What Is A Equivalent Fraction For 3 5
Arias News
Mar 23, 2025 · 5 min read
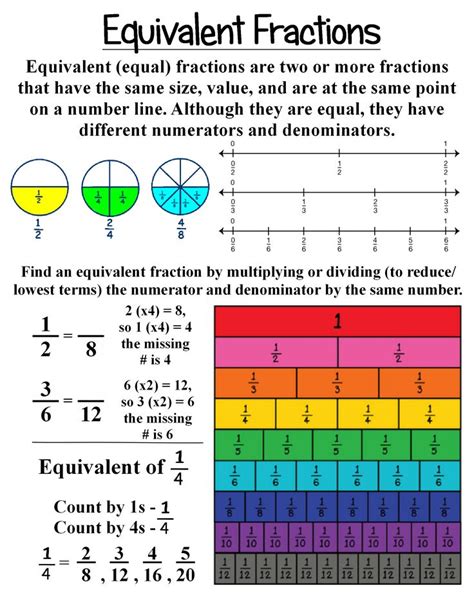
Table of Contents
- What Is A Equivalent Fraction For 3 5
- Table of Contents
- What is an Equivalent Fraction for 3/5? A Deep Dive into Fraction Equivalence
- Understanding Fractions and Their Representation
- What are Equivalent Fractions?
- Finding Equivalent Fractions for 3/5
- Multiplying to Find Equivalent Fractions
- Visualizing Equivalent Fractions
- Simplifying Fractions (Dividing to Find Equivalent Fractions)
- Practical Applications of Equivalent Fractions
- Advanced Concepts and Considerations
- Conclusion: Mastering Equivalent Fractions
- Latest Posts
- Latest Posts
- Related Post
What is an Equivalent Fraction for 3/5? A Deep Dive into Fraction Equivalence
Understanding equivalent fractions is a cornerstone of arithmetic and a crucial stepping stone towards mastering more advanced mathematical concepts. This comprehensive guide delves into the concept of equivalent fractions, specifically focusing on finding equivalent fractions for 3/5. We'll explore the underlying principles, provide numerous examples, and offer practical strategies for identifying and generating equivalent fractions.
Understanding Fractions and Their Representation
Before diving into equivalent fractions, let's solidify our understanding of what a fraction represents. A fraction is a numerical representation of a part of a whole. It's expressed as a ratio of two numbers, the numerator (top number) and the denominator (bottom number). The numerator indicates the number of parts we have, while the denominator indicates the total number of equal parts the whole is divided into.
For example, in the fraction 3/5, the numerator (3) represents the number of parts we have, and the denominator (5) represents the total number of equal parts the whole is divided into.
What are Equivalent Fractions?
Equivalent fractions are different fractions that represent the same value or proportion. They look different, but they represent the same amount. Imagine having a pizza cut into 5 slices and taking 3. Now imagine having the same pizza cut into 10 slices, and taking 6. You've still eaten the same amount of pizza, even though the fractions look different (3/5 and 6/10).
Key Principle: Equivalent fractions are created by multiplying or dividing both the numerator and the denominator by the same non-zero number. This process doesn't change the overall value of the fraction because you're essentially multiplying or dividing by 1 (any number divided by itself equals 1).
Finding Equivalent Fractions for 3/5
To find equivalent fractions for 3/5, we follow the principle of multiplying or dividing both the numerator and denominator by the same non-zero number. Let's explore some examples:
Multiplying to Find Equivalent Fractions
We can multiply both the numerator and denominator of 3/5 by any whole number greater than 1.
- Multiplying by 2: (3 x 2) / (5 x 2) = 6/10
- Multiplying by 3: (3 x 3) / (5 x 3) = 9/15
- Multiplying by 4: (3 x 4) / (5 x 4) = 12/20
- Multiplying by 5: (3 x 5) / (5 x 5) = 15/25
- Multiplying by 10: (3 x 10) / (5 x 10) = 30/50
All these fractions – 6/10, 9/15, 12/20, 15/25, 30/50 – are equivalent to 3/5. They all represent the same proportion or amount.
Visualizing Equivalent Fractions
Imagine a rectangle divided into 5 equal parts, with 3 parts shaded. This represents 3/5. Now, imagine dividing each of those 5 parts into 2 equal parts. You now have 10 parts, and 6 of them are shaded (the same area as before). This visually demonstrates that 3/5 is equal to 6/10. This visual representation reinforces the concept of equivalent fractions.
Simplifying Fractions (Dividing to Find Equivalent Fractions)
Sometimes, you'll encounter a fraction that needs simplifying. Simplifying a fraction means reducing it to its lowest terms. This is done by dividing both the numerator and the denominator by their greatest common divisor (GCD). While we've been multiplying to find equivalent fractions, dividing helps us simplify them to their most basic form. For example, consider the fraction 15/25. The GCD of 15 and 25 is 5. Dividing both by 5 gives us 3/5, the original fraction.
This process of simplification demonstrates that larger fractions can be reduced to smaller, simpler, but still equivalent fractions.
Practical Applications of Equivalent Fractions
Understanding and utilizing equivalent fractions is vital in various real-world scenarios and mathematical applications:
- Adding and Subtracting Fractions: Before you can add or subtract fractions, you often need to find equivalent fractions with a common denominator.
- Comparing Fractions: Equivalent fractions make it easier to compare which fraction is greater or smaller.
- Measurement Conversions: Converting between different units of measurement (e.g., inches to feet, centimeters to meters) frequently involves using equivalent fractions.
- Ratio and Proportion Problems: Solving problems involving ratios and proportions relies heavily on the concept of equivalent fractions.
- Geometry and Area Calculations: Calculating areas and proportions of shapes often necessitates working with equivalent fractions.
Advanced Concepts and Considerations
The concept of equivalent fractions extends to more complex scenarios:
-
Improper Fractions and Mixed Numbers: Equivalent fractions can also be found for improper fractions (where the numerator is larger than the denominator) and mixed numbers (a whole number and a fraction). For example, 7/5 (an improper fraction) is equivalent to 14/10, 21/15, etc. The mixed number 1 2/5 is equivalent to 7/5.
-
Decimals and Fractions: Decimals and fractions are closely related. Many fractions have decimal equivalents, and you can convert between them. For example, 3/5 is equivalent to 0.6.
-
Percentages and Fractions: Percentages are also related to fractions. A percentage represents a fraction with a denominator of 100. For example, 60% is equivalent to 60/100 which simplifies to 3/5.
Conclusion: Mastering Equivalent Fractions
Equivalent fractions are a fundamental concept in mathematics with far-reaching applications. Understanding how to find and use equivalent fractions is essential for building a strong foundation in arithmetic and tackling more advanced mathematical problems. By mastering this concept, you'll gain confidence in your ability to manipulate and solve problems involving fractions, ratios, and proportions, paving the way for success in various mathematical and real-world applications. Remember the key principle: multiplying or dividing both the numerator and denominator by the same non-zero number creates an equivalent fraction, maintaining the same value while changing the representation. Practice consistently, explore different methods, and visualize the concept to build a deep and intuitive understanding of equivalent fractions. Through practice and understanding, you will become proficient in working with equivalent fractions, which will be a valuable asset in your mathematical journey.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Was Simon Cannibalized In Lord Of The Flies
Mar 26, 2025
-
If A Right Circular Cone Is Intersected By A Plane
Mar 26, 2025
-
How Many Cups Of Pecans Is A Pound
Mar 26, 2025
-
1 10 Oz Gold Is How Many Grams
Mar 26, 2025
-
How Many Peaches Are In A Can
Mar 26, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Is A Equivalent Fraction For 3 5 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
