Which Is Bigger A Millimeter Or A Centimeter
Arias News
Apr 01, 2025 · 6 min read
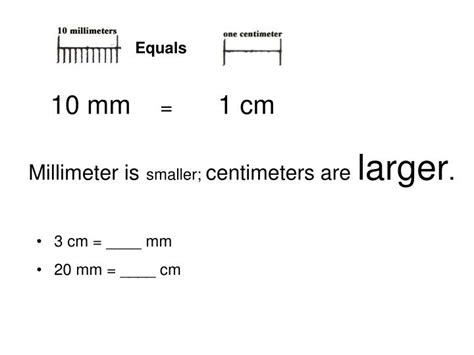
Table of Contents
Which is Bigger: A Millimeter or a Centimeter? A Deep Dive into Metric Units
Understanding the metric system is fundamental to various fields, from science and engineering to everyday life. While seemingly simple, the difference between units like millimeters and centimeters can sometimes cause confusion. This comprehensive guide will delve into the specifics of millimeters and centimeters, explaining their relationship, providing practical examples, and highlighting their importance in different contexts. We’ll explore the conversion factors, use real-world analogies, and even touch upon the history of the metric system to fully grasp this seemingly basic yet crucial concept.
Understanding the Metric System: A Foundation in Ten
The metric system, officially known as the International System of Units (SI), is a decimal system based on powers of ten. This means that units are related by factors of ten, making conversions remarkably straightforward. This is a stark contrast to the imperial system (used in the United States and a few other countries), where conversions involve less intuitive factors. The base unit for length in the metric system is the meter (m). From the meter, we derive smaller and larger units by multiplying or dividing by powers of ten.
Key Metric Prefixes: Milli and Centi
To understand the difference between millimeters and centimeters, we need to focus on two crucial prefixes:
-
Milli (m): This prefix represents one-thousandth (1/1000) of a unit. Therefore, a millimeter (mm) is one-thousandth of a meter.
-
Centi (c): This prefix represents one-hundredth (1/100) of a unit. Therefore, a centimeter (cm) is one-hundredth of a meter.
The Crucial Difference: Centimeters are Bigger than Millimeters
Now, to answer the central question: a centimeter is bigger than a millimeter. Specifically, one centimeter is equal to ten millimeters (1 cm = 10 mm). This is a direct consequence of the prefixes: since a centimeter is one-hundredth of a meter and a millimeter is one-thousandth of a meter, a centimeter is ten times larger than a millimeter.
Think of it this way: if you divide a meter into 100 equal parts, each part is a centimeter. If you divide the same meter into 1000 equal parts, each part is a millimeter. Clearly, the 100 parts are larger than the 1000 parts.
Visualizing the Difference: Real-World Analogies
Abstract numbers can be difficult to grasp. Let's use some real-world analogies to visualize the difference between a millimeter and a centimeter:
-
Fingernail: The width of an average adult fingernail is roughly one centimeter. A millimeter would be about one-tenth of that width – a very small segment.
-
Pencil Lead: The diameter of a standard pencil lead is approximately 2 millimeters. It would take five such pencil leads to equal the width of one centimeter.
-
Ruler: Most rulers have markings for both centimeters and millimeters. Observe the markings carefully – you'll see that ten millimeter markings fit into one centimeter marking.
-
Paper Thickness: The thickness of a standard sheet of paper is typically around 0.1 millimeters. It would take 100 sheets of paper stacked together to make up 1 centimeter.
These tangible examples should help solidify the understanding of the relative sizes of millimeters and centimeters.
Conversion Between Millimeters and Centimeters: A Simple Equation
Converting between millimeters and centimeters is exceptionally easy because of the metric system's decimal nature. The fundamental conversion factor is:
1 cm = 10 mm
Therefore:
-
To convert centimeters to millimeters, multiply by 10. For example, 5 cm = 5 cm * 10 mm/cm = 50 mm
-
To convert millimeters to centimeters, divide by 10. For example, 70 mm = 70 mm / 10 mm/cm = 7 cm
These simple calculations make working with these units incredibly efficient.
Applications of Millimeters and Centimeters: Precision in Diverse Fields
Millimeters and centimeters find applications across a vast spectrum of disciplines:
Science and Engineering:
-
Microscopy: Millimeters are crucial in microscopy, measuring the size of cells, microorganisms, and other minute structures.
-
Electronics: The dimensions of electronic components, such as integrated circuits and transistors, are often expressed in millimeters.
-
Mechanical Engineering: Precise measurements in millimeters are essential for the design and manufacturing of mechanical parts and systems.
-
Construction and Architecture: While centimeters are more frequently used, millimeters often come into play for precise measurements in detailing and intricate designs.
Everyday Life:
-
Photography: Focal lengths of lenses and sensor sizes are often specified in millimeters.
-
Cooking and Baking: While less common than grams and liters, millimeters can be used for precision measuring of ingredients in specialized baking or culinary techniques.
-
Sewing and Crafts: Centimeters are widely used for measuring fabric, patterns, and other crafting materials.
-
Map Reading: Scale distances on maps are often represented using centimeters and millimeters.
The Historical Context: Evolution of the Metric System
The metric system, a product of the French Revolution, aimed to create a standardized and universally understandable system of measurement. Its decimal nature, based on powers of ten, proved to be far more efficient and less prone to errors than previous, less standardized systems. The development of the meter itself involved careful scientific measurements, contributing to the system's accuracy and precision. The millimeter and centimeter arose as logical subdivisions of the meter, making precise measurements possible at both macro and micro scales. The widespread adoption of the metric system highlights its superiority in simplifying measurement and fostering global collaboration.
Beyond Millimeters and Centimeters: Exploring the Broader Metric Landscape
While this article focuses on millimeters and centimeters, it's important to remember that these are just two units within the broader metric system. Other important units of length include:
- Kilometer (km): 1000 meters, used for measuring large distances.
- Decimeter (dm): 0.1 meters, less commonly used than centimeters.
- Micrometer (µm): 0.000001 meters (one-millionth of a meter), essential in microscopy and nanotechnology.
- Nanometer (nm): 0.000000001 meters (one-billionth of a meter), crucial in nanoscience and nanotechnology.
Understanding the relationships between these units provides a more holistic grasp of the metric system's functionality and its vital role in scientific, engineering, and everyday applications.
Conclusion: Mastering the Fundamentals of Measurement
Understanding the difference between a millimeter and a centimeter is a fundamental step in grasping the metric system. The simple relationship between these units (1 cm = 10 mm) makes conversion straightforward, enabling efficient calculations across various fields. By utilizing real-world analogies and appreciating the historical context, you can solidify your understanding of these crucial units of measurement, further enhancing your ability to navigate the world of science, technology, and everyday life with greater precision and confidence. Remember that mastering these fundamental concepts opens doors to a deeper understanding of the broader metric system and its importance in a globally connected world.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
How Many Sides Do A Pentagon Have
Apr 02, 2025
-
Dallas Vs San Antonio Vs Houston To Visit
Apr 02, 2025
-
How Many Ounces Of Cottage Cheese In A Cup
Apr 02, 2025
-
What Does 925 Sun Mean On Jewelry
Apr 02, 2025
-
How Many Fingers Does A Turtle Have
Apr 02, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Which Is Bigger A Millimeter Or A Centimeter . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
