Which Of These Pieces Of Hardware Is Used For Telecommunication
Arias News
Mar 29, 2025 · 6 min read
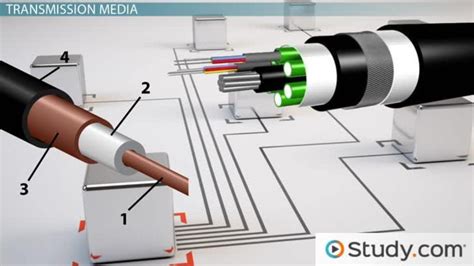
Table of Contents
Which Pieces of Hardware are Used for Telecommunication? A Deep Dive
Telecommunication, the transmission of information over significant distances, relies on a complex interplay of hardware components. From the simplest phone call to high-speed data transfer across continents, numerous pieces of equipment work together seamlessly to facilitate communication. This article delves into the core hardware used in telecommunication, exploring their functionalities and significance in the modern interconnected world.
The Foundation: Transmission Media
Before we discuss specific devices, let's understand the foundational elements enabling communication: transmission media. These are the physical pathways that carry signals.
1. Copper Wires:
- Functionality: Copper wires, historically the backbone of telecommunications, transmit signals using electrical current. Twisted pair cables, a common type, minimize interference between pairs of wires. Coaxial cables offer better shielding and higher bandwidth, suitable for cable television and older internet connections.
- Significance: While gradually being replaced in many applications, copper wires still form a significant part of the last-mile connection to many homes and businesses, especially in areas with less advanced infrastructure. They are relatively inexpensive to install and maintain, although bandwidth is limited compared to fiber optics.
- Applications: Traditional telephone lines, DSL internet connections, older cable television networks.
2. Fiber Optic Cables:
- Functionality: Fiber optic cables utilize pulses of light to transmit data through thin strands of glass or plastic. This allows for significantly higher bandwidth and longer transmission distances compared to copper wires.
- Significance: Fiber optics are the cornerstone of modern high-speed data networks, including the internet backbone and long-distance communication infrastructure. Their superior capacity and speed make them crucial for supporting bandwidth-intensive applications.
- Applications: High-speed internet, long-distance telephony, cable television, data centers.
3. Wireless Transmission Media:
- Functionality: Wireless transmission uses electromagnetic waves to transmit signals through the air. This includes various technologies like radio waves, microwaves, and infrared signals.
- Significance: Wireless technology has revolutionized telecommunications, offering mobility and accessibility. It's crucial for cellular networks, Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, and satellite communications.
- Applications: Cellular phones, Wi-Fi networks, Bluetooth devices, satellite television, GPS systems.
Core Telecommunication Hardware:
Now let's explore the key hardware components that utilize these transmission media:
1. Modems (Modulator-Demodulator):
- Functionality: Modems translate digital data into analog signals for transmission over analog lines (like traditional phone lines) and vice-versa. They are essential for connecting digital devices to networks using analog infrastructure.
- Significance: Modems were crucial in the early days of internet access via dial-up connections. While less common for broadband internet access now, they still find applications in connecting remote areas with limited infrastructure.
- Applications: Dial-up internet access, connecting to older telephone systems.
2. Routers:
- Functionality: Routers direct data packets between networks. They determine the best path for data to travel, ensuring efficient communication across different networks.
- Significance: Routers are essential for connecting multiple devices to a network and for routing traffic between different networks (like the internet and a local area network).
- Applications: Home networks, office networks, internet service providers.
3. Switches:
- Functionality: Switches connect devices within a local area network (LAN). They forward data packets only to the intended recipient, unlike routers, which direct traffic between networks.
- Significance: Switches provide efficient communication within a LAN, improving performance and reducing network congestion.
- Applications: Home networks, office networks, data centers.
4. Multiplexers:
- Functionality: Multiplexers combine multiple signals onto a single transmission line, increasing efficiency. This allows multiple users to share the same communication channel.
- Significance: Multiplexers are crucial for optimizing the use of expensive transmission resources, like fiber optic cables.
- Applications: Telephone systems, cable television networks, data centers.
5. Telephone Handsets:
- Functionality: The ubiquitous telephone handset allows voice communication over a wired or wireless network. Modern handsets often incorporate features beyond basic voice calls.
- Significance: Though constantly evolving, the telephone remains a primary communication tool for many individuals and businesses.
- Applications: Voice communication, often integrated with data services.
6. Cellular Base Stations (Cell Towers):
- Functionality: Cell towers are the radio transceivers that facilitate communication between mobile devices and the cellular network. They receive and transmit radio signals, allowing for mobile connectivity.
- Significance: Cell towers are the foundation of cellular networks, enabling wireless communication across wide geographic areas.
- Applications: Cellular phones, mobile internet access.
7. Satellites:
- Functionality: Satellites act as relay stations for communication signals, enabling long-distance communication and broadcasting across vast distances. They receive signals from one point on Earth and transmit them to another.
- Significance: Satellites are crucial for global communication, providing connectivity in remote areas and enabling satellite television and GPS services.
- Applications: Satellite television, GPS, satellite internet, long-distance telephony.
8. Network Interface Cards (NICs):
- Functionality: NICs allow computers and other devices to connect to a network. They translate digital data into signals that can be transmitted over the network's transmission medium.
- Significance: NICs are the physical interface between a device and the network, enabling data transmission and reception.
- Applications: All networked computers and devices.
9. Servers:
- Functionality: Servers are powerful computers that provide services to other devices on a network. They store and manage data, run applications, and provide access to resources.
- Significance: Servers are the backbone of many telecommunication services, including web hosting, email, and file sharing.
- Applications: Web hosting, email services, file storage, data centers.
The Evolution of Telecommunication Hardware:
The hardware used in telecommunication is constantly evolving. The shift from analog to digital technologies, the rise of wireless communication, and the increasing demand for higher bandwidth have driven significant advancements.
- From Analog to Digital: The transition from analog to digital signals has dramatically increased the capacity and efficiency of telecommunication networks. Digital signals are less susceptible to noise and interference and can carry more information.
- Wireless Revolution: The proliferation of wireless technologies has fundamentally changed how we communicate. Mobile phones, Wi-Fi, and Bluetooth have enabled ubiquitous connectivity.
- Increased Bandwidth Demands: The increasing demand for high-bandwidth applications, such as video streaming and online gaming, is driving the adoption of fiber optics and other high-capacity technologies.
The Future of Telecommunication Hardware:
Future trends in telecommunication hardware include:
- 5G and Beyond: The rollout of 5G and future generations of cellular technology will provide even faster speeds and lower latency, enabling new applications and services.
- Software-Defined Networking (SDN): SDN will allow for more flexible and dynamic management of telecommunication networks, improving efficiency and scalability.
- Internet of Things (IoT): The proliferation of IoT devices will increase the demand for robust and scalable telecommunication networks.
- Quantum Computing: While still in its early stages, quantum computing has the potential to revolutionize telecommunication by enabling secure and high-speed communication.
Conclusion:
The hardware used for telecommunication is a diverse and complex system. From the simple copper wires to sophisticated satellites, each component plays a vital role in enabling the seamless transmission of information across vast distances. The constant evolution of this technology ensures that we remain connected in an increasingly interconnected world. Understanding the different pieces of hardware and their functions is crucial to appreciating the complexity and importance of telecommunications in modern society. The ongoing advancements promise to further enhance speed, efficiency, and accessibility in the years to come.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
How Many Grams Is A Cup Of Cooked Rice
Mar 31, 2025
-
How Many Oz Is A Pint Of Blueberries
Mar 31, 2025
-
How Many 8ths Are In A Qp
Mar 31, 2025
-
14 By 14 Room Size In Square Feet
Mar 31, 2025
-
How Many Quarts Are In 16 Gallons
Mar 31, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Which Of These Pieces Of Hardware Is Used For Telecommunication . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
