Which Number Produces A Rational Number When Added To 0.5
Arias News
Mar 14, 2025 · 5 min read
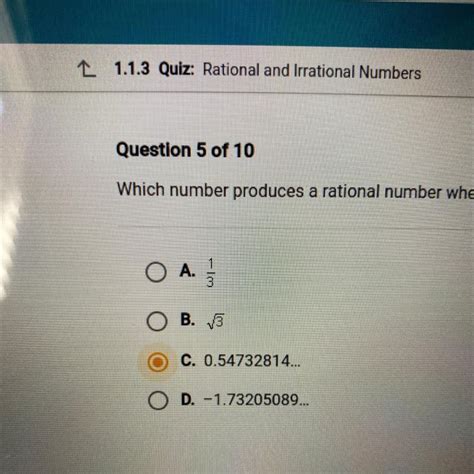
Table of Contents
Which Number Produces a Rational Number When Added to 0.5?
The question, "Which number produces a rational number when added to 0.5?" might seem deceptively simple. However, exploring this question unveils a fascinating journey into the world of rational and irrational numbers, their properties, and how they interact with each other. Let's delve deep into this mathematical puzzle and explore the various facets of this seemingly straightforward problem.
Understanding Rational and Irrational Numbers
Before we dive into the specifics, let's establish a firm understanding of rational and irrational numbers. This foundation is crucial for comprehending the solution to our central question.
What are Rational Numbers?
A rational number is any number that can be expressed as a fraction p/q, where 'p' and 'q' are integers, and 'q' is not equal to zero. This definition encompasses a wide range of numbers, including:
- Integers: Whole numbers, both positive and negative (e.g., -3, 0, 5). These can be expressed as fractions with a denominator of 1 (e.g., -3/1, 0/1, 5/1).
- Fractions: Numbers expressed as ratios of two integers (e.g., 1/2, 3/4, -2/5).
- Terminating Decimals: Decimals that have a finite number of digits (e.g., 0.5, 0.75, 2.375). These can always be converted into fractions.
- Repeating Decimals: Decimals that have a repeating pattern of digits (e.g., 0.333..., 0.142857142857...). These, too, can be expressed as fractions.
What are Irrational Numbers?
Irrational numbers, on the other hand, cannot be expressed as a fraction of two integers. Their decimal representation is neither terminating nor repeating. Famous examples of irrational numbers include:
- π (Pi): The ratio of a circle's circumference to its diameter, approximately 3.14159...
- e (Euler's number): The base of natural logarithms, approximately 2.71828...
- √2 (Square root of 2): The number which, when multiplied by itself, equals 2. Its decimal representation is approximately 1.41421...
Adding to 0.5: The Key to Rationality
The crucial aspect of our question lies in the additive property of rational and irrational numbers. When you add two rational numbers together, the result is always another rational number. This is easily proven:
Let's say we have two rational numbers, a/b and c/d, where a, b, c, and d are integers, and b and d are not zero. Their sum is:
(a/b) + (c/d) = (ad + bc) / (bd)
Since the product and sum of integers are always integers, (ad + bc) and (bd) are integers. Therefore, the sum is a fraction of two integers and thus, a rational number.
However, the addition of a rational and an irrational number always results in an irrational number. To see why, consider this:
Suppose we add a rational number (a/b) to an irrational number (x). If their sum were rational (say, y), we could write:
(a/b) + x = y
This implies that x = y - (a/b). Since y and (a/b) are both rational, their difference (x) would also be rational. This contradicts our initial assumption that x is irrational. Therefore, the sum of a rational and an irrational number is always irrational.
Numbers that Produce a Rational Number When Added to 0.5
Based on the above principles, we can definitively state that any number that, when added to 0.5, yields a rational number must itself be a rational number. This stems directly from the closure property of rational numbers under addition.
Let's explore some examples:
- Adding 0.5 to another rational number: 0.5 + 0.25 = 0.75 (rational)
- 0.5 + 1 = 1.5 = 3/2 (rational)
- 0.5 + (-1) = -0.5 = -1/2 (rational)
- 0.5 + 2/3 = (3/6) + (4/6) = 7/6 (rational)
Notice that in each case, the result is a number that can be expressed as a fraction of two integers.
Numbers that Produce an Irrational Number When Added to 0.5
Conversely, any irrational number added to 0.5 will always result in an irrational number.
- 0.5 + π ≈ 3.64159... (irrational)
- 0.5 + √2 ≈ 1.91421... (irrational)
- 0.5 + e ≈ 3.21828... (irrational)
These sums are neither terminating nor repeating decimals and cannot be expressed as a ratio of two integers.
Practical Applications and Further Exploration
This seemingly basic mathematical concept has far-reaching applications in various fields. The understanding of rational and irrational numbers is fundamental in:
- Computer Science: Representing numbers in computer systems often involves dealing with rational approximations of irrational numbers.
- Engineering: Precise calculations in engineering projects require a deep understanding of how rational and irrational numbers behave when combined.
- Physics: Many physical constants are irrational numbers (like Pi), and understanding their properties is critical for accurate modelling.
- Finance: Calculations involving interest rates, compound growth, and other financial concepts often involve rational numbers and their properties.
This exploration also leads to further mathematical inquiries:
- Density of Rational and Irrational Numbers: Although rational numbers seem plentiful, irrational numbers are infinitely more numerous on the number line. This concept of density is a fascinating aspect of number theory.
- Approximations: It's often necessary to approximate irrational numbers with rational numbers for practical calculations. Understanding the error involved in such approximations is crucial for accuracy.
- Continued Fractions: A unique way to represent rational and irrational numbers is through continued fractions. This offers another perspective on the relationship between these two number types.
Conclusion
The question of which number produces a rational number when added to 0.5 ultimately boils down to the fundamental properties of rational and irrational numbers. Only rational numbers, when added to 0.5, will yield another rational number. This exploration, however, has unveiled a richer understanding of the nature of numbers, their classifications, and their inherent behaviours when subjected to basic mathematical operations. The seemingly simple question serves as a gateway to a broader appreciation of mathematical concepts with far-reaching implications. The ability to distinguish between and work with rational and irrational numbers is a cornerstone of mathematical literacy and has significant applications across numerous fields.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
How Do You Say Excellent In Spanish
Mar 14, 2025
-
How Many Cups Of Water In 4 Quarts
Mar 14, 2025
-
How Many Corners Does A Triangle Have
Mar 14, 2025
-
What Year Was I Born If Im 14
Mar 14, 2025
-
What Is 872 Rounded To The Nearest Ten
Mar 14, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Which Number Produces A Rational Number When Added To 0.5 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
