Lowest Common Multiple Of 6 And 12
Arias News
Mar 21, 2025 · 5 min read
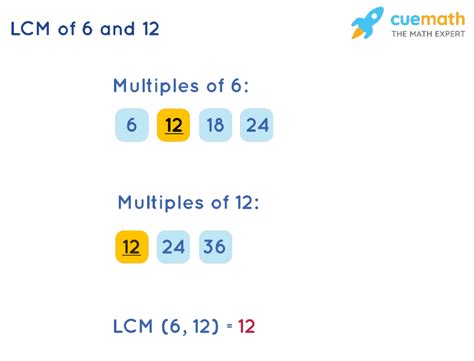
Table of Contents
Unveiling the Secrets of the Lowest Common Multiple: A Deep Dive into LCM(6, 12)
Finding the Lowest Common Multiple (LCM) might seem like a simple arithmetic task, but understanding its underlying principles opens doors to more complex mathematical concepts. This comprehensive guide delves into the LCM of 6 and 12, exploring various methods to calculate it and highlighting its significance in diverse applications. We'll unravel the mystery behind this seemingly simple calculation, demonstrating its importance beyond basic arithmetic.
Understanding the Fundamentals: What is the LCM?
The Lowest Common Multiple (LCM) of two or more integers is the smallest positive integer that is divisible by all the integers without leaving a remainder. It's a fundamental concept in number theory with applications spanning various fields, from scheduling problems to simplifying fractions. Think of it as the smallest number that contains all the prime factors of the given numbers.
For example, the LCM of 2 and 3 is 6 because 6 is the smallest positive integer that is divisible by both 2 and 3.
Calculating the LCM(6, 12): Three Proven Methods
There are several ways to calculate the LCM of two numbers. Let's explore three effective methods to find the LCM of 6 and 12:
Method 1: Listing Multiples
This is the most intuitive method, especially for smaller numbers. We list the multiples of each number until we find the smallest common multiple.
- Multiples of 6: 6, 12, 18, 24, 30, 36...
- Multiples of 12: 12, 24, 36, 48, 60...
The smallest multiple common to both lists is 12. Therefore, LCM(6, 12) = 12.
Method 2: Prime Factorization
This method is more efficient for larger numbers. We find the prime factorization of each number and then construct the LCM using the highest powers of all prime factors present.
- Prime factorization of 6: 2 x 3
- Prime factorization of 12: 2² x 3
The prime factors involved are 2 and 3. The highest power of 2 is 2², and the highest power of 3 is 3¹. Therefore, LCM(6, 12) = 2² x 3 = 4 x 3 = 12.
Method 3: Using the Greatest Common Divisor (GCD)
This method leverages the relationship between the LCM and the Greatest Common Divisor (GCD). The GCD is the largest positive integer that divides both numbers without leaving a remainder. The formula relating LCM and GCD is:
LCM(a, b) = (a x b) / GCD(a, b)
Let's find the GCD of 6 and 12 using the Euclidean algorithm:
- Divide the larger number (12) by the smaller number (6): 12 ÷ 6 = 2 with a remainder of 0.
- Since the remainder is 0, the GCD is the smaller number, which is 6.
Now, we can calculate the LCM:
LCM(6, 12) = (6 x 12) / 6 = 12
Beyond the Calculation: The Significance of LCM(6, 12)
While finding the LCM of 6 and 12 might seem trivial, understanding its applications reveals its broader importance.
Real-World Applications of LCM:
- Scheduling: Imagine you have two machines that complete a cycle in 6 and 12 minutes respectively. The LCM (12 minutes) tells you when both machines will complete a cycle simultaneously. This is crucial in production planning and scheduling.
- Fractions: Finding a common denominator when adding or subtracting fractions involves finding the LCM of the denominators. For example, to add 1/6 and 1/12, we'd find the LCM of 6 and 12 (which is 12), converting the fractions to 2/12 and 1/12 before adding them.
- Music Theory: The LCM plays a role in understanding musical intervals and harmonies. The frequencies of notes are often related by ratios, and the LCM helps determine when notes will align rhythmically.
- Modular Arithmetic: In cryptography and other areas of mathematics, the LCM is essential in solving congruences and working with modular arithmetic.
LCM and Least Common Denominator (LCD): A Close Relationship
The LCM directly relates to the least common denominator (LCD) used in fraction arithmetic. The LCD of two or more fractions is simply the LCM of their denominators. This concept is vital in simplifying complex algebraic expressions involving fractions.
Exploring Larger Numbers and More Variables: Extending the Concepts
The methods discussed—listing multiples, prime factorization, and using the GCD—can be applied to find the LCM of any number of integers, even larger ones. While listing multiples becomes less practical for large numbers, prime factorization and the GCD method remain efficient.
For instance, finding the LCM of 6, 12, and 18:
-
Prime Factorization:
- 6 = 2 x 3
- 12 = 2² x 3
- 18 = 2 x 3²
-
Highest Powers: The highest power of 2 is 2², and the highest power of 3 is 3².
-
LCM: LCM(6, 12, 18) = 2² x 3² = 4 x 9 = 36
Conclusion: Mastering the LCM – A Stepping Stone to Advanced Mathematics
The seemingly simple calculation of the LCM(6, 12) opens the door to a deeper understanding of number theory and its practical applications. Mastering this concept provides a solid foundation for more advanced mathematical concepts. Whether you're a student grappling with fractions or a professional engineer optimizing production schedules, the LCM is an invaluable tool. By understanding its underlying principles and the various methods for calculating it, you empower yourself to solve a wide range of mathematical problems and real-world challenges. This exploration of LCM(6, 12) serves as a testament to the power of seemingly basic mathematical concepts and their far-reaching implications in numerous fields. The ability to find the LCM is not just a mathematical skill but a problem-solving tool with applications far beyond the classroom.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
How Much Is 44 Kilos In Pounds
Mar 28, 2025
-
Is The Diameter Half Of The Radius
Mar 28, 2025
-
What Is Half Of 1 And 1 2 Tablespoons
Mar 28, 2025
-
What Does An Open Circle Mean In Math
Mar 28, 2025
-
Normal Bra Size For 13 Year Olds
Mar 28, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Lowest Common Multiple Of 6 And 12 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
