How Many Angles Does A Rectangle Have
Arias News
Mar 24, 2025 · 5 min read
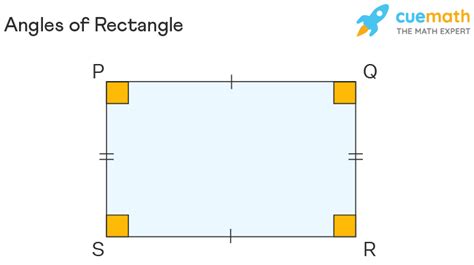
Table of Contents
How Many Angles Does a Rectangle Have? A Deep Dive into Geometry
The seemingly simple question, "How many angles does a rectangle have?" opens the door to a fascinating exploration of geometry, its definitions, properties, and related shapes. While the immediate answer is straightforward, delving deeper reveals a richer understanding of fundamental geometric concepts. This article will not only answer the question directly but also explore the broader implications within the context of geometry and its applications.
Understanding Rectangles: A Fundamental Geometric Shape
A rectangle, in its simplest definition, is a quadrilateral—a polygon with four sides—possessing specific properties that distinguish it from other quadrilaterals. These defining characteristics are crucial to understanding its angles. Let's break them down:
Key Properties of a Rectangle:
- Four Sides: A rectangle, like all quadrilaterals, has four straight sides.
- Four Right Angles: This is the critical property answering our primary question. A rectangle has four angles, and each of these angles measures exactly 90 degrees. This right angle characteristic is what sets a rectangle apart from other quadrilaterals like parallelograms or trapezoids.
- Opposite Sides are Parallel and Equal: The opposite sides of a rectangle are parallel to each other and have equal lengths. This parallel and equal side property contributes to the stability and symmetry often observed in rectangular structures.
- Diagonals Bisect Each Other: The diagonals of a rectangle, lines connecting opposite corners, bisect (divide into two equal parts) each other. This bisecting property is a useful feature in many geometric proofs and constructions.
The Answer: A Rectangle Has Four Angles
To reiterate the core answer: a rectangle possesses four angles. This simple fact serves as the foundational element upon which many geometric principles are built. The consistent 90-degree measurement of each angle is a defining characteristic that distinguishes it from other four-sided shapes.
Exploring Related Shapes and their Angles
Understanding rectangles necessitates exploring related geometric shapes and how their angle properties differ:
Squares: A Special Case of a Rectangle
A square is a special type of rectangle. It inherits all the properties of a rectangle—four sides, four right angles, opposite sides parallel and equal, diagonals bisecting each other. The distinguishing feature of a square is that all four sides are of equal length. Therefore, a square also has four 90-degree angles.
Parallelograms: A Broader Category
Rectangles belong to a larger family of shapes called parallelograms. Parallelograms are quadrilaterals with opposite sides parallel. While rectangles are parallelograms, not all parallelograms are rectangles. Parallelograms can have four angles that are not necessarily 90 degrees. In fact, opposite angles in a parallelogram are equal, but they don't have to be right angles.
Trapezoids: A Different Angle
Trapezoids are quadrilaterals with at least one pair of parallel sides. Unlike rectangles and parallelograms, trapezoids do not necessarily have parallel opposite sides. Consequently, trapezoids don't have the same angle restrictions. They always have four angles, but these angles can be of varying measurements, and they don't have to add up to 360 degrees like in other quadrilaterals. Only special types of trapezoids (isosceles trapezoids) have certain angle relationships.
Rhombuses: Equal Sides, but Not Always Right Angles
A rhombus is a quadrilateral with all four sides equal in length. Similar to squares, all sides are equal. However, unlike rectangles and squares, a rhombus doesn't necessarily have four right angles. Its angles can vary, although opposite angles will always be equal.
The Significance of 90-Degree Angles in Rectangles
The presence of four 90-degree angles in a rectangle has profound implications in various fields:
Construction and Architecture:
The stability and predictability offered by right angles make rectangles the preferred shape for numerous construction projects. Buildings, rooms, windows, doors—all frequently utilize the rectangle’s structural benefits derived from its angles. The predictability of angles simplifies design, material usage, and construction.
Computer Graphics and Design:
In computer graphics and design, rectangles form the basis of many digital elements. The precise angles facilitate easy manipulation and alignment of elements within software, making them essential for creating layouts and interfaces.
Everyday Objects:
Rectangles are ubiquitous in everyday life. From books and screens to tables and photographs, the rectangular shape is incredibly common due to its practical and aesthetically pleasing qualities. The 90-degree angles contribute to ease of stacking, arranging, and fitting objects together.
Mathematical Applications and Proofs
The angle properties of rectangles are fundamental to numerous geometric proofs and theorems. Understanding these properties is essential for solving problems related to area, perimeter, diagonal lengths, and relationships with other geometric figures.
Area Calculation:
The area of a rectangle is simply the product of its length and width. This straightforward calculation is directly linked to the 90-degree angles ensuring the area calculation's accuracy.
Pythagorean Theorem:
The Pythagorean theorem, relating the sides of a right-angled triangle, is frequently applied to problems involving rectangles, as the diagonals of a rectangle create right-angled triangles.
Trigonometry:
Trigonometric functions are frequently used to calculate angles and side lengths in rectangles and related shapes. The 90-degree angles act as reference points in these calculations.
Beyond the Basics: Exploring Advanced Concepts
While the basic properties of a rectangle are relatively simple, more advanced geometric concepts build upon this foundation:
Higher Dimensions:
Rectangles can be extended into higher dimensions. A three-dimensional equivalent is a rectangular prism (cuboid), while extending further leads to hyperrectangles. These higher-dimensional shapes maintain the core principle of right angles (or their higher-dimensional equivalents).
Tessellations:
Rectangles play a significant role in tessellations—covering a plane with repeating geometric shapes without overlaps or gaps. The 90-degree angles facilitate simple and efficient tessellations.
Conclusion: The Enduring Importance of Rectangular Angles
The seemingly simple question of how many angles a rectangle has leads to a much broader understanding of fundamental geometric concepts and their applications in various fields. The four 90-degree angles are not just a defining characteristic but the key to the rectangle's stability, practicality, and mathematical significance. From architecture to computer graphics, the consistent, predictable nature of these angles makes the rectangle an indispensable shape in our world. Its properties provide a solid foundation for further exploration in geometry and related disciplines. Understanding the simple yet powerful properties of a rectangle offers insights into the beauty and utility of geometric principles.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
How Many Tons Are In 6000 Pounds
Mar 26, 2025
-
How Many 2s In A Deck Of Cards
Mar 26, 2025
-
A Quarter Of Weed Is How Many Grams
Mar 26, 2025
-
How Much Is 200 G Of Sugar
Mar 26, 2025
-
The Answer To An Addition Problem Is Called The
Mar 26, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about How Many Angles Does A Rectangle Have . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
