1000 A Week Is How Much A Year
Arias News
Mar 20, 2025 · 6 min read
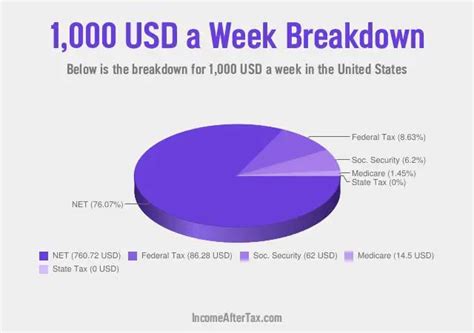
Table of Contents
1000 a Week Is How Much a Year? A Comprehensive Guide to Annual Income Calculation
Making $1000 a week sounds pretty fantastic, right? But what does that translate to annually? Knowing your potential yearly earnings from a weekly income is crucial for budgeting, financial planning, and understanding your overall financial health. This comprehensive guide will not only answer the question, "$1000 a week is how much a year?" but will also delve into the nuances of annual income calculations, taxes, and how to maximize your earnings.
Calculating Your Yearly Income from a Weekly Salary
The simplest calculation is multiplying your weekly income by the number of weeks in a year. However, the precise number of weeks varies slightly depending on whether you consider a standard 52-week year or account for leap years.
Standard Calculation (52 Weeks):
$1000/week * 52 weeks/year = $52,000/year
This is a good starting point, providing a clear, straightforward estimate.
More Accurate Calculation (Considering Leap Years):
While a standard 52-week year is generally used, a more precise calculation considers that there are approximately 52.14 weeks in a year.
$1000/week * 52.14 weeks/year = $52,140/year
This method is marginally more accurate, reflecting the slight variation caused by leap years. The difference, while seemingly small, can accumulate over time.
Important Considerations:
- Pay Periods: Many employers pay bi-weekly (every two weeks) or semi-monthly (twice a month). These payment schedules will affect the exact amount you receive in each paycheck but your annual earnings remain the same.
- Bonuses and Overtime: The $1000/week figure likely excludes bonuses, commissions, or overtime pay, which can significantly increase your total annual income. Remember to factor these in for a realistic yearly projection.
- Taxes and Deductions: The $52,000 or $52,140 figures represent your gross income, meaning before taxes and other deductions. Your net income (take-home pay) will be significantly lower. We will explore this further in the following sections.
Understanding Taxes and Deductions
Your actual take-home pay after taxes and deductions is substantially less than your gross income. Several factors influence your net income:
- Federal Income Tax: The US federal income tax system is progressive, meaning higher earners pay a larger percentage of their income in taxes. Your tax bracket will determine your tax rate.
- State Income Tax: Many states also levy income taxes, with rates varying considerably. If you live in a state with no income tax, your net income will be higher.
- Social Security and Medicare Taxes (FICA): These taxes fund Social Security and Medicare programs. Both the employer and employee contribute.
- Other Deductions: Depending on your circumstances, other deductions might apply, such as health insurance premiums, retirement plan contributions (401k, IRA), and others.
Estimating Net Income: Accurately estimating your net income requires knowing your specific tax bracket, state tax rate, and other deductions. Using online tax calculators or consulting with a tax professional can provide a realistic estimate. Remember that these are estimates; your actual net income might vary slightly based on individual circumstances and tax laws.
Maximizing Your $1000/Week Earnings
While a $1000/week salary is substantial, it's crucial to manage your finances effectively to maximize your potential and achieve your financial goals. Consider these strategies:
- Budgeting: Create a detailed budget to track your income and expenses, ensuring you allocate funds for necessities, savings, and debt repayment.
- Investing: Invest a portion of your income to build long-term wealth. Explore various investment options based on your risk tolerance and financial goals. Consider index funds, ETFs, or real estate.
- Debt Management: Aggressively pay down high-interest debt, such as credit card debt, to reduce your financial burden and free up funds for other priorities.
- Retirement Planning: Start contributing to a retirement account early to take advantage of the power of compounding. Maximize employer matching contributions if available.
- Emergency Fund: Build an emergency fund with 3-6 months' worth of living expenses to handle unexpected financial setbacks.
- Financial Literacy: Continuously expand your financial knowledge through books, courses, or financial advisors. Understanding financial concepts is key to effective money management.
Beyond the Numbers: Lifestyle and Financial Well-being
Earning $1000 a week provides considerable financial flexibility, but it's essential to maintain a balanced perspective. Focus on financial well-being alongside your financial goals:
- Avoid Lifestyle Inflation: As your income grows, resist the temptation to increase your spending proportionally. Maintain a disciplined approach to spending.
- Prioritize Experiences: While material possessions are nice, prioritize experiences and invest in things that enrich your life.
- Give Back: Consider giving back to the community through charitable donations or volunteer work.
- Health and Wellness: Invest in your physical and mental health. Regular exercise, healthy eating, and stress management are crucial for long-term well-being.
Exploring Different Income Streams
While a $1000/week job is a significant achievement, diversification is key to long-term financial security. Consider exploring alternative income streams:
- Side Hustles: Engage in freelance work, online businesses, or part-time jobs to supplement your primary income.
- Investments: Generating passive income through investments can further enhance your financial stability.
- Entrepreneurship: Starting your own business offers significant earning potential but requires dedication, effort, and risk management.
The Bottom Line: Making the Most of Your Income
A $1000-a-week salary provides a solid foundation for a comfortable lifestyle and financial security. However, maximizing your financial potential requires more than simply calculating your yearly income. It involves budgeting, investing, debt management, and a long-term financial plan. By focusing on these strategies, you can build a robust financial future and achieve your financial goals. Remember to regularly review and adjust your financial plan to adapt to changing circumstances and achieve lasting financial well-being. The journey to financial success is ongoing and requires continuous learning, adaptation, and smart financial decision-making. Don't be afraid to seek professional advice when needed, such as consulting a financial advisor or tax professional, to help guide you through the complexities of personal finance.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q: What if I get paid bi-weekly? How do I calculate my annual income?
A: If you get paid bi-weekly, you'll receive 26 paychecks per year. To calculate your annual income, multiply your bi-weekly pay by 26. For a $1000/week salary, that would mean a bi-weekly pay of approximately $2000 (depending on the exact calculation), making it $52,000 annually.
Q: How much will I actually take home after taxes?
A: This depends on various factors, including your tax bracket, state income tax, deductions, and other withholdings. Online tax calculators or tax professionals can provide a more accurate estimate.
Q: What's the best way to save and invest my money?
A: The best saving and investing strategies depend on your risk tolerance, financial goals, and time horizon. Consult with a financial advisor to determine the best course of action.
Q: How can I increase my income beyond $1000/week?
A: Explore opportunities for career advancement, acquire new skills, start a side hustle, or consider investing in income-generating assets.
Q: Are there any financial resources available to help me manage my money better?
A: Many free and paid resources are available online and offline, including books, courses, workshops, and financial advisors.
By addressing these frequently asked questions, this guide aims to provide a holistic understanding of managing a $1000/week income, ensuring its long-term benefit and financial stability. Remember, consistent planning and mindful financial decisions are crucial for achieving lasting financial well-being.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
How Many Cups Of Sour Cream In A Pound
Mar 20, 2025
-
What Makes Tze Yo Tzuh The Antagonist
Mar 20, 2025
-
If A Student Should Decide To Leave School Permanently
Mar 20, 2025
-
If You Were Born In 1966 How Old Are You
Mar 20, 2025
-
What Is The Greatest Common Factor Of 30 And 54
Mar 20, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about 1000 A Week Is How Much A Year . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
