Is 17 A Prime Number Or A Composite Number
Arias News
Mar 19, 2025 · 6 min read
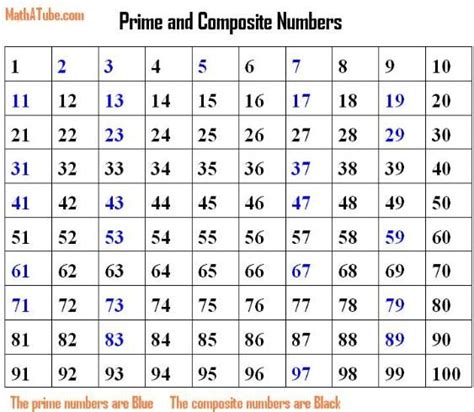
Table of Contents
Is 17 a Prime Number or a Composite Number? A Deep Dive into Number Theory
Determining whether a number is prime or composite is a fundamental concept in number theory. While seemingly simple for small numbers, understanding the underlying principles and exploring the mathematical framework behind prime and composite numbers reveals a fascinating world of mathematical elegance and complexity. This article delves deep into the question: Is 17 a prime number or a composite number? We'll not only answer this specific question but also equip you with the knowledge to confidently classify any integer.
Understanding Prime and Composite Numbers
Before tackling the specific case of 17, let's establish a clear definition of prime and composite numbers. These classifications are based on a number's divisors – the numbers that divide it evenly without leaving a remainder.
Prime Numbers: A prime number is a whole number greater than 1 that has only two distinct positive divisors: 1 and itself. This means it's only divisible by 1 and the number itself. Examples include 2, 3, 5, 7, 11, and so on. Prime numbers are the building blocks of all other integers, a concept central to the Fundamental Theorem of Arithmetic.
Composite Numbers: A composite number is a whole number greater than 1 that has more than two positive divisors. In other words, it can be divided evenly by at least one number other than 1 and itself. Examples include 4 (divisible by 1, 2, and 4), 6 (divisible by 1, 2, 3, and 6), 9 (divisible by 1, 3, and 9), and so forth.
Neither Prime nor Composite: The number 1 is neither prime nor composite. It's a special case with only one positive divisor – itself. This distinction is crucial in many mathematical theorems and proofs.
Determining if 17 is Prime or Composite
Now, let's focus on the number 17. To determine its classification, we need to identify its divisors. We can systematically check for divisors starting from 2 and working our way up.
- Divisibility by 2: 17 is not divisible by 2 because it's an odd number.
- Divisibility by 3: The sum of the digits of 17 (1 + 7 = 8) is not divisible by 3, so 17 is not divisible by 3.
- Divisibility by 4: 17 is not divisible by 4 because it's not an even multiple of 4.
- Divisibility by 5: 17 does not end in 0 or 5, so it's not divisible by 5.
- Divisibility by 6: Since 17 is not divisible by 2 or 3, it's not divisible by 6.
- Divisibility by 7: 17 is not divisible by 7 (17/7 ≈ 2.43).
- Divisibility by 8: 17 is not divisible by 8.
- Divisibility by 9: 17 is not divisible by 9.
- Divisibility by 10: 17 is not divisible by 10.
- Divisibility by 11: 17 is not divisible by 11.
- Divisibility by 13: 17 is not divisible by 13 (17/13 ≈ 1.31)
- Divisibility by 16: 17 is not divisible by 16.
We can stop checking at this point because the square root of 17 is approximately 4.12. If a number has a divisor greater than its square root, it must also have a divisor smaller than its square root. Since we've checked all the integers up to 4 and found no divisors, we can conclude that 17 has no divisors other than 1 and itself.
Therefore, 17 is a prime number.
The Importance of Prime Numbers
The seemingly simple classification of numbers as prime or composite has profound implications across various fields of mathematics and computer science. Here are some key reasons why prime numbers are so significant:
1. Fundamental Theorem of Arithmetic: This cornerstone of number theory states that every integer greater than 1 can be uniquely represented as a product of prime numbers. This means that prime numbers are the building blocks of all other integers. For example, 12 can be expressed as 2 x 2 x 3.
2. Cryptography: Prime numbers are fundamental to many modern encryption algorithms. RSA encryption, widely used to secure online transactions, relies heavily on the difficulty of factoring very large numbers into their prime components. The vastness of prime numbers makes this factoring process computationally expensive, ensuring data security.
3. Number Theory Research: Prime numbers are a continuous source of research in number theory. Many unsolved problems, such as the Riemann Hypothesis, are directly related to the distribution and properties of prime numbers.
4. Hashing Algorithms: Prime numbers are often incorporated into hashing algorithms used in computer science for data storage and retrieval. Their properties help distribute data evenly across a hash table, improving efficiency.
5. Random Number Generation: Prime numbers play a role in generating pseudorandom numbers, which are widely used in simulations, statistical analysis, and cryptography.
Identifying Prime Numbers: Techniques and Algorithms
Determining whether a large number is prime can be computationally challenging. Several algorithms have been developed to efficiently test for primality:
-
Trial Division: This is the most straightforward approach, but it becomes inefficient for large numbers. It involves checking for divisibility by all integers up to the square root of the number in question.
-
Sieve of Eratosthenes: This ancient algorithm is efficient for finding all prime numbers up to a specified limit. It systematically eliminates composite numbers, leaving only primes.
-
Probabilistic Primality Tests: These tests don't definitively prove primality but offer a high probability of correctness. Examples include the Miller-Rabin test and the Solovay-Strassen test. They are crucial for dealing with extremely large numbers where deterministic tests would be computationally prohibitive.
-
AKS Primality Test: This is a deterministic polynomial-time algorithm, meaning it guarantees the correctness of its result and its runtime is polynomial in the size of the input. While theoretically significant, it's not always the most efficient algorithm in practice for extremely large numbers.
Conclusion: The Primacy of 17
We've conclusively shown that 17 is a prime number. Its unique position as a prime number highlights the fundamental nature of these numbers in mathematics and their far-reaching applications in various fields. Understanding the concepts of prime and composite numbers is a key step in grasping more advanced mathematical principles and appreciating the beauty and complexity of number theory. The exploration of prime numbers continues to be a vibrant area of research, and their importance in both theoretical mathematics and practical applications such as cryptography ensures their continued relevance for years to come. The seemingly simple question of whether 17 is prime or composite serves as a gateway to a deeper understanding of a world of mathematical elegance and far-reaching consequences.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
How Many Square Feet In 100 Square Meters
Mar 19, 2025
-
Line S Is The Perpendicular Bisector Of Jk
Mar 19, 2025
-
Why Is Billy Crystal Uncredited In Tooth Fairy
Mar 19, 2025
-
Sum Of Interior Angles Of A Heptagon
Mar 19, 2025
-
How Much Is 1 5 Oz In Cups
Mar 19, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Is 17 A Prime Number Or A Composite Number . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
