How Many Fingers Does A Turtle Have
Arias News
Apr 02, 2025 · 5 min read
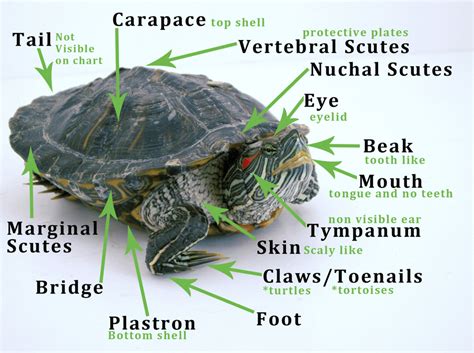
Table of Contents
How Many Fingers Does a Turtle Have? Unraveling the Mystery of Reptilian Limbs
Turtles, those ancient and enigmatic reptiles, have captivated humans for centuries. Their slow, deliberate movements and shelled bodies create an air of mystery, often leading to fascinating questions about their anatomy. One such question, seemingly simple yet surprisingly complex, is: how many fingers does a turtle have? The answer, as we'll explore, isn't a straightforward "five" like on a human hand. The number of "fingers" – more accurately referred to as digits – varies depending on the species and even the limb in question. This article delves into the fascinating world of turtle anatomy, exploring the structure of their limbs and the diversity found across different turtle species.
Understanding Turtle Limbs: Beyond the Shell
Before we delve into digit counts, it's crucial to understand the fundamental structure of a turtle's limb. Unlike the clearly defined fingers and toes of humans and many other mammals, turtle limbs are adapted for their specific lifestyles and environments. Their limbs are designed for a variety of functions, including:
- Propulsion: For swimming, digging, or walking on land.
- Support: To bear the weight of their body and shell.
- Manipulation: While limited, some turtles use their limbs for manipulating food or interacting with their environment.
The structure itself reveals much about their evolution and adaptation:
- Bones: Turtle limbs contain bones homologous (sharing a common ancestor) to those in other tetrapods (four-limbed vertebrates), though often modified and fused.
- Muscles: Powerful muscles control the movements of the limbs, allowing for various locomotion styles.
- Claws: Many turtles have claws on their digits, used for digging, climbing, or gripping prey. The number and shape of claws can vary greatly between species.
- Scales: Scales cover the limbs, providing protection and reducing water loss in terrestrial species.
The Variable Digit Count: A Species-Specific Affair
The number of digits on a turtle's limb isn't consistent across all species. While some might have five digits on their front limbs and five on their back limbs, many deviate from this seemingly simple pattern. This variation reflects the diverse environments and lifestyles of different turtle species.
Sea Turtles: Flippers for Efficient Swimming
Sea turtles, renowned for their graceful underwater movements, possess flippers rather than typical limbs. These flippers are remarkably adapted for efficient swimming:
- Reduced Digits: Their flippers display a reduction in the number of visible digits, often appearing fused or partially obscured by webbing. While the underlying skeletal structure might retain remnants of more digits, the external appearance often presents fewer. This reduction streamlines their bodies for hydrodynamic efficiency.
- Paddle-like Structure: The overall shape of the flipper is paddle-like, maximizing their surface area to propel them through the water.
Therefore, trying to count "fingers" on a sea turtle's flipper is misleading. The functional morphology serves a different purpose entirely.
Terrestrial Turtles: A Range of Digit Numbers
Terrestrial turtles show more diversity in digit counts. While many exhibit five digits on each limb, several species have fewer. This can be attributed to evolutionary adaptations to specific environmental pressures:
- Four Digits: Some terrestrial turtles have four digits on their front or hind limbs. This reduction could be advantageous in specific habitats, reducing the energy required for locomotion or providing better grip on certain surfaces.
- Five Digits: Many common terrestrial turtles, such as red-eared sliders and box turtles, maintain the more generalized five digits on their front and hind feet, reflecting a more versatile limb structure.
- Variations within Species: Even within a single species, slight variations in digit numbers can sometimes occur due to genetic factors or developmental anomalies.
Freshwater Turtles: A Blend of Adaptations
Freshwater turtles exhibit a range of limb adaptations, often representing a blend between terrestrial and aquatic adaptations.
- Webbed Feet: Many freshwater turtles have webbed feet, aiding in swimming and maneuvering in aquatic environments. This webbing can obscure the digits, making counting difficult.
- Clawed Digits: Claws are frequently present on the digits of freshwater turtles, used for digging, climbing, or catching prey.
- Digit Numbers: The number of digits can vary, with some exhibiting five, others four, or even fewer depending on the species.
The Importance of Evolutionary Context
Understanding the number of digits in turtles necessitates considering their evolutionary history. The variations in digit count across different species aren't random; they reflect millions of years of adaptation to diverse environments and lifestyles.
- Convergent Evolution: The reduced digit count in sea turtle flippers is a prime example of convergent evolution, where unrelated species develop similar adaptations in response to similar environmental pressures.
- Natural Selection: Natural selection favors the digit configurations best suited to each species' specific niche. A reduction in digits might improve swimming efficiency or enhance grip on particular surfaces, increasing survival and reproductive success.
- Fossil Evidence: Examining the fossil record of turtles provides insights into the evolutionary changes in their limb structure and digit numbers over time.
Beyond Simple Counting: Functional Morphology Matters
Focusing solely on counting digits misses the bigger picture. The functional morphology of turtle limbs – their overall structure, bone arrangement, musculature, and adaptations – provides a more profound understanding of their biology and evolutionary history.
- Skeletal Analysis: Radiographic or anatomical studies reveal the underlying skeletal structure, revealing more about the digit arrangement even when obscured externally.
- Comparative Anatomy: Comparing the limb structures across different turtle species and other reptiles illuminates the evolutionary relationships and adaptations of different lineages.
- Biomechanics: Studying the biomechanics of turtle locomotion provides further insights into how their limb structure contributes to their movements and efficiency.
Conclusion: The Nuances of Turtle Anatomy
The question "How many fingers does a turtle have?" doesn't have a single, simple answer. The number of digits varies widely depending on the species, with sea turtles exhibiting flippers with reduced visible digits and terrestrial turtles displaying a broader range, from four to five. Understanding the diversity in digit numbers requires appreciating the functional morphology of turtle limbs and their evolutionary adaptations to their specific niches. This variation reflects millions of years of evolution, shaping these remarkable reptiles into the diverse group we know today. Instead of merely counting digits, we should appreciate the intricate adaptations reflected in the entire structure of turtle limbs, a testament to the remarkable power of natural selection. Further research and exploration into turtle anatomy continually unveil new insights into the complexity and beauty of these ancient creatures. The story of turtle digits is a story of adaptation, diversification, and the ongoing wonders of the natural world.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Wine Coolers With The Highest Alcohol Content
Apr 03, 2025
-
Greatest Common Factor Of 48 And 64
Apr 03, 2025
-
What Does It Mean To Empathize With A Monster
Apr 03, 2025
-
What Is The Average Iq For A 15 Year Old
Apr 03, 2025
-
Why Might An Aouthor Choose To Use Third Person Narrator
Apr 03, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about How Many Fingers Does A Turtle Have . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
