How Much Is 55 Grams Of Sugar
Arias News
Apr 02, 2025 · 5 min read
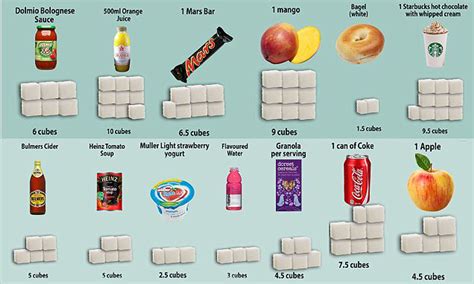
Table of Contents
How Much is 55 Grams of Sugar? A Comprehensive Guide to Sugar Measurement and Consumption
Understanding sugar consumption is crucial for maintaining a healthy lifestyle. While the recommended daily intake of added sugar varies depending on individual needs and health goals, many health organizations suggest limiting added sugar. This article dives deep into what 55 grams of sugar looks like in various forms, its impact on health, and how to effectively manage your sugar intake.
What Does 55 Grams of Sugar Look Like?
55 grams of sugar is a significant amount. It's more than the recommended daily intake for many adults and significantly exceeds the daily limit for children. Visualizing this quantity helps in understanding its impact. It's difficult to give a precise visual representation because the density of different types of sugar varies. However, we can provide estimations using common sugar types:
Granulated Sugar:
- Volume: Approximately ¼ cup of granulated white sugar weighs roughly 55 grams. Imagine a small measuring cup, about a quarter full. This is a considerable amount of sugar to add to a single beverage or food item.
Other Types of Sugar:
The volume of other types of sugar, like brown sugar, powdered sugar, or honey, will differ slightly from granulated sugar due to variations in density and moisture content. Brown sugar, for instance, will occupy slightly more volume than granulated sugar due to the molasses content. Powdered sugar, being finer, will pack more densely. Liquid sugars like honey or maple syrup will have a completely different volume, requiring measurement by weight or using a measuring cup with the appropriate markings for liquid.
Understanding Sugar Sources
It’s important to differentiate between naturally occurring sugars and added sugars.
-
Naturally Occurring Sugars: These are found in fruits, vegetables, and dairy products. While these sugars contribute to the overall sugar intake, they are often accompanied by beneficial vitamins, minerals, and fiber. The focus on limiting sugar intake primarily concerns added sugars.
-
Added Sugars: These are sugars and syrups added to foods and beverages during processing or preparation. This is where the majority of excessive sugar consumption often occurs. This includes granulated sugar, high-fructose corn syrup, corn syrup, honey, maple syrup, and other sweeteners.
The Impact of 55 Grams of Sugar Consumption
Consuming 55 grams of added sugar daily, or even frequently, can have several negative consequences for your health:
Weight Gain and Obesity:
Excess sugar consumption leads to a calorie surplus, contributing to weight gain and increasing the risk of obesity. Sugar is high in calories but lacks essential nutrients, leading to empty calories that don't contribute to satiety.
Type 2 Diabetes:
Regular consumption of high amounts of sugar can lead to insulin resistance, a precursor to type 2 diabetes. The body's inability to efficiently use insulin results in elevated blood sugar levels.
Cardiovascular Disease:
High sugar intake is associated with an increased risk of cardiovascular diseases, including heart disease and stroke. Excess sugar can contribute to high blood pressure, high cholesterol, and inflammation, all risk factors for heart problems.
Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD):
Excessive sugar consumption can contribute to the buildup of fat in the liver, leading to NAFLD. This condition can lead to liver damage and cirrhosis in severe cases.
Tooth Decay:
Sugar feeds bacteria in the mouth, producing acids that erode tooth enamel, leading to cavities and dental problems.
Other Health Concerns:
High sugar intake has also been linked to increased inflammation, impaired cognitive function, increased risk of certain cancers, and mood swings.
How to Reduce Sugar Intake
Managing your sugar intake is essential for maintaining good health. Here's a breakdown of strategies to reduce your daily sugar consumption:
Read Food Labels Carefully:
Pay close attention to the nutrition facts panel and ingredient list. Look for "added sugars" and check the grams of sugar per serving. Be aware that sugar can be listed under various names, such as sucrose, fructose, glucose, dextrose, corn syrup, and high-fructose corn syrup.
Choose Whole Foods:
Focus on consuming whole, unprocessed foods, such as fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and whole grains. These foods naturally contain lower levels of added sugars.
Limit Sugary Drinks:
Sugary drinks, like soda, juice, and sweetened beverages, are significant contributors to excess sugar intake. Opt for water, unsweetened tea, or black coffee instead.
Be Mindful of Hidden Sugars:
Many processed foods contain significant amounts of added sugar, even those that may not taste overtly sweet. Check labels carefully and be aware of hidden sugars in condiments, sauces, and packaged snacks.
Cook More at Home:
Cooking at home allows you to control the amount of sugar added to your meals and snacks. This gives you greater control over your overall sugar intake.
Gradually Reduce Sugar Intake:
Don't try to eliminate sugar completely overnight. Gradually reduce your sugar intake to avoid withdrawal symptoms and cravings. Start by cutting back on obvious sources of sugar and then gradually reduce your intake from other sources.
Find Healthy Substitutes:
If you have a sweet tooth, explore healthy alternatives like stevia, erythritol, or monk fruit. These natural sweeteners contain fewer calories and have a lower impact on blood sugar levels compared to table sugar. However, it is crucial to consume these in moderation as well.
Manage Stress:
Stress can often lead to increased cravings for sugary foods. Practice stress-management techniques, like exercise, meditation, or yoga, to help manage these cravings.
Seek Professional Guidance:
If you have concerns about your sugar intake or specific health conditions, consult a doctor, registered dietitian, or certified nutritionist. They can provide personalized advice based on your individual needs and health goals.
The Significance of Portion Control
Even healthy foods can contribute to excess sugar intake if consumed in large quantities. Portion control is vital, especially when dealing with foods that naturally contain sugars.
In Conclusion:
55 grams of sugar represents a significant amount of added sugar, far exceeding the recommended daily intake for most individuals. Understanding what this quantity looks like, its impact on health, and strategies to reduce sugar consumption are crucial steps towards maintaining a healthy lifestyle. By making conscious choices about food and beverages, reading labels diligently, and adopting healthier cooking habits, you can effectively manage your sugar intake and improve your overall well-being. Remember that consistent effort and mindful choices are key to achieving lasting changes in dietary habits.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
How Many Feet Is 25 Square Meters
Apr 03, 2025
-
How Far Is 90 Miles In Hours
Apr 03, 2025
-
Can A Number Be Both Rational And Irrational
Apr 03, 2025
-
What Is The Upside Down U In Math
Apr 03, 2025
-
What Happened To The Lone Ranger Horse Silver
Apr 03, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about How Much Is 55 Grams Of Sugar . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
