What Is The Greatest Common Factor Of 30 And 54
Arias News
Mar 20, 2025 · 5 min read
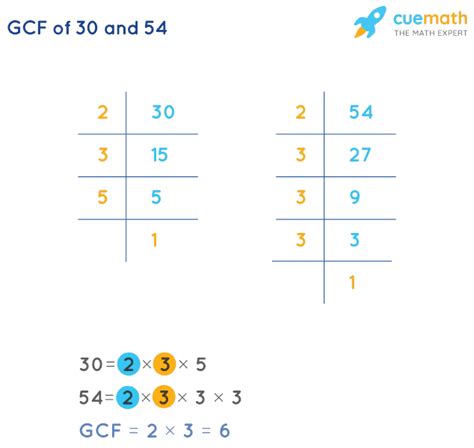
Table of Contents
What is the Greatest Common Factor of 30 and 54? A Deep Dive into Number Theory
Finding the greatest common factor (GCF) of two numbers might seem like a simple arithmetic task, but it's a fundamental concept in number theory with far-reaching applications in mathematics and computer science. This article explores the GCF of 30 and 54, detailing multiple methods for calculating it and illuminating the underlying mathematical principles. We'll go beyond the simple answer, delving into the significance of the GCF and its practical uses.
Understanding the Greatest Common Factor (GCF)
The greatest common factor (GCF), also known as the greatest common divisor (GCD), is the largest positive integer that divides each of the integers without leaving a remainder. In simpler terms, it's the biggest number that perfectly divides both numbers. Understanding the GCF is crucial for simplifying fractions, solving algebraic equations, and understanding various mathematical structures.
Methods for Finding the GCF of 30 and 54
Several methods can be employed to determine the GCF of 30 and 54. Let's explore the most common ones:
1. Listing Factors Method
This is a straightforward approach, particularly useful for smaller numbers. We list all the factors of each number and then identify the largest factor common to both.
- Factors of 30: 1, 2, 3, 5, 6, 10, 15, 30
- Factors of 54: 1, 2, 3, 6, 9, 18, 27, 54
Comparing the lists, we see that the common factors are 1, 2, 3, and 6. The greatest common factor is therefore 6.
2. Prime Factorization Method
This method is more efficient for larger numbers. We find the prime factorization of each number and then identify the common prime factors raised to the lowest power.
- Prime factorization of 30: 2 x 3 x 5
- Prime factorization of 54: 2 x 3 x 3 x 3 = 2 x 3³
The common prime factors are 2 and 3. The lowest power of 2 is 2¹ and the lowest power of 3 is 3¹. Therefore, the GCF is 2 x 3 = 6.
3. Euclidean Algorithm
The Euclidean algorithm is a highly efficient method for finding the GCF, especially for larger numbers. It's based on the principle that the GCF of two numbers does not change if the larger number is replaced by its difference with the smaller number. This process is repeated until the two numbers are equal, which represents the GCF.
Let's apply the Euclidean algorithm to 30 and 54:
- 54 = 30 x 1 + 24
- 30 = 24 x 1 + 6
- 24 = 6 x 4 + 0
Since the remainder is 0, the GCF is the last non-zero remainder, which is 6.
The Significance of the GCF
The GCF is more than just a mathematical curiosity; it has significant applications across various fields:
1. Simplifying Fractions
The GCF is fundamental to simplifying fractions. To simplify a fraction, we divide both the numerator and the denominator by their GCF. For example, the fraction 30/54 can be simplified by dividing both the numerator and the denominator by their GCF, 6:
30/54 = (30 ÷ 6) / (54 ÷ 6) = 5/9
2. Solving Equations
The GCF plays a crucial role in solving certain types of algebraic equations, particularly those involving factoring. Finding the GCF of the terms in an equation can help simplify the equation and make it easier to solve.
3. Geometry and Measurement
The GCF is used in geometry when dealing with problems involving area, perimeter, and volume. For instance, finding the dimensions of the largest square tile that can perfectly cover a rectangular floor requires calculating the GCF of the floor's length and width.
4. Number Theory and Cryptography
The GCF is a cornerstone of number theory, with applications in cryptography. Algorithms used in modern encryption techniques, such as the RSA algorithm, heavily rely on the properties of the GCF and prime numbers.
5. Computer Science
The Euclidean algorithm, used for calculating the GCF, is an essential algorithm in computer science. Its efficiency makes it suitable for various applications, including those dealing with large numbers and computationally intensive tasks.
Beyond the Basics: Exploring Related Concepts
Understanding the GCF opens the door to exploring related concepts in number theory:
1. Least Common Multiple (LCM)
The least common multiple (LCM) is the smallest positive integer that is divisible by both numbers. The LCM and GCF are related by the formula:
LCM(a, b) x GCF(a, b) = a x b
For 30 and 54, the LCM is (30 x 54) / 6 = 270.
2. Relatively Prime Numbers
Two numbers are considered relatively prime (or coprime) if their GCF is 1. For instance, 15 and 28 are relatively prime because their GCF is 1.
3. Modular Arithmetic
The GCF plays a role in modular arithmetic, a system of arithmetic for integers where numbers "wrap around" upon reaching a certain value (the modulus).
Conclusion: The Enduring Importance of the GCF
The seemingly simple task of finding the greatest common factor of 30 and 54 unlocks a world of mathematical concepts and practical applications. From simplifying fractions to underpinning sophisticated cryptographic algorithms, the GCF demonstrates the interconnectedness of mathematical ideas and their relevance in diverse fields. Mastering the calculation of the GCF, through various methods, provides a solid foundation for further exploration of number theory and its wide-ranging impact on our understanding of the world around us. This deep dive highlights that even seemingly basic mathematical operations possess surprising depth and significance. The GCF, therefore, isn't just a number; it's a key that unlocks deeper mathematical understanding and practical problem-solving capabilities. By understanding its principles and applications, you're not just learning arithmetic; you are gaining access to a powerful tool applicable across numerous fields.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Who Or What The Sentence Is About
Mar 21, 2025
-
Animals That Eat Both Plants And Animals
Mar 21, 2025
-
Square Root Of Pi Divided By 2
Mar 21, 2025
-
How Many 20 Oz Bottles Make A Gallon
Mar 21, 2025
-
How Many 100 Ml In A Litre
Mar 21, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Is The Greatest Common Factor Of 30 And 54 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
