Security: Providing retirement, disability, and survivor benefits to eligible citizens. This represents a large-scale public policy aiming to address poverty and ensure economic security in old age.
- Medicare and Medicaid: Government-funded healthcare programs aimed at providing access to healthcare for senior citizens (Medicare) and low-income individuals (Medicaid).
- Unemployment Insurance: Providing temporary financial assistance to individuals who have lost their jobs.
- Affordable Care Act (ACA): A landmark healthcare reform aiming to increase health insurance coverage and affordability.
3. Environmental Policy
- Clean Air Act: Legislation designed to reduce air pollution and protect air quality. This policy involves setting emission standards for vehicles and industries.
- Clean Water Act: Legislation aimed at reducing water pollution and protecting water resources.
- Endangered Species Act: Protecting endangered and threatened species and their habitats.
- Regulations on Greenhouse Gas Emissions: Policies aimed at mitigating climate change through carbon pricing or emission reduction targets.
4. Education Policy
- No Child Left Behind Act (and subsequent Every Student Succeeds Act): Federal legislation focused on improving education standards and accountability.
- Funding for Public Schools: Government allocation of funds to support public education at various levels.
- Curriculum Standards: Setting guidelines for what students should learn at different grade levels.
- Student Loan Programs: Government-backed programs offering financial assistance for higher education.
5. Healthcare Policy
Beyond Medicare and Medicaid, other examples include:
- Drug Regulation: The Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approval process for new drugs and medical devices is a critical aspect of healthcare policy, ensuring safety and efficacy.
- Public Health Initiatives: Government campaigns for vaccination, disease prevention, and public health education.
- Mental Health Policy: Initiatives aimed at improving access to mental health services and reducing the stigma associated with mental illness.
6. Criminal Justice Policy
- Sentencing Guidelines: Rules that dictate the length of prison sentences for various crimes.
- Law Enforcement Funding: Government allocation of funds to police departments and other law enforcement agencies.
- Prison Reform Initiatives: Efforts to improve conditions in prisons and reduce recidivism rates.
7. Immigration Policy
- Visa Requirements: Rules governing the entry of foreign nationals into the country.
- Deportation Policies: Policies regarding the removal of unauthorized immigrants.
- Pathways to Citizenship: Policies that allow certain immigrants to become citizens.
The Policy-Making Process: A Dynamic Interaction
Public policy doesn't emerge in a vacuum. It's the product of a complex and often iterative process involving multiple actors and stages:
- Problem Definition: Identifying a societal problem that requires government attention.
- Agenda Setting: Bringing the problem to the attention of policymakers and ensuring it's considered for action.
- Policy Formulation: Developing potential solutions to the problem. This involves research, analysis, and consultation with stakeholders.
- Policy Adoption: Selecting a particular solution and formally approving it through legislation, regulation, or executive action.
- Policy Implementation: Putting the policy into effect. This often involves government agencies and various bureaucratic processes.
- Policy Evaluation: Assessing the effectiveness of the policy in achieving its goals. This involves collecting data, analyzing outcomes, and making adjustments as needed. This stage often feeds back into the cycle, leading to revisions or even the replacement of the policy.
The Impact of Public Policy: Far-Reaching Consequences
Public policies have a profound impact on individuals, communities, and the broader society. Their effects can be:
- Economic: Impacting employment, income distribution, economic growth, and investment.
- Social: Influencing social welfare, health, education, and crime rates.
- Environmental: Affecting environmental quality, resource management, and climate change mitigation.
- Political: Shaping power dynamics, representation, and governance structures.
Conclusion: Understanding the Ubiquity of Public Policy
Public policy is a fundamental aspect of governance, shaping our lives in countless ways. By understanding its definition, characteristics, processes, and diverse examples, we can better engage in informed civic participation and contribute to shaping a more just and equitable society. Recognizing the pervasive influence of public policy empowers us to understand the forces at play in our communities and advocate for changes that align with our values and priorities. From seemingly mundane regulations to large-scale social programs, every government action – or inaction – is a manifestation of public policy, continually shaping the landscape of our world.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
1 Liter Is How Many Bottles Of Water
Mar 26, 2025
-
Is Nia Peeples Related To Mario Van Peebles
Mar 26, 2025
-
How To Address An Envelope To A Widow
Mar 26, 2025
-
How Many Slices Is 1 2 Pound Of Brisket
Mar 26, 2025
-
How Many Tons Are In 6000 Pounds
Mar 26, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Which Action Is An Example Of Public Policy . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
